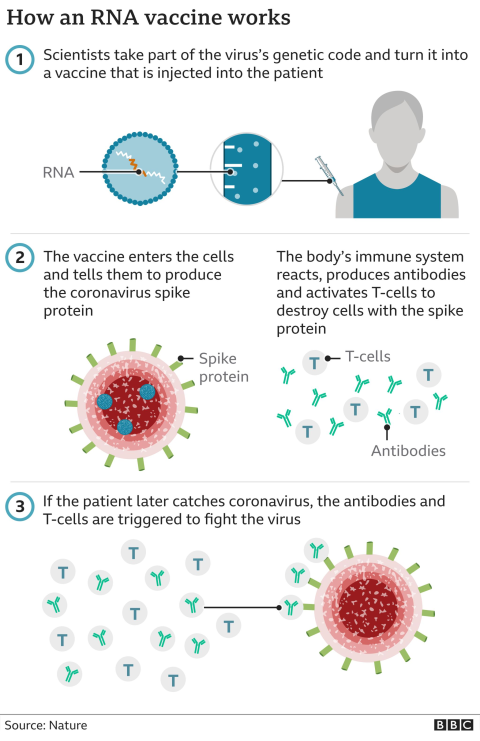
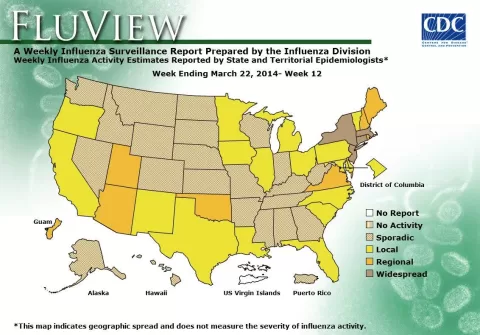
The recent Africa health funding cuts pose a dire threat to the continent’s public health landscape, undermining progress achieved over the past two decades. With a staggering 70% drop in external funding, crucial resources to combat disease outbreaks in Africa have been severely diminished, leaving millions vulnerable to health crises. Such financial reductions have exacerbated the existing maternal health crisis, and the ongoing COVID-19 impact Africa feels creates an urgent need to reassess funding priorities. Additionally, the looming shortages of antiretroviral medication threaten to reverse hard-won gains in the fight against HIV/AIDS, risking countless lives in the process. As African nations grapple with these challenges, a concerted effort to secure sustainable health financing becomes paramount to safeguard the future of their populations.
The significant cuts to health funding across Africa have sparked concerns about the overall well-being of its citizens and the stability of healthcare systems. These reductions, largely stemming from decreased foreign aid, are jeopardizing efforts to manage infectious diseases and address pressing public health issues, including escalating maternal health concerns. With the impact of COVID-19 still resonating throughout the continent, many nations are facing critical shortages in essential health supplies, including antiretroviral therapies. Rising disease outbreaks are further complicating an already precarious health situation, urging leaders to explore innovative financing solutions. As African governments and health authorities strive to navigate these turbulent times, fostering local investments and international collaboration emerges as a beacon of hope for a resilient healthcare future.
The Impact of Africa Health Funding Cuts on Public Health
Africa is currently facing a daunting challenge in public health due to significant cuts in funding. These reductions, notably a staggering 70% decrease in external assistance to health initiatives, threaten to roll back two decades of progress made in maternal and child health. The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) forecasts that these cuts could lead to an additional two to four million deaths each year. This chilling statistic highlights the critical need for sustained funding and resources for public health in Africa to prevent further deterioration of health outcomes.
In particular, the loss of funding severely undermines efforts to combat infectious diseases, which have seen a troubling rise in outbreaks across the continent. The situation is compounded by a lack of domestic investment in health care systems, which leaves vulnerable populations without access to necessary medical resources. The combined effect of these funding cuts amid rising disease outbreaks indicates a looming public health crisis, emphasizing the urgent need for innovative financing solutions and increased commitment from both local governments and international partners.
Addressing Maternal Health Crisis Amidst Funding Reductions
The maternal health crisis in Africa has worsened as funding cuts threaten vital health services. The World Health Organization warns that the loss of external funding plays a crucial role in jeopardizing maternal healthcare, which has already been stretched thin due to inadequate financial support for health programs. With underfunded health systems, many countries struggle to provide essential services, including prenatal and postnatal care, leading to a worrying rise in maternal mortality rates.
Furthermore, with the looming cuts to health funding, African nations are confronted with a dual challenge: ensuring the health of mothers and children while simultaneously managing the rise of disease outbreaks. As funds decrease, resources for maternal health programs diminish, impacting the quality of care that expectant mothers receive. Without immediate action to secure funding for maternal health initiatives, the progress made in this sector risks being unraveled, endangering the lives of mothers and children across the continent.
COVID-19’s Lasting Impact on Africa’s Health Infrastructure
The COVID-19 pandemic has left an indelible mark on Africa’s health infrastructure, with funding cuts exacerbating existing challenges. Health officials have noted that the pandemic redirected resources away from necessary health services, including HIV and maternal health programs. As part of the response to COVID-19, many health systems were overwhelmed, resulting in the neglect of other critical public health needs. These repercussions have further strained already struggling healthcare systems and have hindered progress towards universal health coverage.
Post-pandemic recovery efforts are now intertwined with addressing the negative impacts of funding reductions, particularly in preventive healthcare. As diseases continue to proliferate, the urgency for innovation in financing public health has never been greater. The Africa CDC is exploring various strategies, including partnerships with international agencies to secure funding and support for revitalizing health systems that were debilitated by the pandemic.
Strategies for Combating Antiretroviral Medication Shortages
Antiretroviral medication shortages pose a severe threat to public health in Africa, with funding cuts further complicating the situation. Nations like Uganda and Tanzania face significant challenges in securing the essential medications needed to treat HIV/AIDS, as six countries report nearing depletion of their current stockpiles. Such shortages compromise ongoing treatment efforts, which are crucial for managing the epidemic and preventing further transmission of the virus.
In response to this pressing issue, health officials are calling for innovative financing solutions and increased domestic investment in pharmaceutical production. Promoting local production of antiretroviral medications not only mitigates dependency on external sources but also enhances the resilience of health systems in Africa. Consolidated efforts from both governmental and non-governmental organizations, alongside investment in infrastructure to produce these lifesaving drugs locally, could provide a significant step toward addressing the medication crisis and improving health outcomes for millions.
Collaborative Approaches to Manage Outbreaks in Africa
As Africa grapples with a rising number of disease outbreaks, collaborative approaches are essential to manage public health effectively. The Africa CDC has recognized the need for cross-border cooperation and solidarity among nations to address the complexities of outbreak response. By sharing resources, information, and best practices, countries can work together to mitigate the impact of infectious disease threats, such as mpox and Ebola.
Additionally, establishing frameworks for rapid response during health emergencies can bolster preparedness and significantly reduce the spread of diseases. Strengthening regional health alliances and investing in outbreak surveillance systems will enhance Africa’s ability to respond quickly to new and existing health threats. These collaborative efforts are crucial not only for tackling current outbreaks but also for building a more resilient public health infrastructure on the continent.
Innovative Financing Solutions for Africa’s Health Sector
In the wake of drastic funding cuts, African nations must explore innovative financing solutions to sustain and improve their health sectors. Public health leaders have proposed various strategies, including levies on flights, targeted taxes on luxury items, and local production incentives. Such measures aim to diversify funding sources and lessen reliance on international aid, ultimately promoting greater financial autonomy in managing health programs.
Moreover, engaging the private sector in health financing is critical to overcoming gaps left by reduced external assistance. By promoting public-private partnerships, African governments can foster investment in health infrastructure and crucial health services. Diversifying funding streams not only alleviates the burden of existing funding cuts but also supports the long-term sustainability of health initiatives across the continent.
Revitalizing Health Initiatives through Regional Cooperation
Regional cooperation is vital for revitalizing health initiatives in Africa as funding cuts threaten progress. Collaborative efforts among African nations can yield significant benefits, enabling countries to pool resources and expertise in tackling shared health challenges. By working together, nations can ensure a more coordinated response to public health emergencies, share best practices, and develop a unified approach to maternal and child health, disease outbreaks, and other critical issues.
Strengthening regional health alliances will also empower countries to advocate for increased funding and support from global partners. By presenting a united front, African nations can leverage their collective experience and knowledge to attract attention to their health needs, ultimately influencing funding decisions and policy changes. Regional cooperation, therefore, is not just a strategic move for immediate public health needs but also a cornerstone for building resilient health systems for the future.
The Role of International Partnerships in Strengthening Health Systems
International partnerships are crucial to strengthening health systems in Africa, especially as external funding declines. Collaborations between African nations and global health organizations can provide vital technical assistance, resources, and funding that remains necessary to support various health initiatives. Such partnerships help to fill the gap created by funding cuts, ensuring that critical programs continue to operate despite financial constraints.
Moreover, these collaborations often promote knowledge sharing and capacity building, enabling local health officials and organizations to enhance their skills and expertise. Investing in training and education through international partnerships not only empowers local health systems but also fosters sustainable development within African health sectors. By strengthening these connections, African nations can build more resilient health infrastructures capable of withstanding future funding uncertainties.
Long-Term Implications of Public Health Funding Cuts
The long-term implications of public health funding cuts in Africa are concerning, particularly for the most vulnerable populations. As health budgets shrink, essential healthcare services become less accessible, exacerbating health disparities and increasing mortality rates. Without stabilizing funding levels, the consequences for maternal and child health, chronic disease management, and infectious disease control could be dire.
Furthermore, the potential economic fallout from widespread health crises can lead to a cycle of poverty and health inequities that set back progress for generations. With millions at risk of falling back into poverty due to health-related issues, it is imperative for stakeholders to reconsider funding strategies and prioritize public health investment. Ignoring these long-term implications could jeopardize not only health outcomes but also the broader socioeconomic development of African nations.
The Future of Healthcare Funding in Africa: A Call to Action
The future of healthcare funding in Africa requires urgent action and innovative solutions from both domestic and international stakeholders. As the continent faces unprecedented challenges due to funding cuts, it is essential to rally support for health initiatives that ensure the well-being of millions. Advocating for increased government spending, embracing innovative financing, and fostering public-private partnerships are just some of the ways to forge a path towards sustainable health funding.
Additionally, uniting voices from across Africa to call for equitable funding and resource allocation to health sectors can amplify the need for action. Creating campaigns that highlight the impact of health funding on development and social stability can secure the commitment of partners and stakeholders to invest in Africa’s future. There is a pressing need for a concerted effort to redirect the trajectory of health funding towards building stronger, more resilient health systems capable of facing emerging challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of Africa health funding cuts on public health in Africa?
The recent Africa health funding cuts, which have seen a 70% drop in external assistance, threaten to reverse two decades of progress in public health, particularly impacting maternal and child health. With millions of additional deaths projected annually, these cuts hinder efforts to control disease outbreaks and secure adequate healthcare resources.
How do the funding cuts affect disease outbreaks in Africa?
Africa health funding cuts exacerbate the ongoing rise in disease outbreaks across the continent, with cases increasing from 152 in 2022 to a predicted 213 by 2024. This dramatic decline in funding impedes the response capabilities of African nations to manage and control these infectious diseases effectively.
What is the expected impact of the funding cuts on the maternal health crisis in Africa?
The Africa health funding cuts are anticipated to worsen the maternal health crisis, with the Africa CDC stating that these reductions could lead to an additional two to four million maternal and infant deaths each year as crucial resources for maternal healthcare become even scarcer.
What role does COVID-19 impact have on Africa’s health funding situation?
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerabilities in Africa’s health systems, making the recent funding cuts even more detrimental. As nations grapple with the pandemic’s ongoing effects, diminished external funding threatens efforts to recover and strengthen public health frameworks across the continent.
How are antiretroviral medication shortages linked to the Africa health funding cuts?
With the anticipated depletion of antiretroviral medications in six African countries, the Africa health funding cuts directly jeopardize HIV/AIDS treatment initiatives. Reduced funding from programs like PEPFAR endangers the availability of these life-saving drugs, increasing the risks for those affected by the virus in Africa.
What strategies are being proposed to address the challenges posed by Africa health funding cuts?
In response to Africa health funding cuts, a three-part plan has been developed, emphasizing increased domestic financing, innovative financing strategies, and tackling financing gaps. This plan includes proposals such as raising private-sector investments and introducing targeted taxes to generate essential funding for public health initiatives.
What recent developments in outbreak responses are influenced by funding cuts in Africa?
Funding cuts have impeded outbreak response efforts across Africa, as seen in the management of mpox cases and other health emergencies. Insufficient resources limit testing capabilities and vaccine distribution, leading to ongoing health crises and increased mortality rates in affected regions.
How can African governments improve public health funding amid external aid cuts?
African governments can enhance public health funding by adhering to the Abuja Declaration, which recommends allocating at least 15% of national budgets to health. Other approaches include fostering collaboration among nations, investing in local production of health goods, and exploring innovative financing mechanisms.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| External Funding Cuts | A 70% drop in external health funding, from $81 billion to $25 billion, is expected to result in an additional 2 to 4 million deaths annually. |
| Impact on Infectious Diseases | Funding cuts obstruct efforts to manage infectious diseases, exacerbating health crises across Africa. |
| Domestic Investment Shortfalls | Low domestic investment in health is further worsening the impact of external funding cuts. |
| Abuja Declaration Compliance | Only Rwanda and Botswana are meeting the 15% national health budget allocation target set in the Abuja Declaration. |
| Increasing Health Emergencies | Disease outbreaks in Africa rose from 152 in 2022 to 213 in 2024, risking further strain on health systems. |
| PEPFAR Funding Concerns | Six African nations are at risk of running out of antiretroviral medications due to funding cuts affecting PEPFAR. |
| Three-Part Action Plan | A new plan includes increasing domestic financing, innovative financing strategies, and boosting private-sector investment. |
| Outbreak Updates | Mpox cases have stabilized, but the DRC faces challenges with testing and vaccine shortages, requiring 6.4 million additional doses. |
Summary
Africa health funding cuts are set to have devastating consequences, potentially resulting in millions of additional deaths each year. The reduction in external funding, compounded by low domestic health investments, threatens to reverse hard-won progress in maternal and child health. As diseases increase and health crises intensify, the urgent need for innovative financing and robust domestic health policies becomes increasingly clear.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.