The Clade Ib monkeypox virus (MPXV) has emerged as a pivotal focus of global health due to its association with recent monkeypox outbreaks, which have shifted the landscape of mpox virus transmission. Unlike its counterpart, Clade II, Clade Ib is known for causing more severe infections, raising alarms over its potential to spread more efficiently among human populations. With approximately 100,000 reported cases since 2022, the implications of Clade Ib extend far beyond traditional geographic boundaries, indicating a need for immediate global health responses. Monkeypox symptoms can vary significantly, necessitating increased awareness and preparedness. Understanding the dynamics between Clade I and Clade II is crucial for developing effective strategies against future outbreaks and mitigating risks associated with this evolving virus.
The rise of the mpox virus has highlighted urgent concerns regarding public health and safety, particularly in light of the distinct characteristics exhibited by different genetic variants, including Clade Ib. This strain has been linked to significant outbreaks, demonstrating a shift in transmission patterns from animals to humans, and subsequently between people. The need for comprehensive global strategies becomes critical as health organizations grapple with the implications of these monkeypox cases. Symptoms of mpox can present in diverse ways, complicating diagnosis and necessitating innovative detection methods. As discussions continue around the effectiveness of vaccines and treatments, the global health community is racing to understand and respond to the challenges posed by these growing clusters of infection.
Understanding Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus
Clade Ib monkeypox virus represents a critical focus in understanding the evolution of mpox outbreaks. Emerging evidence indicates that this clade may adapt towards more efficient human-to-human transmission, contrasting significantly with the historical patterns of infection primarily observed in endemic regions of Africa. With recent outbreaks occurring outside these traditional borders, particularly in urbanized environments, health officials are urged to stay vigilant. Current studies point towards a genetic shift in Clade Ib, which could allow the virus to exploit new transmission routes—especially through close personal contact.
The genetic specificity of the Clade Ib monkeypox virus suggests that its characteristics may influence not just transmission dynamics but also clinical symptomatology. Researchers are investigating whether infections caused by this clade result in different or more severe symptoms compared to those attributed to Clade II. Given the historical association of Clade I with more significant health implications, understanding these variations is essential for preparing effective global health responses and managing public health interventions during outbreaks.
Monkeypox Outbreaks: Lessons Learned
Recent monkeypox outbreaks highlight the importance of learning from past experiences, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. As mpox has spread to nonendemic countries, understanding the dynamics surrounding monkeypox outbreaks becomes pivotal. Each outbreak provides crucial data that informs global health strategies to prevent further transmission. The lessons drawn from the behaviors of Clade I and Clade II during these outbreaks emphasize the necessity for robust disease surveillance systems capable of detecting and responding to mpox virus transmission effectively.
In tackling monkeypox outbreaks, public health responses must not only focus on immediate containment but also on long-term educational campaigns aimed at reducing transmission risk. Heightened awareness regarding the symptoms of mpox, including fever, swollen lymph nodes, and rashes, is essential for early detection. Moreover, examining the transmission pathways—particularly through sexual activity—can shape health promotions. As communities worldwide adapt to the evolving epidemiology of mpox, ensuring comprehensive strategies rooted in education and awareness will be vital for future outbreak management.
Clade I vs Clade II: The Genetic Divide in Monkeypox Viruses – An Overview of Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes
The distinctions between Clade I and Clade II of the monkeypox virus are integral to understanding their implications for public health. Clade I, with its history of more severe outcomes, has primarily been recorded in Central Africa, while Clade II has been more prevalent in West African regions. Such genetic nuances affect not only clinical presentation but also epidemiological patterns of monkeypox outbreaks. A thorough grasp of the symptomatology associated with each clade will enable healthcare providers to make more informed decisions when diagnosing and treating affected individuals.
Moreover, this genetic divide underscores the urgency of global health preparedness strategies. With the ongoing suspension of routine smallpox vaccinations, there is increased susceptibility within populations. The presence of both clades highlights the complex interplay between historical transmission patterns and emerging routes. This emphasis on the Clade I vs. Clade II distinction can guide research priorities aimed at further unraveling the genetic mysteries behind mpox transmission mechanisms and outbreak behaviors.
Global Health Responses to Monkeypox
As the frequency of monkeypox outbreaks increases globally, so too must the responses from health authorities at national and international levels. The emergence of the Clade Ib monkeypox virus necessitates a nuanced approach to global health responses. Real-time data collection and genomic surveillance are critical for tracking the virus’s mutations and transmission patterns. Stakeholder collaboration is also crucial for establishing frameworks that can respond dynamically to potential outbreaks. Proactive measures, such as rapid diagnostic testing and vaccine distribution, align with the global health responses necessary to mitigate emerging health threats.
Incorporating a One Health approach, which acknowledges the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, can strengthen responses to monkeypox. Addressing the zoonotic challenges presented by the monkeypox virus, especially in areas where human and animal interactions are prevalent, is vital for curbing future outbreaks. By fostering multidisciplinary collaborations, public health initiatives can work effectively alongside veterinary and ecological studies, allowing for comprehensive strategies that protect communities from evolving health threats such as the mpox virus.
Monkeypox Symptoms and Clinical Considerations
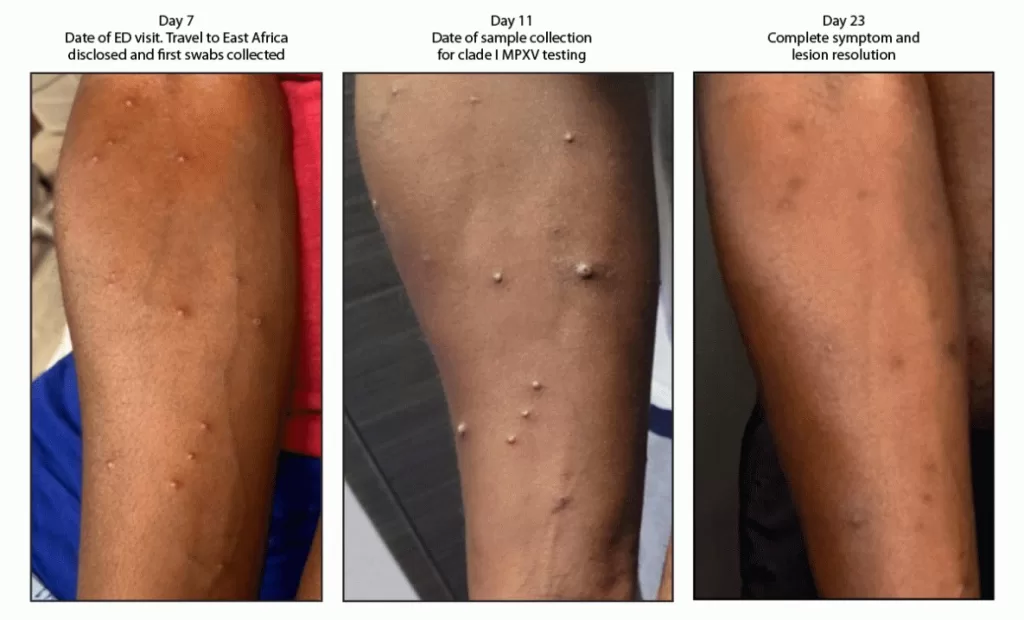
Recognizing monkeypox symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Typical manifestations include fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy which may be accompanied by severe headache and muscle aches. Given the viral evolution and the emergence of Clade Ib, understanding whether this clade produces more severe clinical outcomes compared to others becomes pertinent. Health professionals should remain alert for atypical presentations that may arise as the virus adapts to human populations. Early identification of symptoms can prevent further transmission, particularly in high-risk groups.
Furthermore, effective clinical management of monkeypox involves articulating treatment options based on the severity of symptoms and the likelihood of complications. Current antiviral therapies, while rooted in smallpox treatments, require careful consideration in terms of dosing and efficacy against Clade Ib and its possibly unique clinical manifestations. Significant focus on symptomatic relief is similarly essential for patient care, as is ongoing research to validate optimal therapeutic protocols amidst evolving strains of the mpox virus.
Transmission Pathways of mpox Virus
The intricate pathways of mpox virus transmission have become a focal point of investigation, particularly with the emergence of Clade Ib. Historical consensus posits that monkeypox is primarily zoonotic, with human cases occurring through direct contact with infected animals. However, the recent identification of human-to-human transmission, particularly through intimate contact, has shifted the paradigm of how outbreaks can sparking in previously nonendemic regions. These new transmission patterns emphasize the need for heightened awareness and preventive measures in communities.
In the current landscape, the mpox virus is mainly spread via close physical contact, which encompasses sexual relationships and other intimate behaviors. Educational resources that provide insights into these transmission routes are essential for promoting safe practices. Additionally, the surveillance of potential cases, especially within high-risk communities, can further inform containment efforts. Addressing the stigma associated with monkeypox and its transmission is equally important to encourage open discussions and to promote a more effective public health response.
Diagnostic Challenges in Monkeypox Surveillance
As outbreaks of monkeypox persist, the ability to accurately diagnose cases remains a cornerstone of effective public health strategies. The challenges surrounding mpox diagnostics can be particularly treacherous given the presence of genetic variations such as those found in Clade Ib. Conventional PCR techniques may fail to detect certain viral genomic deletions, leading to underreported cases and delayed responses. To improve the reliability of diagnostics, health authorities must adopt flexible testing strategies that can accommodate the evolving viral landscape.
Enhancing diagnostic capabilities also involves training healthcare providers to recognize monkeypox symptoms promptly and utilize appropriate testing protocols. In response to the increasing complexity of mpox cases, rapid antigen tests could serve as valuable supplementary tools alongside standard PCR methods. Ongoing research into the development of novel diagnostic tests that can differentiate between clades will be instrumental in refining surveillance capabilities and controlling mpox outbreaks effectively.
Future of Vaccination Strategies Against Monkeypox
As the epidemiology of monkeypox evolves, future vaccination strategies must adapt to address the emergence of Clade Ib and its implications for public health. The development of vaccines targeting similarities to smallpox offers a promising avenue for cross-protection, yet their efficacy in light of genetic mutations requires thorough investigation. Authorities must prioritize vaccination campaigns that focus on vulnerable populations to mitigate transmission risks, especially in areas with rising cases. Understanding the vaccination response across different clades will help optimize these strategies.
Moreover, establishing an adaptive vaccination framework that accounts for unique regional challenges will be critical. Continuous genomic surveillance will inform health officials about pressing vaccination needs based on circulating virus strains. Educating the public about the availability and importance of monkeypox vaccinations will foster buy-in and compliance, therefore, supporting global health initiatives aimed at reducing the impact of mpox outbreaks. The cooperation of international health organizations can also facilitate better distribution of vaccines, particularly in low-resource settings.
Conclusions: Addressing the Threat of Mpox Globally
The re-emergence of mpox, prominently influenced by Clade Ib, presents a significant challenge for global health systems. Coordinated international responses are necessary to manage potential outbreaks and reinforce community resilience against viral threats. Comprehensive strategies that integrate effective surveillance, diagnostics, and vaccination programs are vital in combating the threat posed by the mpox virus. The urgency for actionable plans that address both immediate containment and long-term preparedness cannot be overstated.
As threats such as monkeypox become increasingly complex due to viral adaptations, fostering collaboration among governments, health organizations, and communities remains imperative. Public health authorities must leverage learnings from past outbreaks to inform new policies and protocols that can evolve in response to emerging evidence. Success in addressing the global threat of mpox hinges on a commitment to solidarity in health interventions, research, and shared knowledge across borders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus and how does it differ from Clade II?
Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus (MPXV) is a genetically distinct variant of the monkeypox virus that has emerged recently, contributing to new outbreaks globally. It differs from Clade II mainly in its genetic makeup and transmission patterns; Clade Ib is associated with more efficient human-to-human transmission and has caused more severe infections compared to Clade II, which is typically observed in West Africa.
What are the symptoms of monkeypox associated with Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus?
The symptoms of monkeypox associated with Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus are similar to those observed in traditional monkeypox cases, including fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy. However, Clade Ib may be linked to more severe manifestations due to its genetic mutations, making awareness of symptoms crucial for early detection and response.
How does mpox virus transmission occur in Clade Ib outbreaks?
Mpox virus transmission in Clade Ib outbreaks primarily occurs through close physical contact and sexual interactions, which marks a shift from classical zoonotic spillover. This human-to-human transmission emphasizes the importance of understanding how Clade Ib spreads, particularly in urban environments.
What global health responses are being implemented for Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus outbreaks?
Global health responses to Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus outbreaks include enhanced surveillance systems, vaccination campaigns, and public health education. These efforts aim to control and contain the outbreaks while adapting to the unique transmission dynamics associated with Clade Ib.
How does Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus influence strategies for diagnostics and treatment?
The emergence of Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus necessitates revised diagnostic strategies due to potential genetic variations that may affect routine PCR detection. Treatment protocols, including antiviral medications and vaccines, are also being adjusted to ensure efficacy against this clade.
| Key Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction | The emergence of Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus has raised global health concerns due to new transmission routes. |
| Clade Differences | Clade I, including Clade Ib, causes more severe infections mostly in Central Africa, whereas Clade II is found in West Africa. |
| Current Outbreaks | With around 100,000 cases reported since 2022, human-to-human transmission has been a significant factor in nonendemic countries. |
| Genetic Mutations | Clade Ib shows mutations that suggest more efficient human-to-human transmission, raising concerns about urban outbreaks. |
| Diagnostics and Treatment | Diagnostic methods need to adapt to viral variations. Antiviral treatments and vaccines based on smallpox offer some protection. |
Summary
The Clade Ib Monkeypox Virus represents a significant public health threat due to its emergence and the evolving landscape of human transmission. With a rise in cases outside of endemic regions, global health strategies are essential for effective surveillance, diagnostic innovation, and vaccine distribution to mitigate the potential impacts of this virus.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.