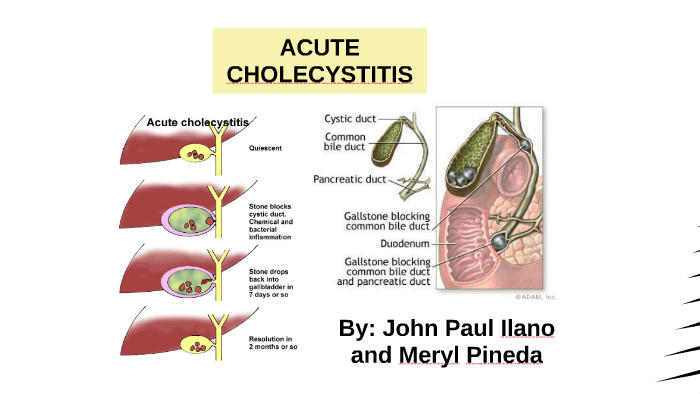
**Acute cholecystitis** is a critical medical condition that arises from the inflammation of the gallbladder, often triggered by the presence of gallstones obstructing the cystic duct. This sudden inflammation can lead to severe complications if not addressed promptly, making it essential for individuals to recognize the **cholecystitis symptoms**, which include intense abdominal pain, nausea, and fever. Diagnosing this condition typically involves imaging techniques such as ultrasound, which is vital for assessing the gallbladder inflammation and determining the appropriate **acute cholecystitis treatment**. In many cases, surgical intervention, specifically a **cholecystectomy**, may be necessary to prevent further complications. Understanding the nuances of acute cholecystitis is crucial for effective management and improved outcomes for patients.
Acute cholecystitis, often referred to as gallbladder inflammation, is a sudden and serious condition that can lead to significant health risks if left untreated. It typically occurs due to the blockage of the gallbladder, primarily from gallstones, leading to a cascade of symptoms that can escalate quickly. Recognizing the signs associated with this inflammatory response is essential for timely diagnosis and management. Medical professionals usually employ various diagnostic tools to confirm the condition and decide upon the most effective treatment options, which may include surgical procedures like cholecystectomy. By understanding the complexities surrounding gallbladder inflammation, both patients and healthcare providers can work together to ensure prompt and appropriate care.
Understanding Acute Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is a rapid-onset condition that significantly affects the gallbladder, primarily due to the obstruction caused by gallstones. This obstruction leads to inflammation, resulting in severe abdominal pain and discomfort. The gallbladder’s inability to drain bile effectively creates a perfect environment for infection, further exacerbating the condition. As such, understanding the nuances of acute cholecystitis is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
The gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver, plays a vital role in digestion by storing bile produced by the liver. When gallstones obstruct the cystic duct, bile accumulates, causing the gallbladder to become inflamed. This inflammation not only leads to pain but can also result in serious complications if not addressed quickly. Acute cholecystitis is thus a medical emergency that must be recognized and treated promptly to prevent further health risks.
Symptoms of Acute Cholecystitis
The symptoms of acute cholecystitis are often unmistakable and serve as critical indicators for medical intervention. Patients typically experience severe abdominal pain, most notably in the right upper quadrant. This pain can be persistent and may radiate to the back or right shoulder, often described as sharp or cramping. Additionally, nausea and vomiting frequently accompany the pain, contributing to the patient’s overall distress.
A low-grade fever is another common symptom, as the body attempts to fight off the inflammation and potential infection within the gallbladder. Tenderness in the abdomen, particularly upon palpation, is a significant finding during clinical examinations. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital, as they can escalate quickly, leading to complications such as gallbladder rupture or peritonitis.
Diagnosis of Cholecystitis
Diagnosing acute cholecystitis typically begins with a thorough clinical evaluation and a review of the patient’s symptoms. The most effective initial imaging technique is an ultrasound, which can reveal gallbladder wall thickening and the presence of gallstones. This non-invasive procedure is particularly useful in emergency settings and can help distinguish acute cholecystitis from other abdominal conditions.
In some cases, further imaging may be required, such as a CT scan or MRI, especially if complications are suspected. These advanced imaging techniques provide detailed views of the gallbladder and surrounding structures, helping to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial, as it directly influences the treatment approach and potential outcomes for the patient.
Acute Cholecystitis Treatment Options
The treatment of acute cholecystitis typically necessitates hospitalization for close monitoring and management. Initial management focuses on stabilizing the patient, which includes administering intravenous fluids to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance. Alongside fluid management, the use of antibiotics is critical, particularly if there is evidence of infection. The choice of antibiotics is guided by clinical guidelines and may vary based on the patient’s health status.
Surgical intervention is often required, with cholecystectomy being the standard procedure for definitive treatment. This surgical removal of the gallbladder can be performed laparoscopically or through open surgery, depending on the case’s complexity. Recent clinical guidelines advocate for early cholecystectomy to minimize complications associated with delayed intervention, underscoring the importance of timely treatment in acute cholecystitis cases.
Recent Guidelines in Managing Acute Cholecystitis
Recent clinical guidelines, particularly the Tokyo Guidelines 2018, provide a structured approach to diagnosing and managing acute cholecystitis. These guidelines emphasize the importance of prompt diagnosis, recommending ultrasound as the first-line imaging modality, followed by surgical consultation when acute cholecystitis is confirmed. Adhering to such structured protocols can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
The guidelines also highlight the necessity of timely surgical intervention, advocating for early cholecystectomy to lower the chances of serious complications, such as perforation or abscess formation. By integrating these recommendations into clinical practice, healthcare providers can enhance the management of acute cholecystitis, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care based on the latest evidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of acute cholecystitis?
Common symptoms of **acute cholecystitis** include severe abdominal pain localized to the right upper quadrant, nausea, vomiting, fever, and tenderness in the abdomen. Recognizing these **cholecystitis symptoms** is crucial for timely medical intervention.
How is acute cholecystitis diagnosed?
The **diagnosis of cholecystitis** typically involves an ultrasound, which can identify gallbladder wall thickening and the presence of gallstones. In some cases, CT or MRI scans may be utilized for further evaluation.
What are the treatment options for acute cholecystitis?
Treatment for **acute cholecystitis** often includes hospitalization for intravenous fluids and antibiotics. Surgical intervention, particularly a **cholecystectomy**, is frequently necessary to remove the gallbladder and prevent complications.
What causes acute cholecystitis?
The primary cause of **acute cholecystitis** is the obstruction of the cystic duct, usually due to **gallstones**. Other factors may include infections and tumors that obstruct bile flow.
Why is early cholecystectomy recommended for acute cholecystitis?
Early **cholecystectomy** is recommended for **acute cholecystitis** to minimize the risk of complications such as perforation and infection. Recent guidelines emphasize timely surgical intervention to improve patient outcomes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Acute Cholecystitis | An inflammation of the gallbladder often caused by gallstones that obstruct the cystic duct. |
| Symptoms | Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and tenderness in the right upper quadrant. |
| Causes | Gallstones, infections, tumors, or other obstructions of the cystic duct. |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound is the preferred method, with CT or MRI used in complex cases. |
| Treatment Options | Initial management includes IV fluids and antibiotics, with surgical cholecystectomy often required. |
| Recent Guidelines | Tokyo Guidelines 2018 recommend timely diagnosis and surgical intervention to improve outcomes. |
Summary
Acute cholecystitis is a critical condition that requires immediate attention to prevent serious complications. It is characterized by the inflammation of the gallbladder, primarily due to gallstone obstruction. Symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, and fever are essential indicators for diagnosis. Timely intervention, including effective diagnostic imaging and appropriate treatment options like cholecystectomy, is crucial for patient recovery. By adhering to updated clinical guidelines, healthcare providers can enhance patient outcomes and minimize the risks associated with acute cholecystitis.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.