Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that can occur within minutes of exposure to an allergen, making it a critical topic for anyone concerned about health and safety. Understanding the symptoms, causes of anaphylaxis, and treatment options is essential for effective management of this life-threatening condition. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, swelling, and rapid pulse, which require immediate attention. Treatment for anaphylaxis primarily involves the administration of epinephrine, a powerful medication that can reverse the reaction’s effects. Moreover, awareness of anaphylaxis is not only relevant for humans but also crucial for pet owners, as anaphylaxis in pets can stem from similar triggers such as food allergies or insect stings.
The term anaphylaxis refers to an acute allergic response that can escalate quickly, often leading to serious health consequences. This intense allergy reaction necessitates prompt recognition of its symptoms and understanding of its underlying causes, which can range from food items to medications and environmental factors. Individuals experiencing anaphylactic symptoms must receive immediate treatment, typically involving epinephrine injections, to counteract the body’s extreme response. Additionally, it is important to recognize that pets can also experience this severe allergic reaction, which underscores the broader implications of allergy management. By educating ourselves about the risks and responses associated with anaphylaxis, we can better safeguard our health and that of our loved ones.
Understanding Anaphylaxis Symptoms
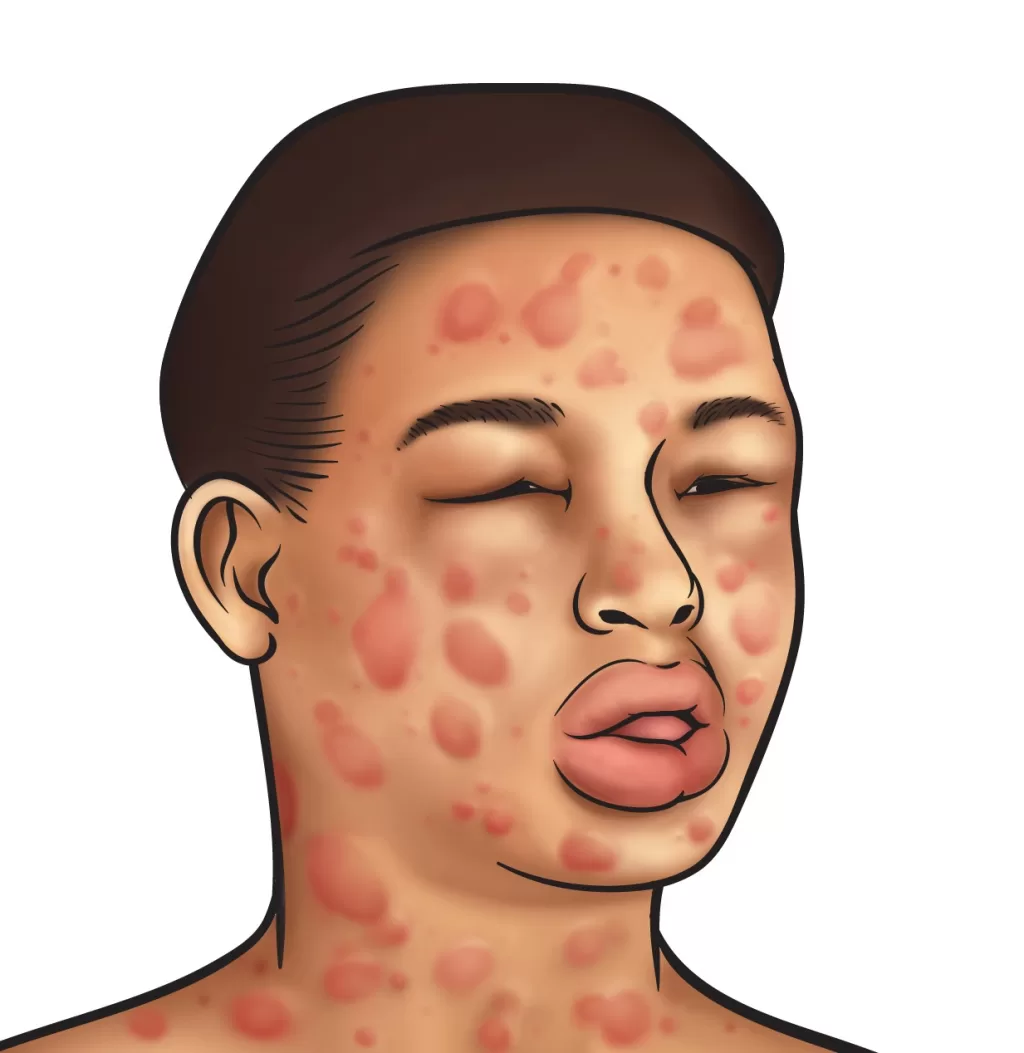
Recognizing the symptoms of anaphylaxis is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat and tongue, rapid heartbeat, and skin reactions like hives or itching. These symptoms can escalate quickly, leading to potential respiratory failure or cardiovascular collapse if not addressed immediately. It is essential for individuals with known allergies to be vigilant and aware of their bodies’ reactions to potential allergens.
In some cases, anaphylaxis can also manifest with gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. These symptoms may initially be mistaken for a less severe allergic reaction or food intolerance. Therefore, having knowledge of the full range of anaphylaxis symptoms can empower individuals to seek emergency medical help promptly, potentially saving lives by ensuring that appropriate treatment is administered without delay.
Causes of Anaphylaxis: What Triggers a Reaction?
Anaphylaxis can be triggered by a variety of allergens, with some of the most common causes being specific foods, insect stings, medications, and latex. Foods such as peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, and dairy are often implicated in allergic reactions that can escalate to anaphylaxis. Understanding these triggers is vital for individuals at risk, as avoidance is the primary method of prevention.
Insect bites, particularly from bees and wasps, are another frequent cause of anaphylaxis. People who have experienced previous reactions to insect stings should take precautions, such as carrying an epinephrine auto-injector. Additionally, certain medications, notably penicillin and other antibiotics, have been known to cause severe allergic reactions. Awareness of these causes enhances preparedness, allowing individuals to manage their allergies effectively.
Emergency Treatment for Anaphylaxis
The immediate treatment for anaphylaxis involves the administration of epinephrine, which can rapidly reverse the symptoms of a severe allergic reaction. It is crucial for individuals with known allergies to have an epinephrine auto-injector accessible at all times. Upon administering epinephrine, seeking emergency medical assistance is necessary to ensure further evaluation and treatment. Supportive care may include antihistamines and corticosteroids to alleviate the symptoms, but these should not replace epinephrine.
Timely recognition and treatment of anaphylaxis are paramount. Delays in administering epinephrine can lead to worsening symptoms and more severe complications, including potential death. Therefore, educating oneself and others about the signs of anaphylaxis and the correct use of epinephrine can significantly improve outcomes in emergency situations.
Recent Research on Anaphylaxis and Treatment Confusion
Recent studies have highlighted a concerning trend: the confusion surrounding anaphylaxis treatment among patients and caregivers. Research presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology suggests that many individuals are unaware of the proper protocols for using epinephrine during an allergic emergency. This lack of knowledge can lead to tragic outcomes, emphasizing the need for clearer communication and education in allergy management.
Moreover, the link between certain medications, such as lipid-lowering drugs, and increased risk of severe anaphylactic reactions has prompted further investigation. Awareness of these connections can lead to better-informed decisions regarding medication use in individuals at risk for anaphylaxis. Continuous education and updates on emerging research are essential for improving the safety and well-being of those affected by severe allergies.
Anaphylaxis in Pets: Recognizing and Responding to Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is not limited to humans; our pets can also experience severe allergic reactions that require immediate attention. Dogs, for example, may develop anaphylaxis due to insect bites or certain food allergies. Recognizing the symptoms in pets, which can include swelling, difficulty breathing, and gastrointestinal upset, is crucial for pet owners. Immediate veterinary care is often necessary to manage these emergencies effectively.
Pet owners should be aware of their pets’ allergies and have an action plan in place, similar to how individuals manage their own allergies. Preventative measures, such as avoiding known allergens and being cautious with foods and treats, can help mitigate the risk of anaphylaxis in pets. Educating oneself about the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis in animals can save lives and ensure prompt treatment in critical situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis symptoms can manifest rapidly and severely. Common signs include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat and tongue, rapid pulse, skin reactions such as hives or itching, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Recognizing anaphylaxis symptoms promptly is crucial for effective treatment.
What are the primary causes of anaphylaxis?
The causes of anaphylaxis typically involve exposure to specific allergens. Common triggers include certain foods (like peanuts and shellfish), insect stings (from bees or wasps), medications (such as penicillin), and latex. Understanding these causes is essential for preventing allergy reactions.
How is treatment for anaphylaxis administered?
The immediate treatment for anaphylaxis involves administering epinephrine, which can be delivered via an auto-injector (like an EpiPen) or by injection. Following epinephrine administration, it is critical to seek emergency medical assistance, as additional supportive care may be necessary to alleviate symptoms.
Can pets experience anaphylaxis and what should be done?
Yes, anaphylaxis in pets can occur, often triggered by insect bites or food allergies. Symptoms in pets may include swelling, difficulty breathing, and gastrointestinal distress. Immediate veterinary attention is vital for pets experiencing signs of anaphylaxis.
What should individuals with known allergies do to prepare for potential anaphylaxis?
Individuals with known allergies should carry an epinephrine auto-injector at all times and have a clear action plan for emergencies. Education on recognizing anaphylaxis symptoms and understanding treatment protocols is crucial to ensure quick and effective responses in case of an allergy reaction.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Anaphylaxis is an acute allergic reaction that occurs rapidly after exposure to allergens. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling, rapid pulse, skin reactions, nausea, and dizziness. |
| Causes | Common triggers include foods (e.g., peanuts), insect stings, medications, and latex. |
| Treatment | Immediate administration of epinephrine, followed by emergency medical assistance. Antihistamines may also be used. |
| ICD-10 Code | T78.2 |
| Anaphylaxis in Pets | Pets can also experience anaphylaxis, requiring immediate veterinary attention. |
Summary
Anaphylaxis is a critical health concern that demands immediate recognition and action. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for effective emergency management. The recent studies underline the importance of education regarding potential medication risks and treatment protocols to mitigate confusion among patients and caregivers. Whether it affects humans or pets, prompt recognition and response can save lives. By enhancing awareness and preparedness for anaphylaxis, we empower ourselves and our communities to handle allergic emergencies effectively.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.





Hair Type
Great post. I used to be checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Extremely useful info particularly the final phase :) I maintain such information much. I used to be looking for this certain information for a long time. Thanks and best of luck.
Hairstyles Color
hi!,I like your writing very much! share we communicate more about your article on AOL? I need a specialist on this area to solve my problem. May be that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
Hairstyles VIP
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I do not know who you are but definitely you are going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already ;) Cheers!