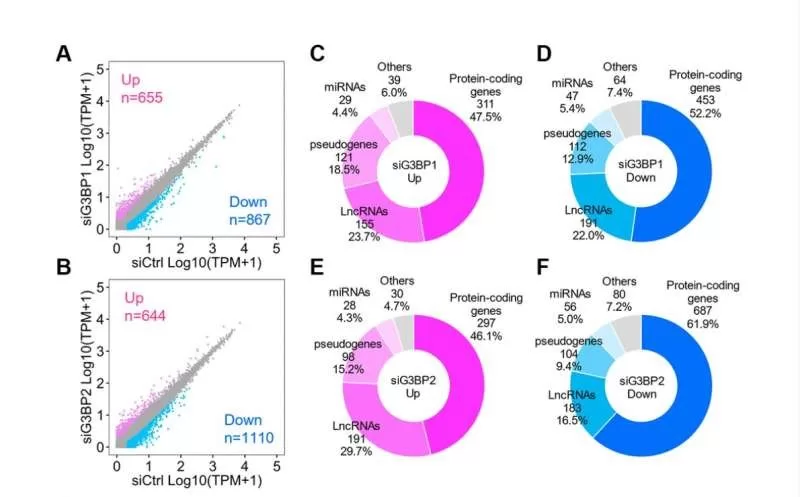
Alzheimer’s disease stress granules have emerged as a focal point in recent scientific research, potentially unearthing the root cause of this devastating condition. These stress granules, which are aggregates of proteins and RNA that form in response to cellular stress, play a crucial role in cellular function and stability. Such discoveries highlight their connection to critical markers of Alzheimer’s, including tau tangles and inflammation, offering new avenues for understanding Alzheimer’s disease symptoms. As researchers delve deeper into stress granules, the potential for breakthroughs in preventing Alzheimer’s disease becomes increasingly tangible. With estimates suggesting that nearly 13 million Americans could face Alzheimer’s by 2050, exploring these cellular phenomena could pave the way for effective interventions and management strategies.
The topic of Alzheimer’s disease stress granules has gained traction among scientists exploring the intricate mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration. These cellular aggregates, formed during periods of biological distress, are being investigated for their role not only in Alzheimer’s but also broader neurodegenerative disorders. As research progresses, terms such as ‘cytoplasmic aggregates’ and ‘stress-related protein clumps’ may come into play, further enriching the dialogue around the pathological processes involved. Increased understanding of tau tangles, inflammation, and the overall impact of cellular stress provides valuable insights into the complexity of this condition. Ultimately, the study of these stress granules not only sheds light on current Alzheimer’s disease symptoms but also opens up possibilities for revolutionizing preventative strategies for future generations.
Understanding Stress Granules in Alzheimer’s Disease
Recent groundbreaking studies highlight the potential of stress granules as a fundamental contributor to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. These stress granules, composed of proteins and RNA, form during biological stress, interfering with crucial cellular processes. They temporarily appear to protect cells from immediate danger, but in the context of Alzheimer’s, they fail to disassemble, leading to chronic cellular dysfunction. This dysfunction catalyzes the accumulation of toxic tau tangles and initiates inflammation, key markers associated with the disease.
As scientists delve into the mechanisms behind stress granules, the implications for Alzheimer’s disease treatment could be profound. Understanding how these proteins misbehave in stress conditions may unravel new therapeutic avenues. The hope lies in developing interventions that can encourage the disassembly of these granules, restoring cellular functionality and potentially reversing or slowing the disease’s progression.
The Link Between Tau Tangles and Stress Granules
Alzheimer’s disease symptoms are heavily linked to the presence of tau tangles, which disrupt neuronal function and lead to cell death. These tangles are tightly associated with the maladaptive formation of stress granules. Research indicates that stress granules can exacerbate the formation of tau tangles by creating an environment conducive to tau hyperphosphorylation—a process central to tangle development. This relationship underscores the importance of stress granules in understanding the intricate biology orchestrating Alzheimer’s pathology.
The inflammatory response triggered by tau tangles further complicates the landscape of Alzheimer’s disease. Chronic inflammation can arise from the body’s attempt to clear away neurotoxic proteins, but it often leads to more damage. By focusing on stress granules as a potential root cause, researchers aim to disrupt this cycle of inflammation and tau toxicity, ultimately providing strategies for preventing the onset or progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease Through Stress Granules Research
Preventing Alzheimer’s disease requires a multifaceted approach, and understanding the role of stress granules could significantly influence prevention strategies. With emerging evidence linking lifestyle factors to the formation of these granules, there is an opportunity for individuals to adopt healthier habits. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and cognitive engagement may help mitigate the biological stress that leads to the formation of detrimental stress granules.
Furthermore, continued research into stress granules may lead to pharmaceutical interventions that can specifically target their formation and the biological stress response. By keeping stress granules in check, it may be possible to prevent the cascade of events leading to tau tangle accumulation and associated Alzheimer’s symptoms. This proactive approach transforms the narrative from merely managing the disease in its later stages to potentially circumventing its development altogether.
The Role of Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Progression
Inflammation contributes to Alzheimer’s disease progression, severely impacting overall brain health. When stress granules form in cells under biological stress, they can trigger inflammatory pathways that exacerbate neurodegeneration. This inflammatory response, while protective initially, becomes detrimental when chronic, leading to ongoing neuronal damage and the worsening of Alzheimer’s disease symptoms.
Recent research focuses on the interplay between stress granules, inflammation, and tau tangles in the brain. By elucidating these relationships, scientists aim to identify therapeutic targets that can alleviate inflammation and ultimately stall the progression of Alzheimer’s. Developing treatments to mitigate inflammation while addressing the root cause—stress granules—may be essential in changing the course of the disease.
Genetic Factors and Stress Granules in Alzheimer’s Disease
Genetic predispositions play a significant role in the likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Variations in genes related to cellular stress responses and the formation of stress granules can predispose individuals to the disease. Understanding how these genetic factors influence the behavior of stress granules could provide insights into personalized prevention and treatment strategies.
The ongoing exploration of genetic influences on stress granule formation represents a growing field of research in Alzheimer’s studies. By identifying specific genetic mutations that affect stress granule dynamics, researchers can better understand the early triggers of Alzheimer’s development. This knowledge is crucial for developing specific interventions tailored to genetic risk profiles.
Impact of Lifestyle on Stress Granule Formation
Lifestyle choices significantly influence the formation and dynamics of stress granules in the brain. Factors such as diet, physical activity, social engagement, and mental stimulation have been shown to modulate biological stress levels, potentially impacting the formation of stress granules. A balanced diet, for instance, may help reduce cellular stress and the consequent formation of harmful protein aggregates associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Moreover, maintaining an active lifestyle is key to promoting brain health. Regular exercise has been linked to reduced inflammation and improved metabolic health, which in turn may aid in reducing the risk of chronic stress granule formation. By emphasizing healthy habits, individuals may lower their chances of Alzheimer’s disease risk and improve their overall cognitive resilience.
How Biological Stress Influences Alzheimer’s Disease
Biological stress, as opposed to psychological stress, plays a critical role in the pathological development of Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers define biological stress as the cellular response to various internal and external stressors that can disrupt normal cellular functions. Exposure to toxins or oxidative stress can lead to the unwanted formation of stress granules, affecting neuronal health and function.
Understanding the nuances of biological stress and its impact on neurons is vital in Alzheimer’s research. Research indicates that controlling exposure to certain stressors might help mitigate the formation of stress granules, thereby protecting against Alzheimer’s onset. Future studies may provide insights into developing stress-modulating therapies as a preventative measure against the disease.
The Necessity for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for effective management and intervention. Recognizing symptoms such as memory loss, decreased cognitive function, and behavioral changes allows for timely care and therapeutic approaches. Recent studies emphasize the role of stress granules and tau tangles as early biomarkers that could signify the onset of Alzheimer’s long before significant symptoms manifest.
With advancements in research, there is optimism that early detection methods focused on recognizing the formation of stress granules could transform Alzheimer’s care. Implementing routine cognitive screenings could facilitate earlier interventions that slow the progression of symptoms and improve quality of life for those at risk, ultimately changing the narrative surrounding Alzheimer’s diagnosis and treatment.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Treatment: Targeting Stress Granules
The future of Alzheimer’s treatment may lie in innovative approaches targeting stress granules. As research progresses, medications designed to prevent or reverse the harmful effects of these proteins could revolutionize treatment modalities. By addressing the core mechanism of stress granules, new therapeutic strategies could emerge, aiming to restore cellular function and halt the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations are essential for leveraging insights from genetics, biology, and clinical studies. By combining efforts, scientists can better understand the mechanisms underlying stress granules and their role in Alzheimer’s, paving the way for targeted therapeutic interventions. This focus on the root causes of disease pathophysiology offers hope for patients and families affected by Alzheimer’s.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do stress granules play in the development of Alzheimer’s disease?
Recent research suggests that stress granules, which are aggregates of proteins and RNA formed in response to cellular stress, may be a root cause of Alzheimer’s disease. These granules are implicated in disrupting essential cellular procedures, such as gene expression and cell survival, ultimately contributing to the development of Alzheimer’s symptoms like tau tangles and inflammation.
How do stress granules affect tau tangles and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease?
Stress granules can hinder the movement of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm of cells, disrupting crucial biological functions. This disruption is linked to the formation of tau tangles and increased inflammation, both of which are key markers of Alzheimer’s disease.
Can preventing stress granule formation help in delaying Alzheimer’s disease symptoms?
While more research is needed, targeting the formation of stress granules holds potential as a therapeutic approach for preventing Alzheimer’s disease symptoms. Understanding how to regulate these granules could lead to strategies that mitigate their negative impact on cellular functions and ultimately slow disease progression.
What are the common Alzheimer’s disease symptoms associated with stress granules?
Common Alzheimer’s symptoms include memory loss, confusion, and difficulty making decisions. These symptoms may be exacerbated by the cellular dysfunction caused by persistent stress granules, which disrupt normal brain function and contribute to the progression of the disease.
How can lifestyle changes help in preventing Alzheimer’s disease related to stress granules?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle characterized by a balanced diet, regular exercise, and social engagement may help reduce biological stressors that contribute to the formation of stress granules. This, in turn, could lower the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Is there a direct link between biological stress and Alzheimer’s disease through stress granules?
Yes, biological stress—arising from various factors like toxins or genetic mutations—can lead to the formation of stress granules. These granules can interfere with vital cellular processes and have been identified as a potential root cause of Alzheimer’s disease.
Are there treatments targeting stress granules being researched for Alzheimer’s disease?
Research is currently exploring ways to target stress granule formation and function as a novel approach to treating Alzheimer’s disease. Advances in understanding how to manipulate these granules may pave the way for innovative therapies in the future.
What are the implications of identifying stress granules as a root cause of Alzheimer’s disease?
Identifying stress granules as a root cause of Alzheimer’s disease challenges previous assumptions and opens new avenues for research and therapeutic intervention. Understanding this link could lead to breakthroughs in treating or even preventing disease progression.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Root Cause of Alzheimer’s Disease | Formation of stress granules is proposed as a potential root cause of Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Definition of Stress Granules | Clumps of proteins and RNA formed under stress affecting cell function. |
| Impact on Biological Processes | Disrupts cell survival, gene expression, and contributes to Alzheimer’s markers like tau tangles and inflammation. |
| Alzheimer’s Disease Statistics | Affects nearly 7 million Americans, predicted to increase to 13 million by 2050. |
| Common Confusion | Alzheimer’s is often confused with dementia; it’s a specific brain disease. |
| Known Risk Factors | Genetic predisposition, age, environmental influences, and lifestyle choices. |
| Symptoms of Alzheimer’s | Early signs include memory loss, confusion, and changes in personality. |
| Research Findings | The study published in ‘Alzheimer’s & Dementia’ suggests stress granules may inhibit important cellular processes. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s disease stress granules represent a significant breakthrough in understanding the potential root cause of this condition. Recent studies indicate that the formation of stress granules, made up of proteins and RNA, may disrupt essential cellular activities and contribute to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. By examining how these stress granules develop and their effects on cellular functionality, researchers are hopeful that this knowledge can lead to new treatment strategies. Understanding Alzheimer’s disease stress granules could usher in a new era of targeted therapies aimed at preventing or mitigating the effects of this debilitating neurodegenerative disorder.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.