Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening condition characterized by rapid onset of severe respiratory failure. This syndrome manifests through a combination of symptoms, including severe shortness of breath and hypoxemia, often resulting from underlying causes such as trauma, pneumonia, or sepsis. The pathophysiology of ARDS involves complex inflammatory responses that lead to fluid accumulation in the lungs, severely impairing gas exchange. Recent advancements in ARDS treatment, particularly in the context of COVID-19, have highlighted the need for timely diagnosing ARDS to improve patient outcomes. With ongoing research into effective therapies and management strategies, healthcare providers are gaining valuable insights that could revolutionize ARDS care in critical settings.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), often referred to as acute lung injury, represents a critical state of respiratory failure that can arise from various medical conditions. This serious syndrome is marked by an abrupt onset of symptoms, including difficulty in breathing and decreased oxygen levels in the blood. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, or pathophysiology, of ARDS is essential for developing effective treatment options. Recent studies focusing on ARDS treatment advances, especially in relation to COVID-19, emphasize the importance of early detection and diagnosis. As researchers continue to explore the challenges and innovations in managing ARDS, the medical community is better poised to address this complex condition.
Understanding the Symptoms of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
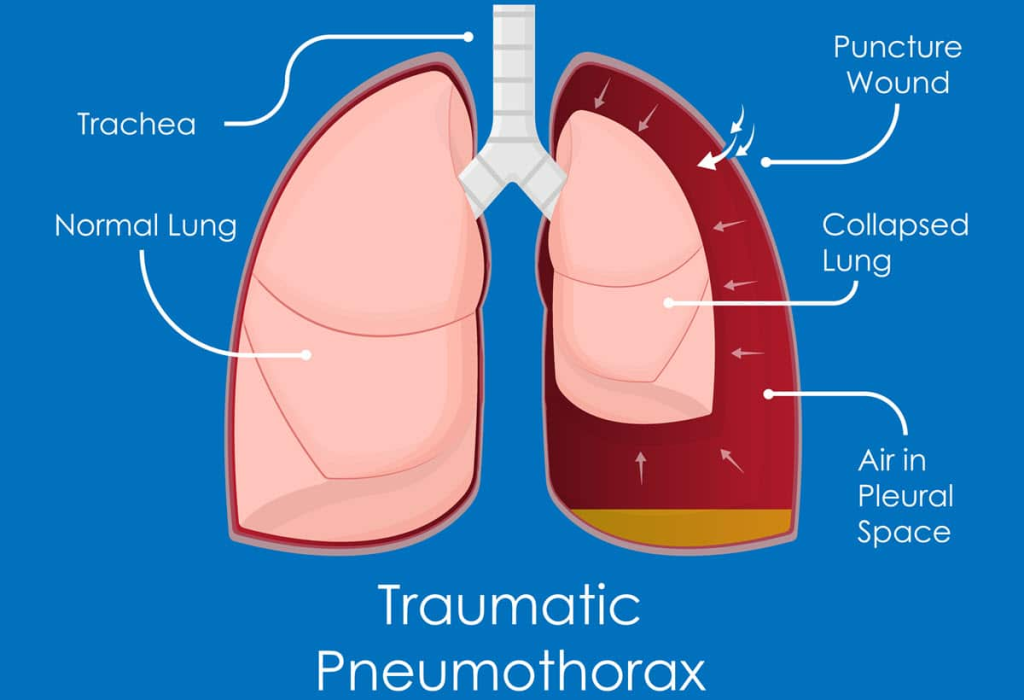
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) manifests with distinct symptoms that can escalate quickly, making early recognition vital for effective intervention. One of the hallmark symptoms is rapid and shallow breathing, which often indicates that the lungs are struggling to facilitate adequate gas exchange. Patients may find it increasingly difficult to take deep breaths, which can lead to severe hypoxemia—a critical condition where oxygen levels in the blood drop dangerously low. These symptoms often progress rapidly, necessitating immediate medical attention.
In addition to rapid breathing, patients with ARDS commonly experience severe shortness of breath. This symptom can become acute, leading to feelings of panic and distress. Furthermore, cyanosis, characterized by a bluish tint to the lips and skin, may be evident, indicating significant oxygen deprivation. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for healthcare providers, as timely diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for patients suffering from ARDS.
Diagnosing Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Key Methods
Diagnosing Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome involves a comprehensive clinical assessment that includes various diagnostic tools and imaging techniques. Initially, physicians rely on a detailed patient history and physical examination, followed by imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans to visualize lung condition. These imaging tests are essential for identifying fluid accumulation in the alveoli, a defining characteristic of ARDS. Moreover, measuring blood oxygen levels is critical to assess the severity of hypoxemia and guide treatment decisions.
In addition to imaging, laboratory tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions that could mimic ARDS symptoms. This thorough diagnosis process is pivotal, as ARDS can develop in response to a range of causative factors, including pneumonia, sepsis, or trauma. Accurate and timely diagnosis ensures that healthcare providers can implement appropriate treatment strategies, ultimately improving the prognosis for patients with ARDS.
Key Advances in ARDS Treatment: Innovations on the Horizon
The landscape of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome treatment has seen significant advancements in recent years. One notable development is the approval of Gohibic, a targeted therapy specifically designed for ARDS patients related to COVID-19 who are on systemic corticosteroids. This treatment represents a major breakthrough, as it aims to mitigate the severe inflammatory responses that characterize ARDS, particularly in critically ill patients. Such innovations could drastically alter the management of ARDS, especially during viral outbreaks.
Moreover, ongoing clinical trials are exploring additional therapeutic options that may enhance recovery and reduce complications associated with ARDS. Researchers are investigating the role of anti-inflammatory agents and advanced supportive care techniques, which are essential for managing the complexities of this syndrome. These treatment advances underscore the importance of continuous research and development in improving patient outcomes for those affected by ARDS.
The Pathophysiology of ARDS: Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
Understanding the pathophysiology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies. ARDS is characterized by a complex interplay of inflammatory responses, endothelial injury, and altered coagulation processes. These mechanisms lead to increased permeability of the alveolar-capillary membrane, resulting in pulmonary edema and impaired gas exchange. The intricate biological pathways involved highlight the need for targeted interventions that address the underlying causes of lung injury.
Recent research has uncovered new insights into the mechanical instability often observed in the lungs of ARDS patients. Such findings not only enhance our understanding of ARDS but also pave the way for innovative therapeutic approaches. By focusing on the underlying pathophysiological processes, healthcare providers can develop more effective management strategies, ultimately improving the prognosis for patients suffering from ARDS.
The Impact of COVID-19 on ARDS Management Practices
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly influenced the management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, bringing new insights and adaptations to clinical practices. The influx of patients with severe respiratory distress due to the virus has prompted healthcare providers to refine their treatment strategies, leading to improved outcomes. Adaptive approaches that emerged during the pandemic, such as enhanced ventilatory support and the use of novel pharmacological agents, have potential applications for all types of ARDS, not just those related to COVID-19.
Furthermore, the experience gained from managing ARDS cases during the pandemic has provided invaluable lessons for critical care practices. Health professionals have developed a more profound understanding of the syndrome’s complexities, allowing for quicker and more effective responses in acute situations. This evolving knowledge base is crucial for preparing healthcare systems to handle future respiratory crises, ensuring that providers are equipped with the best practices for treating ARDS.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?
Common symptoms of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) include rapid, shallow breathing, severe shortness of breath, and cyanosis, which is a bluish tint to the lips and skin indicating low oxygen levels. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
How is diagnosing ARDS conducted in clinical settings?
Diagnosing ARDS typically involves a comprehensive clinical assessment, which includes imaging tests like chest X-rays or CT scans to identify lung inflammation and fluid accumulation. Additionally, blood oxygen levels are assessed to confirm hypoxemia, a key characteristic of ARDS.
What recent advances have been made in the treatment of ARDS?
Recent advances in ARDS treatment include the approval of Gohibic, a targeted therapy for patients with ARDS related to COVID-19. This represents a significant development in managing ARDS, especially during viral pandemics, and could improve patient outcomes by offering more effective treatment options.
What is the pathophysiology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?
The pathophysiology of ARDS involves complex interactions between inflammatory responses, endothelial injury, and coagulation processes that lead to lung tissue damage and increased permeability. This cascade results in pulmonary edema, severely impairing gas exchange and oxygen delivery.
How has COVID-19 influenced the management of ARDS?
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly influenced ARDS management by introducing new adaptive treatment strategies. Lessons learned from treating COVID-19 related ARDS cases have improved critical care practices, potentially benefiting all ARDS patients by refining treatment protocols and enhancing patient care.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview of ARDS | ARDS is a severe respiratory failure condition caused by trauma, pneumonia, or sepsis, leading to lung inflammation and hypoxemia. |
| Recent Research Insights | New mechanisms of lung instability identified, opening avenues for improved therapies. |
| Treatment Advances | EU approval for Gohibic, a treatment for ARDS related to COVID-19, enhancing treatment options. |
| Impact of COVID-19 on ARDS Management | Experience from COVID-19 has improved critical care practices for ARDS treatment. |
| Symptoms of ARDS | Key symptoms include rapid breathing, severe shortness of breath, and cyanosis. |
| Diagnosis | Diagnosis involves imaging tests and assessments of blood oxygen levels. |
| Causes of ARDS | Common causes include sepsis, trauma, pneumonia, and inhalation injuries. |
| Pathophysiology | Involves inflammatory responses and endothelial injury leading to lung damage. |
| Future Directions | Ongoing trials and AI integration are exploring new treatments for ARDS. |
Summary
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a critical condition that poses significant challenges in clinical environments. Recent developments in understanding the mechanisms behind ARDS, along with advancements in treatment options, are paving the way for better patient management. The insights gained from the COVID-19 pandemic have also contributed to improved practices in treating ARDS, emphasizing the importance of timely diagnosis and intervention. As research continues to evolve, it is anticipated that new therapies will emerge, enhancing the overall care for patients facing this severe respiratory condition.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.