Angioedema is a medical condition characterized by rapid swelling, particularly in the deeper layers of the skin, which can pose significant health risks if not properly managed. This swelling often affects areas such as the lips, face, and throat, making it crucial for individuals to recognize angioedema symptoms early on. The causes of angioedema are diverse, ranging from allergic reactions to hereditary factors, and understanding these triggers is vital for effective treatment. Recent advances in angioedema treatment have introduced innovative therapies, including medications specifically designed to prevent hereditary angioedema attacks. As research continues to evolve, staying informed about angioedema may empower patients and healthcare providers to collaborate on optimal management strategies.
Angioedema, often referred to as acute swelling or localized edema, encompasses a range of conditions that lead to sudden, non-pitting swellings beneath the skin. This medical issue can manifest due to various triggers, including allergens and genetic predispositions, as seen in hereditary angioedema. Identifying the underlying causes is essential for devising effective management plans. The landscape of treatment options is rapidly changing, with new developments offering hope for improved patient outcomes. By understanding these alternative terms and concepts related to angioedema, individuals can better engage with their healthcare providers and advocate for themselves.
Understanding Angioedema Symptoms
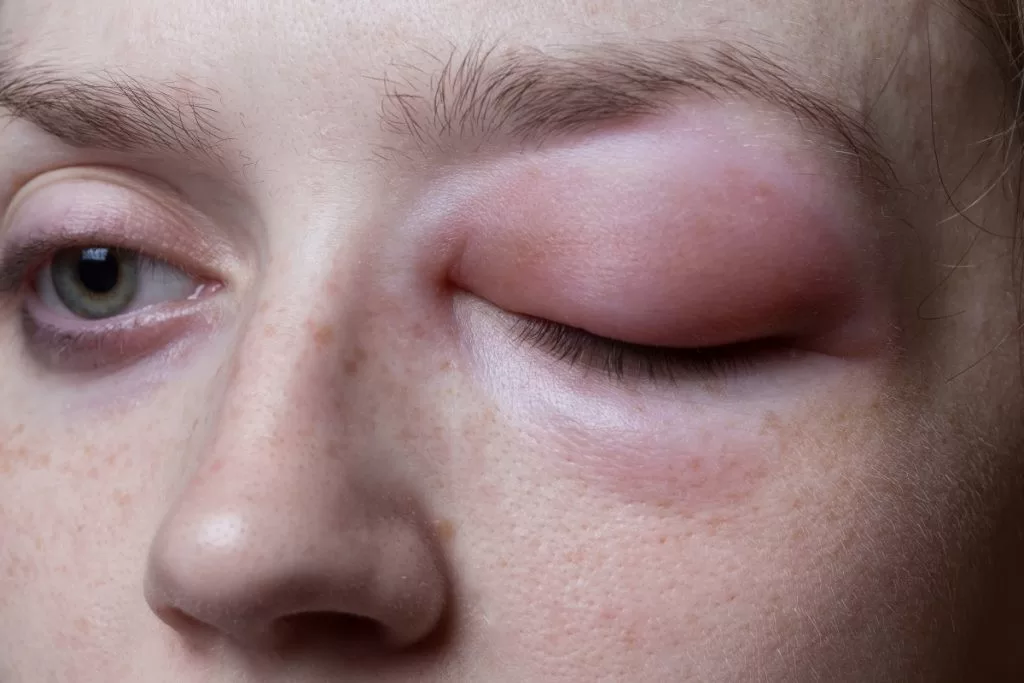
Angioedema symptoms can manifest quite suddenly, often causing significant alarm for those who experience them. The swelling typically affects the lips, eyelids, and throat, leading to potentially life-threatening complications. Notably, the swelling is characterized by being non-pitting and non-pruritic, which means that pressing the swollen area does not leave a dent, nor is it itchy. This can often lead to confusion with other conditions, underscoring the importance of awareness in recognizing the unique symptoms of angioedema.
In severe cases, the symptoms can escalate quickly and lead to airway obstruction, particularly if the swelling involves the throat or tongue. This critical aspect highlights the need for immediate medical intervention when such symptoms are observed. Individuals with a history of angioedema, or those who experience unexplained swelling, should seek medical evaluation to ensure timely and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Angioedema
The causes of angioedema can be multifactorial, encompassing both allergic reactions and genetic predispositions. Common triggers include medications, particularly ACE inhibitors, specific food items, and insect stings. Allergic responses can prompt significant swelling, necessitating prompt identification and avoidance of these triggers to prevent recurrence. Being proactive about known allergens is essential for managing symptoms effectively.
In addition to allergic triggers, hereditary angioedema (HAE) represents a significant subset of this condition. This inherited form is often linked to mutations in the C1 inhibitor gene, affecting fluid regulation in blood vessels. As a result, individuals with HAE may experience recurrent, spontaneous episodes of angioedema, often beginning in childhood. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for developing effective management strategies and informing treatment decisions.
Recent Advances in Angioedema Treatment
Recent advancements in angioedema treatment have significantly changed the landscape for affected individuals. One notable development is the approval of Andembry (garadacimab), which has been shown to prevent hereditary angioedema (HAE) attacks. Administered monthly, this medication targets factor XIIa, demonstrating promising results in clinical trials and improving the quality of life for patients. Such innovations represent a major step forward in managing this chronic condition.
Additionally, Sebetralstat has emerged as a potential long-term prophylactic option for patients with HAE. Data presented at recent medical conferences have highlighted its efficacy, further emphasizing the ongoing commitment to research and development in this field. These therapeutic advances provide renewed hope for patients, allowing for more effective management of their condition and reducing the frequency and severity of angioedema attacks.
Treatment Strategies for Angioedema
Effective treatment strategies for angioedema often hinge on identifying the underlying cause of the swelling. For many patients, mild cases resolve on their own, requiring little to no medical intervention. However, for those with more severe symptoms, treatment options may include the use of antihistamines to alleviate swelling and corticosteroids for more pronounced reactions. Understanding the appropriate course of action is essential for managing the condition effectively.
In tandem with pharmacological interventions, avoidance of known triggers plays a critical role in treatment. Patients are often encouraged to maintain a detailed record of their symptoms and potential triggers, working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a tailored management plan. This proactive approach not only helps mitigate the impact of angioedema but also empowers patients to take control of their health.
The Importance of Education on Angioedema
Education plays a pivotal role in managing angioedema, both for patients and healthcare providers. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and latest treatment options empowers individuals to recognize potential flare-ups early and seek appropriate care. Resources such as visual aids and informational websites can enhance awareness and understanding, making it easier to identify the condition when it arises.
Furthermore, ongoing education fosters a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare teams, ensuring that treatment plans are informed by the most current research and therapeutic options. Continuous dialogue about angioedema, including recent advances in treatment, is essential for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common angioedema symptoms to watch for?
Common symptoms of angioedema include sudden swelling of the lips, eyelids, or throat, which may not be itchy or painful. This swelling is typically non-pitting, meaning it does not indent when pressed. Symptoms can resolve within days, but swelling in the throat may require immediate medical attention.
What are the primary causes of angioedema?
Angioedema can be triggered by allergic reactions to medications, foods, or insect stings. It can also be caused by hereditary factors, particularly in hereditary angioedema (HAE), which is an inherited condition. Other medical conditions like autoimmune diseases and infections may also contribute to angioedema.
What treatments are available for angioedema?
Treatment for angioedema varies based on the cause and severity. Mild cases often resolve on their own, while antihistamines and corticosteroids may be prescribed for more severe cases. Avoiding known triggers is also crucial in managing symptoms effectively.
What is hereditary angioedema and how is it treated?
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a genetic condition that leads to recurrent episodes of severe swelling. Recent treatments like Andembry (garadacimab) and Sebetralstat show promise in preventing HAE attacks, offering patients better management options and improving their quality of life.
What are the recent advances in angioedema treatment?
Recent advances in angioedema treatment include the approval of Andembry for preventing hereditary angioedema attacks and promising data on Sebetralstat for long-term prophylaxis. These advancements highlight ongoing research aimed at improving treatment options for patients with angioedema.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Angioedema is localized swelling affecting deeper skin layers, often occurring with hives. |
| Symptoms | Includes abrupt swelling of lips, eyelids, or throat; non-itchy swelling that resolves in days. |
| Recent Developments | New treatments like Andembry and Sebetralstat show promise for managing hereditary angioedema. |
| Causes | Triggers include allergic reactions, genetic factors, and other medical conditions. |
| Treatment | Options range from self-resolution, medications like antihistamines and corticosteroids, to trigger avoidance. |
Summary
Angioedema is a serious condition characterized by localized swelling that can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Recent advancements in therapy, such as Andembry and Sebetralstat, offer hope for improved quality of life for those affected. Continuous education and awareness of angioedema can empower patients and healthcare providers to work together in preventing and managing this potentially life-threatening disorder.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.