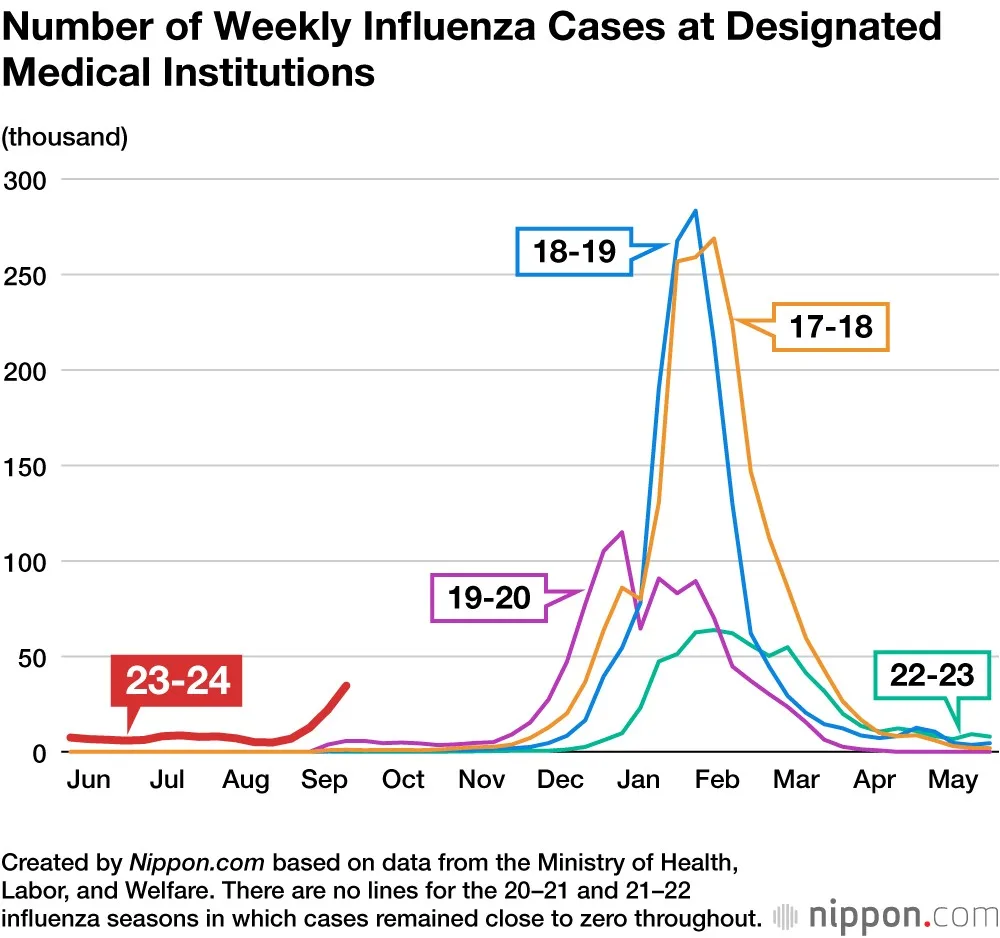
The Japan influenza season 2023 is already shaping up to be a notable chapter in the country’s public health narrative, as officials have declared an early epidemic amidst a surge in influenza cases in Japan. This year, the flu outbreak has garnered attention not only for its timing, beginning approximately five weeks ahead of the usual schedule, but also for the alarming rates of infection reported in key regions like Tokyo and Okinawa. With over 6,000 reported cases and numerous school closures, health experts are closely monitoring the situation. Children under 14 are particularly vulnerable, making up a significant portion of those hospitalized. As this influenza epidemic evolves, concerns about the potential for wider outbreaks across Asia and Europe loom large, highlighting the interconnected nature of viral spread in our globalized world.
As Japan grapples with a challenging flu season in 2023, the current surge in influenza infections has raised significant public health concerns. This year’s early onset of flu activity has prompted health officials to classify the situation as an epidemic, particularly affecting populous areas like Tokyo and Okinawa, which are witnessing unprecedented flu rates. The unexpected increase in influenza cases has also led to disruptions in educational settings, with numerous schools shuttering their doors. With thousands of documented infections and hospitalizations predominantly impacting younger populations, the urgency to address this health crisis is palpable. Experts warn that the ramifications of this outbreak may extend beyond Japan, possibly influencing flu dynamics in neighboring regions.
Japan Influenza Season 2023: An Overview
The Japan influenza season 2023 has begun with an alarming increase in influenza cases, prompting health officials to declare an epidemic early in the month. Historically, Japan experiences its flu activity peak towards the end of November, but this year has seen a startling start, with cases rising approximately five weeks ahead of the norm. The rapid spread of the influenza virus has resulted in significant disruptions, including the closure of over 100 schools across the country, indicating the severity of the situation.
As of October 10, health authorities reported over 6,000 recorded influenza cases, with a concerning number of hospitalizations, particularly among children. The data highlights that 287 individuals have been hospitalized due to influenza-related illnesses, emphasizing the vulnerability of younger populations under the age of 14. This unprecedented early flu season could have implications not just for Japan, but for neighboring regions as experts caution about potential outbreaks extending beyond national borders.
Impact of the Influenza Outbreak on Tokyo and Okinawa
Both Tokyo and Okinawa are currently central to the ongoing flu outbreak, experiencing particularly high rates of infection. In Tokyo, the dense population and urban lifestyle contribute to the rapid transmission of the virus, making it a focal point for health officials. Meanwhile, Okinawa’s region, known for being a tourist hotspot, faces unique challenges in managing flu cases, especially as the influx of visitors coincides with rising flu rates.
The health sector in these regions is on high alert as cases continue to climb, and it is imperative to monitor the situation closely. Public health campaigns emphasizing vaccination and hygiene have become crucial as officials strive to curb the spread of influenza. Additionally, the consequences of this outbreak are not limited to health impacts; economic activities and travel plans are also being disrupted as the flu season continues to escalate in these regions.
Understanding Early Flu Seasons: What to Expect
The early flu season of 2023 is a concern for both health officials and the public, given that flu seasons usually peak later in the year in Japan. This unusual timing poses questions regarding the types of circulating strains and their implications. Health experts have noted that an early epidemic can lead to sustained transmission rates, allowing the virus to spread more widely among the population, thus increasing the number of influenza cases significantly as winter approaches.
Furthermore, the unpredictability of flu strains complicates preparations for public health responses. With the early onset of influenza activity, more attention must be paid to develop vaccines that can address the most pressing strains. This preparation is critical not only for managing the current outbreak in Japan but also in curbing potential influenza pandemics in Asia and Europe, where the repercussions of an unmanaged flu season could be severe.
Preventing the Spread of Influenza in Japan
As the influenza season kicks into high gear, preventive measures are being emphasized by health authorities throughout Japan. Vaccination remains the most effective way to protect against severe illness. With millions of doses administered each year, health officials encourage both adults and children to get vaccinated, especially considering the growing number of flu cases in schools and communities. Public awareness campaigns have been launched to inform citizens about the importance of vaccination during the Japan flu outbreak.
In addition to vaccination, simple hygiene practices such as regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and staying home when symptomatic are being promoted. These measures play a crucial role in mitigating the spread of the virus and protecting vulnerable populations, particularly children and the elderly. Communities are being urged to take action collectively to reduce the burden of influenza as we navigate this challenging flu season.
Hospitalizations During Japan’s Influenza Epidemic
With over 287 individuals hospitalized due to the influenza outbreak as of early October, the pressure on healthcare systems in Japan has become a major concern. The demographic most affected includes children under the age of 14, who represent more than half of the hospitalizations recorded. This trend raises alarms about the need for adequate medical resources and preparedness to handle a surging number of cases.
Healthcare organizations are working tirelessly to ensure that medical facilities are not overwhelmed and that those in need receive appropriate care. This necessitates increased staffing, availability of antiviral medications, and continuous monitoring of the situation to respond effectively to patient needs. The priority remains to safeguard the health of the community, particularly the young and those with underlying health conditions.
The Role of Schools in Flu Transmission
Schools have been identified as critical transmission points for influenza, which has prompted the closure of over 100 institutions in response to the current epidemic. With children being among the most susceptible to infections, school environments can facilitate rapid spread among students. Many educational institutions are now stepping up their health protocols, including enhanced sanitation measures, educational programs on disease prevention, and in some cases, vaccination drives on campus.
These proactive measures aim to minimize outbreaks within the classroom setting, as the effects of influenza can ripple throughout communities. By addressing health at schools, officials hope to control the outbreak more effectively and mitigate the risks associated with influenza cases, particularly as the virus continues to impact daily life in Japan.
Monitoring Influenza Case Trends in Japan
Keeping track of influenza cases during the early flu season 2023 is essential for public health responsiveness. Continuous monitoring of infection rates in prefectures, particularly in hotspots like Okinawa and Tokyo, aids health officials in making informed decisions regarding interventions and resource allocation. The data collected can also provide insights into the types of influenza strains circulating, guiding vaccine development for future seasons.
Furthermore, the ability to quickly identify trends in hospitalization rates can impact emergency preparedness strategies. As Japan progresses through this unusually early flu season, it remains critical to establish a robust surveillance system that considers both local and national influenza activity, ensuring that information is disseminated effectively and timely across the healthcare network.
Possible Regional Consequences of Japan’s Flu Outbreak
The ongoing influenza epidemic in Japan has raised concerns about the potential for regional consequences beyond its borders. Given the interconnectedness of countries in Asia, the transmission of influenza could easily cross borders, leading to outbreaks in neighboring regions. Health experts emphasize the importance of international collaboration on surveillance and response strategies to mitigate the spread of the virus.
Increased travel during cultural festivities and holidays poses an additional risk for inflating case numbers. Countries surrounding Japan are advised to strengthen their health measures, including vaccination drives and public health campaigns to prepare for potential influxes of influenza cases stemming from Japan. Understanding the patterns and progression of this outbreak is essential for curbing a wider epidemic that could affect millions.
Public Health Messaging During Flu Seasons
Effective public health messaging is critical during the influenza season, particularly as Japan faces heightened activity this year. Authorities are working to disseminate clear and actionable information regarding flu prevention, vaccination, and symptom recognition. Utilizing multiple platforms, including social media, community events, and educational outreach, health organizations aim to increase awareness and encourage responsible health behaviors among the population.
As misinformation can lead to public panic or complacency, accurate communication is essential for maintaining trust in health guidance. By fostering a well-informed community, authorities can better equip citizens to navigate flu season effectively, understanding the importance of preventive actions that can protect themselves and others against the circulating strains of the influenza virus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current status of the Japan influenza season 2023?
The Japan influenza season 2023 has started early and is considered severe, with health officials declaring an influenza epidemic. As of October 10, there are over 6,000 recorded cases, and more than 100 schools have closed due to the outbreak.
Why is the flu season in Japan starting earlier this year?
Typically, Japan experiences its increased influenza activity at the end of November. However, the flu season in Japan for 2023 has begun approximately five weeks earlier than usual, leading to a rapid rise in influenza cases.
What are the current influenza rates in Tokyo and Okinawa during the 2023 flu outbreak?
Tokyo and Okinawa are currently seeing particularly high rates of influenza infections. The situation is serious enough to prompt health officials to warn of potential outbreaks extending beyond Japan in the near future.
How many influenza cases have been reported in Japan as of October 2023?
As of October 10, 2023, Japan has recorded approximately 6,013 influenza cases, with 287 individuals hospitalized due to their illnesses, primarily among children under 14 years old.
What impact could the Japan influenza season 2023 have on international health issues?
Experts have expressed concern that the current influenza outbreak in Japan could trigger further outbreaks across Asia and Europe, given the interconnected nature of viral infections.
What measures are being taken in Japan to combat the 2023 influenza epidemic?
In response to the early influenza epidemic, health officials in Japan are closely monitoring reported cases and may implement educational campaigns and health advisories to reduce the spread of the influenza virus.
What precautions can individuals take during the early flu season 2023 in Japan?
During the early flu season in Japan, individuals are encouraged to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, wearing masks in crowded areas, and getting vaccinated if eligible.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Early Influenza Season | Japan is experiencing an influenza season that has started approximately five weeks earlier than usual. |
| Epidemic Declaration | Health officials declared an influenza epidemic earlier this month due to rising viral activity. |
| School Closures | Over 100 schools have closed as a result of the influenza outbreak. |
| High Infection Rates | Okinawa and Tokyo are reporting particularly high rates of influenza infection. |
| Hospitalizations | As of October 10, there are 287 hospitalizations, with over half being children under 14. |
| Virus Strains | Officials have not yet provided information about the circulating virus strains. |
| Potential Outbreaks | Experts are concerned that infections in Japan may lead to outbreaks in Asia and Europe. |
Summary
The Japan influenza season 2023 has started with alarming intensity, with health officials declaring an epidemic as early as October. This unusual early onset has prompted widespread school closures and heightened concerns over public health. As recorded cases rise, particularly among children, experts are gearing up for potential regional implications, making it crucial for health authorities to monitor the situation closely.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.