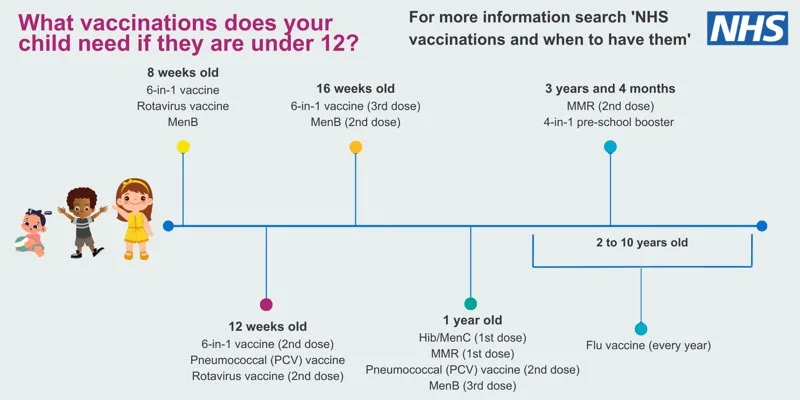
Childhood vaccinations are a critical component of public health, helping to protect children against preventable diseases. Recent studies reveal a rising trend of vaccine hesitancy among parents, with one in six opting out of some childhood vaccinations. This trend is particularly pronounced among parents who identify with certain political movements, highlighting differing attitudes towards vaccines like the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) and polio, which still enjoy high confidence ratings at 90% and 88%, respectively. However, concerns regarding the safety of newer vaccines, such as the COVID-19 vaccine and the influenza vaccine, persist, with only 43% of parents deeming the COVID-19 vaccine safe for their children. With 81% of respondents supporting mandatory vaccinations for school entry, the conversation around childhood vaccinations is more important than ever, intersecting with essential issues of public health and parental confidence in health agencies.
Vaccines for children play a pivotal role in safeguarding against infectious diseases that can have serious health consequences. Yet, a significant number of parents are expressing doubts about vaccination safety, influenced by growing child vaccination hesitancy and distrust in health organizations. Confidence levels vary significantly across different vaccines, with traditional vaccines like the measles and polio showing robust acceptance, while newer vaccines such as those for seasonal influenza and COVID-19 are met with skepticism. This hesitance is exacerbated by emerging public concerns and debates over the necessity of certain vaccines, leading many parents to question the recommendations made by health authorities. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for addressing misconceptions and improving vaccination rates among children.
Understanding Childhood Vaccinations: Importance and Statistics
Childhood vaccinations play a crucial role in ensuring the health and safety of children against various infectious diseases. Vaccines such as the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) and polio have historically demonstrated high safety and efficacy rates, garnering confidence from 90% and 88% of parents, respectively, as reported in a recent KFF public opinion poll. These immunizations not only protect the vaccinated child but also contribute to herd immunity, which is vital for safeguarding those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical conditions.
However, despite the substantial support for certain vaccines, there exists a troubling trend of vaccine hesitancy among parents. The survey revealed that 1 in 6 parents may choose to forgo recommended vaccinations, a figure that rises dramatically among specific demographic groups, including those identifying as MAGA supporters. This hesitancy can lead to outbreaks of preventable diseases and poses a significant public health risk, highlighting the importance of ongoing education about the benefits and safety profiles of childhood vaccinations.
The Impact of Vaccine Hesitancy on Public Health
Vaccine hesitancy represents a growing challenge in the realm of public health, especially concerning childhood vaccinations. Parents’ concerns about vaccine safety, as illustrated in the KFF poll, reveal that many associate childhood vaccines with potential health risks. This hesitancy can lead to lower vaccination rates, which ultimately increases the susceptibility of children to outbreaks of diseases such as measles and polio. Additionally, the divide in confidence levels toward traditional vaccinations versus seasonal vaccines for COVID-19 and influenza indicates a troubling discrepancy in public perception.
Addressing vaccine hesitancy requires comprehensive communication strategies focused on building trust within communities. Public health authorities must prioritize transparency about vaccine development processes, potential side effects, and statistical safety data, including motivations for compulsory vaccinations in schools. Furthermore, engaging with younger parents and those leaning towards alternative education methods may foster a better understanding of vaccine importance and alleviate misconceptions regarding vaccine safety.
MMR Vaccine Confidence: A Beacon of Hope
The MMR vaccine stands out as a significant beacon of hope in the fight against childhood diseases. With a confidence level at 90% among surveyed parents, it reflects a robust trust in the effectiveness and safety of vaccines designed to prevent measles, mumps, and rubella. This high degree of confidence is critical, as it reassures parents that vaccinating their children against these serious diseases is not only safe but necessary for their well-being and the health of those around them.
Moreover, the MMR vaccine’s proven track record in reducing disease incidence underscores its value within the vaccination schedule. Health officials must leverage this confidence to advocate for increased awareness and education surrounding vaccination programs, addressing fears relating to other vaccines, particularly those that inspire more skepticism, like the COVID-19 vaccine. Reinforcing the importance of the MMR vaccine can help bridge the gap and encourage comprehensive vaccination practices among children.
Polio Vaccine Statistics: A Legacy of Efficacy
Polio vaccination has played a pivotal role in nearly eradicating a once-prevalent disease, serving as a powerful reminder of the benefits of vaccination. With confidence levels for the polio vaccine standing at 88%, as indicated by the recent KFF poll, parents recognize the importance of protecting their children from this debilitating illness. The robust statistics demonstrating reduced polio incidence following widespread immunization serve as a testament to the vaccine’s efficacy over the years.
Despite the remarkable success of the polio vaccination campaign, health officials face challenges concerning complacency in vaccination practices as the disease becomes less visible. It is essential to maintain awareness and education about the real risks of polio, especially as some parents may question the need for vaccination, viewing it as less urgent. By communicating the historical context and significance of polio vaccination, public health campaigns can reinforce its importance in maintaining community health.
COVID-19 Vaccine Safety: Addressing Parental Concerns
Concerns surrounding the safety of COVID-19 vaccines for children have emerged prominently, with only 43% of surveyed parents considering them safe. This hesitancy emphasizes the need for awareness and education about the rigorous testing and monitoring processes these vaccines undergo before approval. Overcoming skepticism and misconceptions regarding vaccine safety is paramount to achieving public health goals and ensuring high vaccination rates among children.
Promoting transparent and accessible information about adverse events, while also highlighting the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in preventing severe illness, will help reduce the perceived risks associated with vaccination. Public health campaigns should focus on personal testimonials from healthcare professionals and parents who have vaccinated their children, helping to construct a more positive narrative around COVID-19 vaccine safety for the younger population.
Influenza Vaccine Concerns: Navigating Misinformation
Influenza vaccine concerns evolve primarily from ongoing misinformation and lack of understanding regarding the vaccine’s role in protecting children’s health. A disappointing statistic shows that only 65% of parents believe flu vaccines are safe, indicating a gap in knowledge and trust. Addressing this gap requires targeted communication strategies that provide factual, science-based information about the efficacy of flu shots and their importance in preventing severe disease.
Health authorities must also address common myths associated with the influenza vaccine, including misconceptions about side effects and efficacy rates. Engaging parents through community events, informative workshops, and one-on-one discussions with healthcare providers can help build confidence in the influenza vaccine. Thrusting forward with education and outreach efforts will promote a better understanding and greater acceptance of influenza vaccinations in childhood immunization schedules.
The Role of Confidence in Federal Health Agencies
The recent KFF poll highlights a stark reality: only 14% of parents have substantial confidence in federal health agencies like the CDC and FDA. This lack of trust presents significant obstacles in persuading parents to vaccinate their children. Addressing this issue requires strategic efforts aimed at restoring community trust in these critical organizations. Transparency in communication and acknowledgment of public concerns can help bridge the gap between healthcare officials and hesitant parents.
Furthermore, federal health agencies need to mobilize resources to engage with the public effectively. Utilizing social media platforms, local health events, and partnerships with trusted community figures can offer essential support in disseminating accurate vaccine information. Improving public confidence in these agencies can ultimately enhance acceptance rates for childhood vaccinations and reduce instances of vaccine hesitancy.
Demographic Differences in Vaccine Hesitancy
The survey reveals that younger parents, particularly those under 35, display more prominent concerns regarding vaccine safety than older generations. This demographic is also more inclined to voice opinions about the number of vaccines recommended by the CDC, with 26% believing current recommendations are excessive. Understanding these demographic trends is crucial for tailoring communication and educational outreach efforts to effectively address the unique concerns of different age groups.
By focusing on the specific hesitations and beliefs of younger parents, healthcare professionals can design interventions that resonate more profoundly with them. This might entail creating platforms for discussion, providing clear, relatable information about vaccine benefits, and debunking myths that escalate concerns about safety. Ultimately, these targeted efforts can help foster a more favorable attitude towards childhood vaccinations in younger parents.
Public Demand for Mandatory Childhood Vaccinations
In light of the survey findings exposing varying levels of confidence in vaccines, it is uplifting to note that 81% of parents support mandatory childhood vaccinations for essential vaccines, specifically the MMR and polio vaccines. This strong backing suggests that many parents recognize the crucial role vaccinations play in public health, providing protection not just for their children but for the community at large.
However, the challenge lies in translating this support into action. Policymakers must listen to public demand and work to strengthen vaccination requirements without further alienating hesitant parents. Ensuring that health communications emphasize the benefits of vaccinations while also engaging with communities on their concerns can help in achieving both public health goals and enhanced compliance with vaccination schedules.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is childhood vaccination hesitancy and how does it affect vaccination rates?
Childhood vaccination hesitancy refers to the reluctance or refusal to vaccinate children despite the availability of vaccines. Recent surveys indicate that 1 in 6 parents are skipping some childhood vaccinations due to concerns about safety and effectiveness, impacting overall vaccination rates.
What are the statistics on confidence in childhood vaccinations like the MMR and polio vaccines?
Confidence in childhood vaccinations remains high for the MMR and polio vaccines, with approximately 90% and 88% of parents expressing confidence in these vaccines, respectively. These statistics show strong support for these essential immunizations in public health.
What are the concerns parents have regarding the COVID-19 vaccine safety for children?
Concerns about COVID-19 vaccine safety for children are significant, with only 43% of parents believing these vaccines are safe. This hesitancy is driven by uncertainty about long-term effects and the perceived necessity for vaccinating children against COVID-19.
How do parents view the influenza vaccine in terms of safety for children?
Vaccine concerns surrounding the influenza vaccine show that only 65% of parents believe it is safe for their children. This highlights ongoing discussions about the safety and necessity of seasonal vaccinations in pediatric populations.
What is the public opinion on mandatory childhood vaccinations like the MMR and polio vaccines?
Support for mandatory childhood vaccinations is strong, with 81% of survey respondents favoring the requirement for public school students to receive vaccines like the MMR and polio. This reflects a collective understanding of the importance of vaccinations in public health.
Why do some younger parents express concerns about childhood vaccinations?
Younger parents, particularly those under 35 or homeschooling their children, often express concerns about the safety of childhood vaccinations. This demographic tends to be more critical of vaccine recommendations from health authorities, impacting their confidence in vaccination programs.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Parents forgoing vaccinations | 1 in 6 parents are not vaccinating their children, rising to 1 in 4 among MAGA parents. |
| Confidence in vaccines | 90% confidence in MMR vaccine, 88% in polio vaccine. |
| Concerns about seasonal vaccines | 65% consider flu vaccines safe; 43% for COVID-19 vaccines. |
| Support for mandatory vaccinations | 81% support mandatory MMR and polio vaccines for public school students. |
| Confidence in federal health agencies | Only 14% have ‘a lot’ of confidence in agencies like the CDC and FDA. |
| Concerns about vaccine recommendations | 26% believe the CDC recommends too many vaccines. |
| Vaccine safety concerns | Most frequently cited reason for not vaccinating children. |
Summary
Childhood vaccinations are vital for protecting children against various infectious diseases. The recent KFF public opinion poll has highlighted significant concerns among parents regarding vaccinations, particularly for newer vaccines like COVID-19 and flu vaccines. Despite these apprehensions, a strong majority still support mandatory vaccinations for essential vaccines like MMR and polio, indicating a complex landscape of trust and perception regarding childhood vaccinations. Building trust and providing accurate information about the safety of all vaccines remains crucial in ensuring public health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.