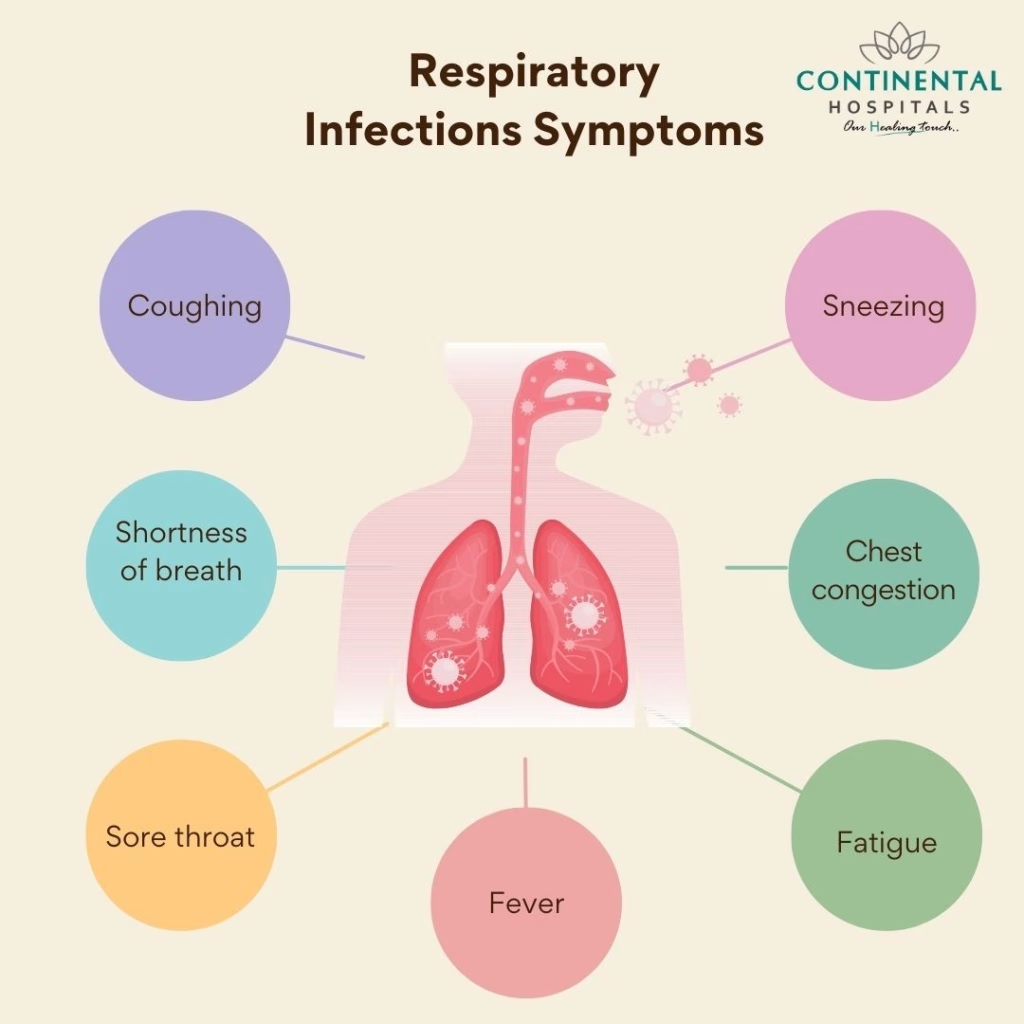
Respiratory illness is on the rise, fueled by a surge in diseases like whooping cough, seasonal influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and COVID-19 cases. As we progress through the 2025–26 respiratory season, public health authorities are grappling with the impact of these illnesses across the United States. The spike in pertussis (or whooping cough) has become particularly alarming, especially in regions like Arkansas, where reported cases have reached an all-time high. Additionally, the influenza A subclade K strain has led to a concerning increase in hospital visits and mortality rates nationwide. With over 7.5 million estimated illnesses attributed to influenza alone this season, it underscores the urgent need for vaccination and preventive measures against respiratory illnesses.
Breathing-related conditions are increasingly causing concern as various pathogens circulate during the chilly months, leading to widespread health complications. Known alternatively as pulmonary ailments, these disorders encompass a range of infections, including pertussis and viral infections like flu and RSV. Recent trends highlight a troubling rise in respiratory infections, particularly with a notable increase in cases of whooping cough and seasonal flu. Amid the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, health officials face unprecedented challenges as they monitor surging infection rates across multiple states. To combat these respiratory threats, effective vaccination strategies and public health interventions are crucial in safeguarding the health of communities.
Understanding Respiratory Illness Activity
As we navigate through the 2025-26 respiratory season, it’s crucial to recognize the escalating activity of respiratory illnesses across the United States and various global regions. Diseases such as pertussis, seasonal influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and COVID-19 are significantly contributing to this surge. The convergence of these respiratory viruses can overwhelm public health systems and lead to increased hospitalizations, highlighting the importance of both awareness and preventive strategies.
Respiratory illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations like young children and the elderly, require immediate attention. For instance, the recent rise in cases of whooping cough has been alarming, emphasizing the need for vaccinations and timely healthcare interventions. Public health officials warn that as we see flu and RSV cases climb, the compounding effect of these illnesses could lead to severe respiratory complications, underlining the importance of ongoing surveillance and proactive healthcare measures.
Arkansas’ Pertussis Challenge: A State Perspective
In 2025, Arkansas has witnessed an alarming spike in pertussis cases, with over 500 infections reported—the highest since the state began monitoring these cases 15 years ago. This increase is particularly concerning as it highlights how communicable respiratory illnesses can rapidly spread within communities. More than 50 counties have reported cases, showcasing that whooping cough is not confined to select areas, thus demanding a statewide public health response.
The demographics of the reported cases reveal that the majority of those affected are children and adolescents, with particularly vulnerable infants under one year old comprising a significant percentage of hospitalizations. The death of a child linked to pertussis this year serves as a tragic reminder of the devastating impact of vaccine-preventable diseases. Strong advocacy for vaccinations is essential to control outbreaks and protect at-risk groups from serious respiratory complications.
The Rise of Seasonal Influenza and Its Impacts
As the respiratory season progresses, current reports from the CDC indicate that seasonal influenza activity is not only high but continues to escalate across the nation. A significant factor in this development is the dominance of the A(H3N2) influenza viruses, particularly the emerging subclade K, which has contributed to increased morbidity rates. The distinction of this subclade K demonstrates how evolving flu strains can affect overall flu activity by causing earlier outbreaks and heightened transmission.
The statistics are concerning, with millions of flu-related illnesses reported this season. The CDC’s estimation of over 7.5 million illnesses, alongside substantial hospitalization figures, suggests that the public must remain vigilant. As medical experts emphasize, annual vaccination remains the best defense against seasonal influenza, aiding in the reduction of severe cases and fatalities, thus mitigating the burden on healthcare systems during peak illness periods.
COVID-19 and Its Continuous Impact on Health
The latest updates from the CDC are revealing a concerning trend, as COVID-19 cases are on the rise in 39 states, accompanied by increasing hospitalizations. The persistent presence of COVID-19, alongside concurrent flu and RSV infections, signals a compounded public health challenge. The resurgence of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for continued vigilance, even amidst widespread vaccination efforts, as severe disease remains a significant threat, especially to older adults and those with pre-existing health conditions.
Additionally, while vaccination efforts have contributed to a decline in severe disease among certain demographics, uptake remains disappointingly low in high-risk groups across various regions. The WHO has noted the need for stronger initiatives to increase vaccine coverage, which could play a pivotal role in controlling the spread of COVID-19 and reducing hospitalizations from respiratory illnesses. The integration of vaccination campaigns addressing all prevalent respiratory pathogens, including COVID-19, could provide a comprehensive strategy for better public health outcomes.
The Alarming Increase in RSV Cases
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) continues to surge across various regions, compounding the impact on public health systems already strained by influenza and COVID-19. This increase has been particularly pronounced in vulnerable populations such as infants and the elderly, who are at greater risk for severe respiratory complications. The dynamics of RSV outbreaks, which often peak in winter months, are contributing significantly to the overall rise in respiratory illness activity this season.
The recent CDC data indicating that RSV infections are likely growing in 41 states calls for immediate public health attention. Strategies to manage RSV include encouraging vaccinations for fluid-borne respiratory pathogens and preventative measures for susceptible groups. Increased healthcare communication regarding RSV symptoms and the necessity for medical intervention can help mitigate severe outcomes among the most affected populations.
Vaccination: A Key Preventative Measure
Vaccination remains the linchpin in the fight against the rising tide of respiratory illnesses, including whooping cough, influenza, RSV, and COVID-19. Public health campaigns are increasingly focusing on the importance of vaccinations across all age groups. The evidence consistently underscores that proper vaccination can significantly reduce the severity of respiratory illnesses and lower hospitalization rates, thereby alleviating pressure on healthcare systems especially during peak respiratory seasons.
Moreover, experts reiterate that engagement from healthcare providers is critical to improve vaccination rates, particularly in communities with rising respiratory illness cases. Strategies to address common hesitancies and educate the public on the benefits of immunization could amplify the impact of vaccination initiatives. Ultimately, building a robust vaccination framework could create a resilient public health response capable of combating multiple respiratory illnesses simultaneously.
Community Preparedness for Respiratory Illnesses
Preparation at the community level is essential for managing surges in respiratory illnesses. As plethoras of respiratory pathogens emerge, communities are urged to develop comprehensive preparedness plans that encompass vaccination drives, public health education, and contingency protocols for healthcare facilities. This collective approach fosters a sense of responsibility among residents to be proactive, thereby improving community resilience against potential outbreaks.
Additionally, integrating communication strategies that inform the public about the symptoms and transmission of respiratory illnesses can empower individuals to seek timely medical intervention. As respiratory illness activities escalate, such preparedness can significantly mitigate the impacts of these illnesses, reducing transmission rates and subsequent hospitalizations. Collaborative efforts between local health departments and community organizations are essential in crafting a responsive framework to tackling the burden of respiratory illnesses.
Monitoring Trends in Respiratory Illnesses
Ongoing surveillance and monitoring of respiratory illnesses are imperative as we navigate the complexities of the 2025–26 respiratory season. Tracking data related to pertussis, influenza, RSV, and COVID-19 will provide invaluable insights necessary for public health officials to respond effectively. Trends indicate not only the prevalence of these illnesses but also inform strategies for prevention and treatment, including vaccination recommendations.
The role of technology and data analytics in enhancing monitoring capabilities cannot be understated. With real-time data collection and analysis, health officials can identify outbreaks swiftly, allowing for prompt public health interventions. It also opens avenues for community awareness campaigns targeted at reducing transmission, especially as seasonal patterns evolve and new strains of pathogens emerge.
The Role of Health Insurance in Respiratory Health
Access to healthcare, including vaccinations and treatments for respiratory illnesses, is significantly influenced by health insurance coverage. Individuals without adequate health insurance may face barriers in seeking timely care and vaccinations, increasing their risk for severe respiratory complications. The disparities in access raise critical questions about equity in healthcare, particularly during rising respiratory illness seasons.
Healthcare policies should aim to enhance coverage for preventative services such as vaccinations, especially for high-risk groups. By reducing financial barriers for those most vulnerable to respiratory illnesses, it is possible to improve health outcomes and overall community resilience. Moving forward, advocacy for comprehensive health insurance initiatives that prioritize respiratory health can have profound implications for public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current situation regarding whooping cough (pertussis) cases in Arkansas?
Arkansas has reported over 500 cases of whooping cough (pertussis) this year, marking the highest number since data collection began 15 years ago. The cases are widespread, affecting more than 50 counties, with a significant number of hospitalizations, especially among infants under one year old. Public health officials emphasize vaccination as the most effective prevention strategy.
How is seasonal influenza contributing to respiratory illness activity this year?
Seasonal influenza is currently elevated, with high activity levels reported across the United States. Influenza A(H3N2), particularly the subclade K strain, is driving this surge, resulting in millions of illnesses and thousands of hospitalizations and deaths. Vaccination is recommended for everyone aged 6 months and older to help mitigate the risks associated with seasonal influenza.
What trends are we seeing in COVID-19 cases across the United States?
Recent reports indicate that COVID-19 cases are increasing in 39 states, contributing to a rise in hospitalizations and fatalities. The World Health Organization (WHO) continues to stress the importance of vaccination, which remains effective in reducing severe disease, particularly in high-risk groups.
What role does the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) play in respiratory illnesses this season?
RSV infections are reported to be increasing in 41 states this season, adding to the overall burden of respiratory illnesses such as COVID-19 and influenza. Given its impact, especially on young children and the elderly, it’s crucial to monitor RSV trends as part of the respiratory illness landscape.
Why is vaccination so important for preventing respiratory illnesses like whooping cough and influenza?
Vaccination is a critical prevention strategy against respiratory illnesses, including whooping cough (pertussis) and seasonal influenza. Vaccines effectively reduce the incidence of these diseases, hospitalizations, and related complications, especially among vulnerable populations such as infants and the elderly.
| Disease | Key Statistics | Impact | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pertussis (Whooping Cough) | > 500 cases in Arkansas (highest in 15 years) | Majority are children; 50+ hospitalizations; 1 death reported | Vaccination emphasized; prompt antibiotic treatment recommended |
| Influenza | 7.5 million illnesses, 81,000 hospitalizations, 3,100 deaths this season | Seasonal activity elevated; particularly affecting children | Annual vaccination recommended for ages 6 months and older |
| COVID-19 | Infections increasing in 39 states; growing hospitalizations in Europe | Severe impact among older adults and individuals with chronic conditions | Vaccination still effective; low uptake in high-risk groups noted |
| Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) | Infections growing in 41 states | Particularly concerning for infants and young children | Preventive measures include good hygiene and vaccination where applicable |
Summary
Respiratory illness is on the rise globally, fueled by numerous infectious diseases such as pertussis, influenza, RSV, and COVID-19. With alarming statistical spikes in cases—especially in regions like Arkansas for whooping cough—public health officials stress the importance of vaccination and other preventive measures. In particular, the increase in influenza cases, predominantly from a newly identified strain, highlights the urgency for annual vaccinations, especially among vulnerable populations like children and the elderly. As we navigate through this respiratory season, continued awareness and action can help mitigate the impact of respiratory illnesses.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.