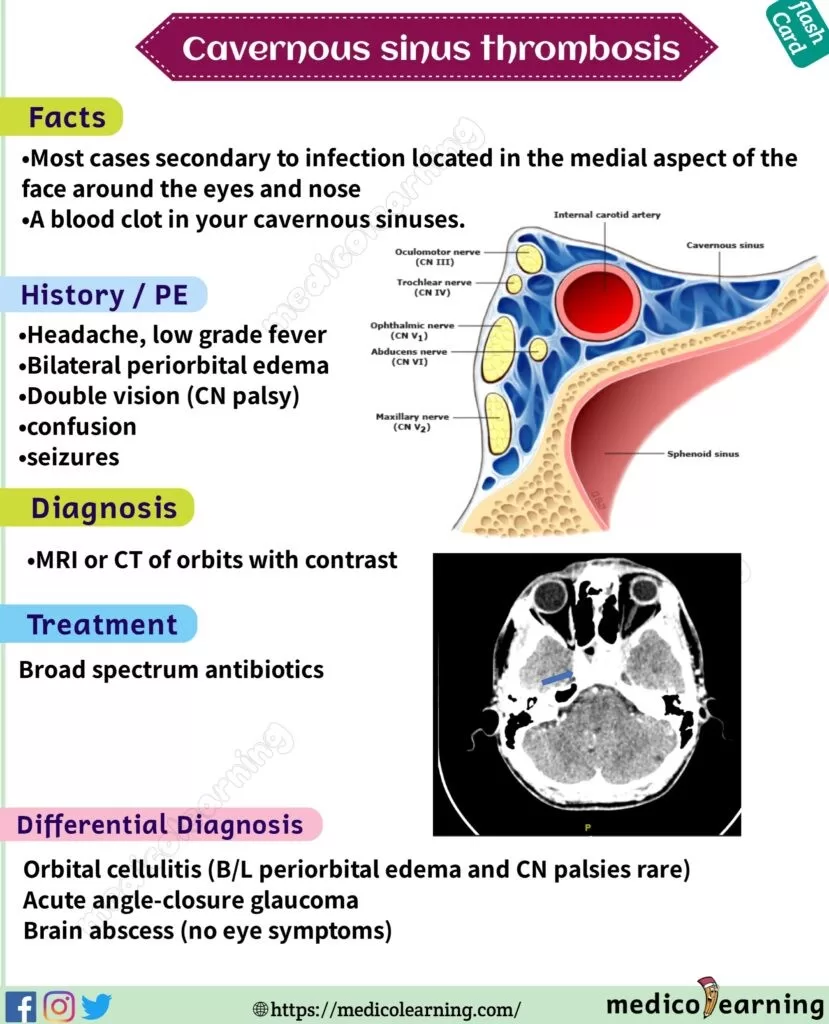
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is a rare yet life-threatening condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, an intricate cavity at the base of the skull. This serious medical issue can arise from various causes, primarily infections that originate in the face or from dental procedures, making early detection crucial. Recognizing CST symptoms, such as severe headaches, facial pain, and vision disturbances, can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Quick action and appropriate CST treatments, including antibiotics and anticoagulants, are essential to prevent severe complications like neurological damage. Understanding the link between infections, blood clots in the skull, and the serious nature of cavernous sinus thrombosis can empower individuals to seek immediate medical attention when symptoms arise.
Cavernous sinus thrombosis, often referred to as CST, can also be described as a critical vascular event occurring within the intricate network of veins at the base of the skull. This condition may stem from various sources, including facial infections or surgical complications, and can result in significant health implications due to its proximity to important neurological structures. When a blood clot impedes normal blood flow in this area, it can lead to debilitating symptoms, making recognition and timely intervention essential. The treatment landscape for this condition includes antibiotics to combat underlying infections and anticoagulants to address the clot itself, underscoring the importance of comprehensive care. Awareness of CST is vital for those experiencing related symptoms, as swift action can be life-saving.
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Symptoms: Early Recognition is Key
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) presents with a range of symptoms that can develop rapidly, typically within 5 to 10 days following an infection or facial trauma. One common symptom is a severe, progressively worsening headache that can be debilitating. Patients often describe this headache as different from their usual headaches, indicating the potential severity of the condition. Other facial symptoms may present, including pain and swelling around the eyes and nose, which can easily be mistaken for other less severe conditions like sinusitis.
Moreover, CST can lead to significant vision disturbances due to the involvement of cranial nerves; this can manifest as blurred or double vision. These symptoms occur because the thrombus puts pressure on the cranial nerves that are responsible for eye movement. Additionally, the presence of fever can suggest an underlying infection that may have led to the thrombosis, emphasizing the need for immediate medical evaluation in individuals exhibiting these signs.
Understanding the Causes of Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
The development of cavernous sinus thrombosis is primarily associated with infections, particularly those originating from the face, like sinusitis or dental abscesses. These infections can lead to the formation of blood clots in the cavernous sinus due to inflammation and subsequent obstruction of the normal venous drainage pathways. In some cases, recent facial or cranial surgery can also increase the risk of CST, as surgical manipulation may introduce bacteria or compromise normal blood flow.
Moreover, individuals with underlying conditions that predispose them to blood clotting, such as dehydration or certain clotting disorders, are at a higher risk for CST. Recognizing these risk factors is vital for prevention, particularly in patients with a history of facial infections or significant dental issues, as they may need closer monitoring for early signs and symptoms.
Diagnosis of Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis: Imaging and Examination Techniques
Diagnosing cavernous sinus thrombosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and advanced imaging techniques. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is often the preferred method due to its ability to visualize the thrombus and assess any accompanying inflammatory changes in the surrounding tissues. In cases where MRI may not be available or suitable, a Computed Tomography (CT) scan can be an effective alternative to identify the presence of a blood clot in the cavernous sinus.
In addition to imaging, a thorough physical examination and detailed review of the patient’s medical history are crucial in identifying potential underlying risk factors. Healthcare providers will look for signs related to cranial nerve dysfunction and infection, which can aid in forming a comprehensive diagnosis. The alignment of symptoms with imaging findings ensures accurate diagnosis and paves the way for prompt treatment intervention.
Treatment Options for Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis: Prompt Intervention is Essential
Effective treatment of cavernous sinus thrombosis is critical and often requires a multi-faceted approach. Initial management typically begins with administering high doses of intravenous antibiotics to combat any underlying infections, as well as anticoagulants to assist in the dissolution of the blood clot. The timing of these interventions is crucial; delays in treatment can lead to severe complications, including neurological damage.
In cases where medical therapy alone is insufficient, surgical intervention may be necessary. This could involve procedures aimed at relieving pressure on the cranial nerves or excising infected tissue contributing to the thrombosis. Supportive care is equally important, focusing on managing symptoms such as pain and vision disturbances, thus ensuring comprehensive care throughout the patient’s recovery process.
Prognosis and Recovery from Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
The prognosis for patients diagnosed with cavernous sinus thrombosis heavily depends on the speed of diagnosis and the initiation of treatment. Research indicates that early therapeutic intervention significantly improves recovery outcomes, reducing the likelihood of long-term neurological deficits. However, for those who experience delays in receiving care, the potential for severe complications, including irreversible neurological damage and even death, becomes notably higher.
Following recovery from CST, patients may require ongoing assessments to monitor for any lingering effects from the condition or its treatment. Rehabilitation and physical therapy may also be beneficial to address any residual symptoms, particularly those related to vision or facial motor function. By staying informed and vigilant, patients can further mitigate potential long-term complications associated with CST.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis (CST)?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) symptoms typically develop around 5 to 10 days after a facial infection. Common signs include severe headache, facial pain and swelling, vision disturbances (such as blurred or double vision), cranial nerve dysfunction, and fever. Early recognition of these CST symptoms is crucial for effective treatment.
What causes Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis (CST)?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is primarily caused by infections, particularly facial infections like sinusitis, cellulitis, or complications from dental abscesses. Recent surgeries around the face and skull, dehydration, or clotting disorders can also increase the risk of developing CST.
How is Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis diagnosed?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is diagnosed through imaging studies such as MRI and CT scans. These modalities help visualize the blood clot in the cavernous sinus and assess any associated swelling or changes in surrounding tissues. A thorough clinical evaluation is also essential.
What treatment options are available for Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis (CST)?
Treatment for AV cavernous sinus thrombosis includes high-dose antibiotics if an infection is present, anticoagulants to help dissolve the blood clot, and in some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure or remove infected tissue. Continuous monitoring and supportive care are also key components of treatment.
What is the prognosis for individuals with Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis (CST)?
The prognosis for cavernous sinus thrombosis largely depends on the promptness of diagnosis and treatment initiation. Early intervention enhances recovery prospects and reduces the risk of severe complications such as permanent neurological deficits or death.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Definition | A rare but serious condition characterized by a blood clot in the cavernous sinus, which can lead to severe complications. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms develop 5-10 days post-infection and include severe headache, facial pain/swelling, vision disturbances, cranial nerve dysfunction, and fever. |
| Causes | Often results from infections (facial, dental, etc.), recent facial surgeries, or dehydration/clotting disorders. |
| Diagnosis | Utilizes MRI and CT scans to visualize clots and assess surrounding tissues. A physical exam and medical history review are also conducted. |
| Treatment | Includes antibiotics, anticoagulants, potential surgical intervention, and ongoing monitoring. |
| Prognosis | Depends on early diagnosis and treatment; delayed intervention can lead to severe neurological complications or death. |
Summary
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a critical medical condition that can have dire consequences if not addressed promptly. Recognizing its symptoms—such as severe headaches, facial pain, and vision disturbances—plays a vital role in seeking timely medical intervention. This condition often arises from infections or recent surgeries, highlighting the importance of understanding its underlying causes. With accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, including medications and possibly surgery, patients can significantly improve their prognosis. Early recognition and swift action are paramount when it comes to cavernous sinus thrombosis; therefore, awareness and education about this serious condition can save lives.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.