Neurocysticercosis is a severe and often underdiagnosed infection of the central nervous system, primarily caused by the larval stage of the *Taenia solium* tapeworm, but can also result from related species such as *Taenia crassiceps*. This intriguing condition significantly impacts neurological health, leading to symptoms like seizures, headaches, and cognitive decline. Diagnosis of neurocysticercosis can be complex, often requiring advanced techniques such as serological testing and molecular methods to identify the presence of the parasite. These challenges are heightened in cases of subarachnoid neurocysticercosis, where timely intervention is crucial for effective treatment and preventing lasting neurological damage. Understanding neurocysticercosis symptoms is vital for healthcare professionals, as early recognition can lead to successful management and treatment, ensuring better outcomes for affected individuals.
Neurocysticercosis, often referred to as larval cysticercosis, is a leading cause of epilepsy and other neurological disturbances worldwide. It arises from the infection of the brain with the larvae of *Taenia* species, most commonly *T. solium* and the rarer *T. crassiceps*. The condition primarily presents with a range of neurogenic symptoms, making cysticercosis diagnosis essential for effective treatment strategies. Proper neurocysticercosis treatment typically involves antiparasitic medications like albendazole and praziquantel, especially crucial when considering cases like subarachnoid neurocysticercosis. Understanding the intricacies of this infection not only helps in patient management but also raises awareness about the importance of preventing zoonotic infections through proper control measures.
Understanding Neurocysticercosis: A Brief Overview
Neurocysticercosis is a significant health concern globally, primarily caused by the larval stages of the *Taenia solium* tapeworm. This infection can lead to severe neurological complications and is often associated with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. By understanding the life cycle and modes of transmission, we can better advocate for preventive measures. Notably, while *Taenia solium* is the most common causative agent, *Taenia crassiceps* has also been identified in human cases, albeit more rarely.
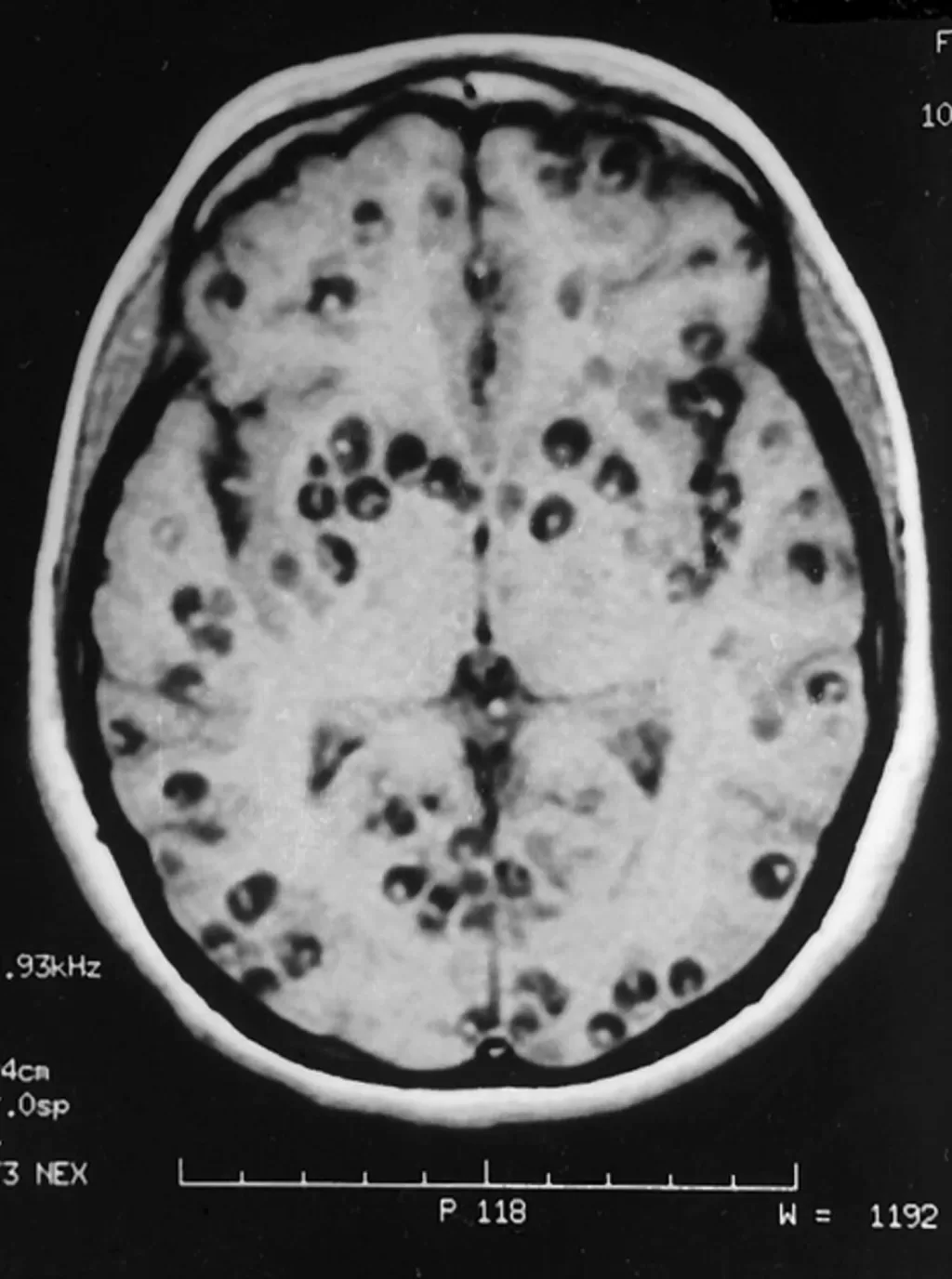
Patients with neurocysticercosis may exhibit a range of symptoms, including seizures, headaches, and cognitive impairment, which can drastically affect their quality of life. Diagnosing the condition can be challenging, often requiring advanced imaging techniques such as MRI, serological tests, and in some cases, molecular methods for confirmation. Early identification and treatment are crucial in preventing severe complications.
The Role of Taenia crassiceps in Human Infections
Although commonly associated with *Taenia solium*, neurocysticercosis can also be induced by *Taenia crassiceps*, a less prevalent but significant pathogen responsible for neurological infections. This parasite typically resides in carnivorous hosts but can infect humans who inadvertently ingest its eggs via contaminated food or water. Understanding the pathology of *T. crassiceps* is essential for epidemiology, particularly as cases in immunocompetent individuals increase.
In particular, the elderly populations, like the case discussed from Slovenia, exhibit heightened vulnerability to complications resulting from *T. crassiceps* infections. Symptoms may mirror those of other forms of neurocysticercosis, leading to potential misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. Therefore, awareness about the presentation of neurocysticercosis due to *Taenia crassiceps* is vital for timely intervention.
Identifying Neurocysticercosis Symptoms
Neurocysticercosis presents a wide array of neurological symptoms due to the location and number of parasites within the central nervous system. Patients may experience seizures, headaches, and cognitive changes, which can vary in intensity and progression. This variability often leads to a broad differential diagnosis, complicating clinical assessments. In cases where *T. crassiceps* is involved, understanding these symptoms can be even more critical given their atypical presentation.
Monitoring the progression of symptoms in neurocysticercosis is crucial for adjusting treatment regimens. For instance, this can help discern between inflammatory responses connected to treatment and recurring infection. The complexity and overlap between neurological conditions necessitate a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management of neurocysticercosis.
Cysticercosis Diagnosis: Challenges and Techniques
Diagnosing neurocysticercosis can be fraught with challenges due to the variable presentations and the potential for overlap with other neurological diseases. Identification often relies on imaging techniques like MRI, which can reveal cyst-like lesions in the brain. However, the presence of *T. crassiceps* may not always produce typical imaging findings, complicating diagnosis.
Furthermore, serological tests like those for IgG antibodies can yield equivocal results. In the case from Slovenia, intricate laboratory confirmation via molecular techniques was required due to initial inconclusive findings. This underscores the importance of advanced diagnostic methods, especially in atypical presentations of neurocysticercosis.
Exploring Neurocysticercosis Treatment Options
Treatment for neurocysticercosis often involves antiparasitic drugs such as albendazole and praziquantel, aimed at eliminating the cysts. In cases where inflammation and neurological symptoms persist, corticosteroids may be administered to mitigate symptoms and prevent adverse effects of therapy. The regimen may vary depending on the severity of infection and individual patient factors, such as age and underlying health.
In the presented case, a multidisciplinary approach was adopted, involving prolonged dual therapy to address the recurrence of symptoms after initial treatment. This highlights the necessity for ongoing evaluation and adjustment when managing neurocysticercosis, particularly in patients demonstrating resilience against conventional therapies.
The Importance of Neurological Monitoring
Continuous neurological monitoring is paramount in managing patients with neurocysticercosis, especially those with serious complications such as meningitis. Regular follow-ups enable healthcare providers to assess the efficacy of treatment and recognize any potential recurrence of symptoms. This case illustrates how neurological decline can occur despite apparent treatment success, emphasizing the need for vigilant monitoring.
Implementing routine assessments, including lumbar punctures and imaging, can help ensure that any changes in a patient’s condition are promptly addressed. This proactive approach not only improves patient outcomes but also contributes to the broader understanding of how neurocysticercosis evolves over time.
Preventing Neurocysticercosis: Strategies for Awareness
Preventing neurocysticercosis involves raising awareness about the parasite’s transmission routes, which is vital for communities at risk. Public health initiatives should focus on promoting hygiene practices, proper cooking of pork, and regular veterinary care for pets, as these play critical roles in breaking the transmission cycle of *T. solium* and *T. crassiceps*. Regular deworming of domestic animals can also help mitigate human infection risks.
Educational programs that inform the public about the signs and symptoms of neurocysticercosis can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment, ultimately reducing morbidity associated with this infection. These strategies are especially important in regions where human cases have been reported, enhancing community health and safety.
Research Advances in Neurocysticercosis
Ongoing research plays a crucial role in understanding the complexities of neurocysticercosis, particularly with regards to rare causative agents like *Taenia crassiceps*. Investigations into the genetic and immunological aspects of the infection can provide invaluable insights that may guide future therapeutic approaches. For example, understanding how the immune response differs in cases caused by different *Taenia* species could lead to tailored treatments.
Additionally, investments in diagnostic technologies and methodologies are essential, as they could significantly improve detection rates and outcomes in cases of neurocysticercosis. There is a significant need for further studies focusing on the efficacy of various treatment protocols and the long-term impacts of different management strategies.
A Case Study: Lessons from Slovenia
The case of neurocysticercosis in Slovenia serves as a stark reminder of the complexities surrounding this rare infection. This case not only highlights the role of *Taenia crassiceps* but also emphasizes the importance of thorough diagnostic procedures. The patient’s journey underscores how serological testing can often return equivocal results, necessitating advanced molecular techniques for accurate identification.
Furthermore, the clinical management of this patient illustrates the multifaceted approach required to treat neurocysticercosis effectively. The need for prolonged dual therapy following recurrence and the ongoing adjustments to treatment regimens reflect the reality many clinicians face. This case contributes significantly to the growing body of literature on neurocysticercosis, offering lessons for future cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is neurocysticercosis and what causes it?
Neurocysticercosis is a severe infection of the central nervous system caused primarily by the larvae of the tapeworm *Taenia solium*, though it can also be caused by *Taenia crassiceps*. This infection occurs when humans accidentally ingest eggs of the parasite, leading to cyst formation in the brain.
What are the common neurocysticercosis symptoms to watch for?
Common neurocysticercosis symptoms include severe headaches, seizures, nausea, vomiting, cognitive decline, and neurological problems such as gait disturbances and weakness. In advanced cases, it may lead to meningitis, as seen in cases involving *Taenia crassiceps*.
How is cysticercosis diagnosed in humans?
Cysticercosis diagnosis typically involves a combination of serological testing, imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans, and molecular methods such as PCR. For neurocysticercosis, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis may reveal elevated white blood cell counts and specific indicators of infection.
What are the treatment options for neurocysticercosis?
The treatment for neurocysticercosis usually includes antiparasitic medications such as albendazole and praziquantel, often supplemented with corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. The treatment duration can vary depending on the severity and type of infection.
Is subarachnoid neurocysticercosis caused by *Taenia crassiceps* more severe than other forms?
Subarachnoid neurocysticercosis caused by *Taenia crassiceps* can be particularly severe due to its rarity and the potential for significant neurological impairment, as evident in recent cases of prolonged symptoms and complications despite treatment efforts.
What precautions can be taken to prevent neurocysticercosis infection?
Preventative measures include practicing good hygiene, cooking food properly, ensuring clean drinking water, and regular deworming of pets, especially canines, as they can be carriers of *Taenia crassiceps* and *Taenia solium* eggs.
Can neurocysticercosis recur after treatment?
Yes, neurocysticercosis can recur after treatment, especially if the initial infection was severe or if the treatment was not sufficient. Continuous monitoring and possibly long-term treatment with albendazole may be required to prevent recurrence of symptoms.
How does neurocysticercosis affect cognitive function?
Neurocysticercosis can lead to cognitive decline due to the formation and inflammation of cysts within the brain, which can impair neurological functions and cause significant neurological symptoms like confusion, memory loss, and seizures.
Are there any notable cases of *Taenia crassiceps* neurocysticercosis in humans?
Few human cases of *Taenia crassiceps* neurocysticercosis have been reported, with one recent case in Slovenia highlighting its occurrence in an elderly, otherwise healthy patient, leading to severe neurological symptoms and complications.
What role does immunocompetence play in neurocysticercosis severity?
Immunocompetent individuals can still develop severe neurocysticercosis, as shown in some cases, although those with immunocompromising conditions may be at higher risk for severe symptoms and complications, indicating the infection can affect anyone regardless of immune status.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Patient Background | 74-year-old woman from Slovenia, no underlying diseases, symptoms worsened over time. |
| Symptoms | Gait ataxia, left-sided tetraparesis, urinary incontinence, cognitive decline. |
| Diagnosis | Confirmed through lumbar puncture (aseptic meningitis) and PCR tests for *T. crassiceps*. |
| MRI Findings | Enlarged ventricular system indicating subarachnoid neurocysticercosis. |
| Treatment | Dual therapy with albendazole and praziquantel, plus dexamethasone to reduce inflammation. |
| Outcome | Improved cognitive status, but persistent spastic tetraparesis, moved to nursing home. |
Summary
Neurocysticercosis is a severe infection of the central nervous system primarily caused by the larvae of the *Taenia solium* tapeworm, although rare cases have been reported from other *Taenia* species, including *Taenia crassiceps*. This case study highlights the challenges in diagnosing and treating neurocysticercosis, especially in elderly patients without immunosuppressive conditions. The treatment regimen combined with thorough monitoring provides valuable insights into managing this rare parasitic infection. Given that neurocysticercosis infections are increasing, especially in domesticated animals, awareness and preventive measures are crucial to controlling the spread of this life-threatening condition.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.