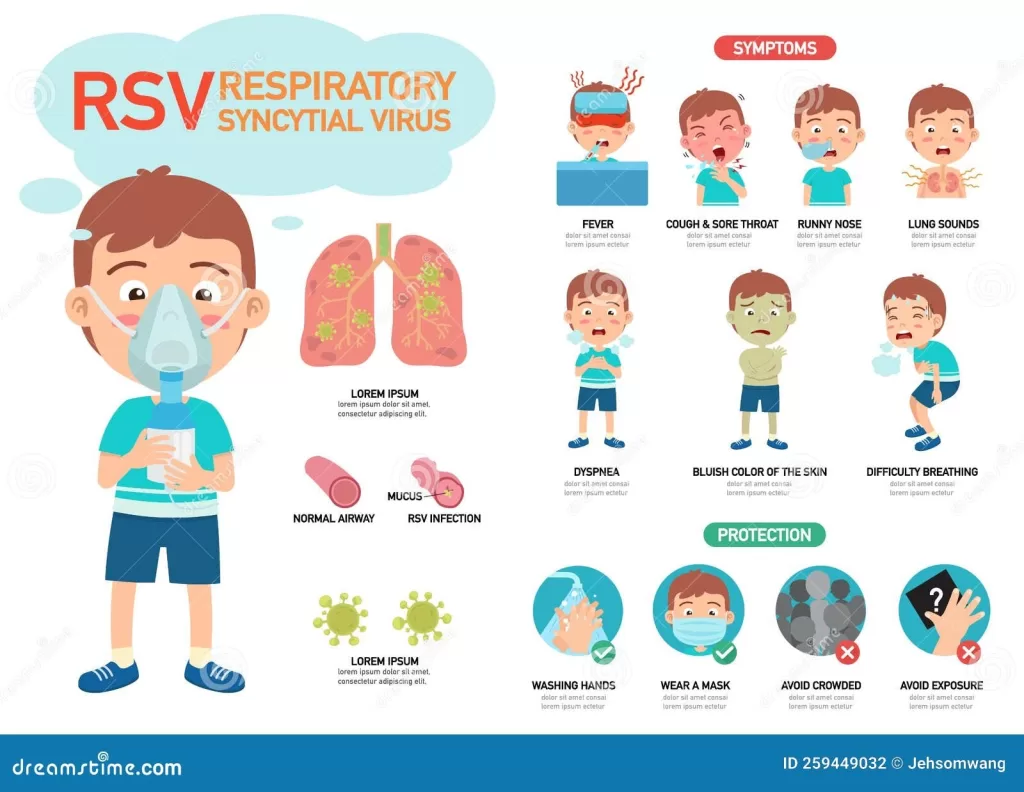
Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Adults (RSV) is a serious threat that poses a 2.7-fold increased risk of death within a year for those infected, particularly after experiencing an acute respiratory infection. This virus, known for its high contagion, primarily targets the respiratory system, leading to potentially severe health complications like pneumonia, especially in older adults and those with chronic conditions such as COPD. The impact of RSV is often underestimated in adult populations, despite it being a major cause of hospitalizations each winter. Recent studies have highlighted the alarming frequency of COPD exacerbations and other respiratory issues following RSV infections, underscoring the urgent need for awareness and preventive measures, including the RSV vaccine. This research not only illuminates the severity of RSV-ARI but also emphasizes the importance of targeted interventions for high-risk individuals.
Adult respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is frequently overlooked despite its significant health implications. Commonly associated with childhood illnesses, this virus can cause acute respiratory infections in adults, resulting in heightened mortality and increased healthcare costs. Individuals suffering from chronic respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are particularly vulnerable, facing exacerbated symptoms post-infection. Understanding the broader impacts of RSV and the necessity for effective vaccination strategies is critical to safeguarding health in older adult populations. Further research into this prevalent yet underestimated virus will aid in optimizing treatment and prevention methods.
Understanding Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in Adults
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is commonly known for its impact on infants and young children; however, it poses significant risks to adults as well. Particularly concerning is how RSV manifests in adults, leading to acute respiratory infections that can exacerbate pre-existing health conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. As noted in recent studies, adults who contract RSV are more likely to experience severe complications, prompting a need for greater awareness among both healthcare providers and the public about the risks associated with RSV in adults.
The 2025 research conducted in Denmark underscored the alarming correlation between RSV infections in adults and increased mortality rates. The study revealed that adults with RSV-ARI faced a 2.7-fold higher risk of death compared to their healthy counterparts. Moreover, health complications associated with RSV are not limited to respiratory issues; they extend into chronic health exacerbations, leading to significant healthcare burdens and costs. This highlights the necessity of educating the adult population about RSV and the importance of early detection and intervention.
The Severe Implications of RSV-Associated Acute Respiratory Infection
Acute respiratory infections, particularly those caused by RSV, can significantly worsen the health landscape for adults. Patients with RSV-ARI experience exacerbations of underlying conditions like COPD, with occurrences reported at a staggering rate of 3.1 times more than the general population. Furthermore, those suffering from asthma experienced even more adverse effects, with exacerbation rates 4.6 times higher among RSV-infected individuals. These health complications necessitate a closer evaluation of how RSV can potentially catalyze more severe, long-term health issues among vulnerable adults.
In addition to the clinical implications of RSV infections, the economic burden cannot be overlooked. According to the findings of the Danish study, the average healthcare costs for individuals impacted by RSV-ARI were more than double those incurred by their non-infected counterparts. This demonstrates that not only does RSV lead to increased morbidity and mortality, but it also places a significant financial strain on healthcare systems. Prioritizing preventive measures, including vaccination and education, can help mitigate these risks and reduce the consequences associated with RSV infections.
COPD and RSV: A Dangerous Interaction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) form a dangerous interaction that can rapidly deteriorate a patient’s health status. For individuals already suffering from COPD, the introduction of RSV can lead to severe respiratory complications, requiring advanced and often costly medical interventions. The Danish study indicates that patients with RSV-ARI have dramatically increased rates of hospital admissions, highlighting the urgent need for targeted treatment strategies for those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Continuing to study the relationship between RSV and COPD exacerbations is critical, as it opens doors to potential therapeutic strategies that may alleviate the intensifying health complications associated with the virus. Understanding this interplay allows healthcare providers to formulate targeted interventions that mitigate the impacts of RSV on patients with COPD, ultimately improving health outcomes and reducing hospitalization rates.
Preventive Measures Against RSV and Boosting Vaccinations
As the study regarding RSV-ARI emphasizes significant health complications and the risk of death in adults, the call for effective preventive measures has never been clearer. Vaccination emerges as a leading strategy in combating the effects of RSV, especially among high-risk populations such as the elderly and those with underlying respiratory conditions. Recent advancements in RSV vaccine development, including those approved by the European Medicines Agency, offer promising hope in reducing RSV-associated hospitalizations and fatalities among older adults.
Public health initiatives must focus on increasing awareness and accessibility of RSV vaccines. Studies indicate that timely vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of acute respiratory infections and their sequelae. Efforts should be made to encourage vaccination among vulnerable adults, coupled with educational campaigns to inform about the symptoms and risks associated with RSV. Targeted approaches in vaccination and preventive care could alleviate the burden of RSV-related healthcare complications.
The Economic Burden of RSV in Adults
Beyond the individual health risks posed by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), there are extensive economic implications for healthcare systems. The findings of the Danish cohort study revealed an alarming correlation between RSV infections and increased healthcare costs, with RSV-ARI patients carrying an average cost of €20,181 within a 365-day follow-up. This represents a significant economic burden that highlights the pressing need for effective public health strategies to combat RSV and its serious health outcomes.
For healthcare organizations, addressing the economic implications of RSV requires an in-depth understanding of both direct medical costs and the long-term impacts associated with RSV complications. Investing in prevention strategies such as vaccination and patient education can potentially lower these costs. Additionally, prioritizing research into effective management and treatment options for adults suffering from RSV-associated respiratory complications can ultimately enhance health outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare resources.
Long-Term Health Outcomes Post-RSV Infection
One of the striking findings from the recent study on RSV-ARI is the prolonged adverse impact it has on patients, even long after the initial infection has resolved. Adults suffering from RSV are likely to experience ongoing health complications, resulting in a diminished quality of life. According to Dr. Maria João Fonseca, the lead author of the study, many patients continue to face more severe health challenges than the general population, underscoring the serious and potentially enduring effects of respiratory syncytial virus infections.
The persistence of health issues post-RSV infection emphasizes the need for continued monitoring and support for affected individuals. Healthcare providers should be aware of the potential for long-term complications such as chronic respiratory disorders. This proactive approach could lead to early interventions that might improve patients’ health outcomes and overall well-being, creating a more responsive healthcare environment for those impacted by RSV.
Understanding RSV and Its Global Impact
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is not only a burden in one country but poses a global health challenge, particularly during the winter months in temperate climates. The virus is highly contagious and has the potential to cause severe respiratory illness across different age groups. An estimated 9,000 hospitalizations in older adults each year, paired with thousands more in younger populations, highlights the extensive reach of RSV’s impact internationally, emphasizing the need for a coordinated global response to mitigate its effects.
The prevalence of RSV across various populations underscores the importance of ongoing research and intervention strategies aimed at controlling this viral infection. Efforts to understand the global epidemiology of RSV will drive public health initiatives aimed at prevention and treatment, particularly in vulnerable groups. Collaboration between countries in sharing data and resources can lead to improved vaccination strategies and healthcare policies, ultimately reducing the burden of respiratory syncytial virus across the globe.
The Future of RSV Vaccination Strategies
As we look towards the future, the advancements in vaccine development for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) provide a beacon of hope in combatting the respiratory complications and health risks associated with this virus. The approval of several vaccines, such as GSK’s ‘Arexvy’ and Pfizer’s ‘Abrysvo,’ highlights an important step forward in protective measures against RSV in at-risk populations. These developments mark crucial progress in public health that could transform how we address respiratory viruses in older adults.
Continuous innovation in vaccine formulations and delivery methods will be vital to enhancing immunization coverage rates. Future vaccination strategies should prioritize outreach to high-risk populations to ensure equitable access to these preventive tools. Vigilant vaccination campaigns, along with education about the risks associated with RSV, are essential components in the fight against RSV-related health complications, mortality, and healthcare costs.
RSV: A Health Priority in Older Adults
Given the substantial health risks and economic implications of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in adults, particularly in older adults, it is critical to treat RSV as a priority in public health initiatives. Targeted strategies should focus on high-risk populations, utilizing data from studies like the Danish cohort study to inform policies and practices. By identifying those most vulnerable to severe outcomes, healthcare systems can tailor resources and interventions effectively.
Prioritizing research into RSV’s long-term effects on adults, alongside vaccination promotion, will strengthen the healthcare response to this significant public health concern. Collaboration between stakeholders in the health sectors, including governments, healthcare providers, and researchers, is necessary to ensure comprehensive action is taken. Addressing RSV effectively will not only protect individuals but will also reduce overall healthcare costs associated with managing severe respiratory infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the health complications of RSV in adults?
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can lead to serious health complications in adults, particularly those with pre-existing conditions. Complications include pneumonia and exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Adults infected with RSV-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI) experience 3.1 times more frequent COPD exacerbations and 4.6 times more frequent asthma attacks. This can result in increased hospitalizations and even a heightened risk of death within a year of infection.
How does Respiratory Syncytial Virus increase the risk of death in adults?
Research indicates that adults infected with respiratory syncytial virus-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI) have a 2.7-fold higher risk of death within one year compared to the general population. The severe health complications associated with RSV, especially in individuals with existing respiratory conditions like COPD and asthma, significantly contribute to this increased mortality risk.
What is the significance of RSV vaccines for adults?
Vaccination against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is crucial for protecting vulnerable populations, particularly older adults and those with chronic respiratory diseases. The first vaccines for RSV, such as Arexvy and Abrysvo, have been approved for use in adults over 60. These vaccines aim to reduce severe health complications from RSV-ARI, thereby decreasing hospitalizations and associated healthcare costs, and ultimately lowering the risk of death.
Can RSV lead to COPD exacerbations in adults?
Yes, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection can significantly worsen chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in adults. In patients with RSV-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI), COPD exacerbations are recorded as 3.1 times more frequent compared to those in the general population, highlighting the importance of monitoring and managing RSV infections in individuals with pre-existing lung conditions.
What should adults do to prevent RSV-related acute respiratory infections?
To reduce the risk of respiratory syncytial virus-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI), adults, especially those with underlying health conditions, should prioritize vaccination, practice good hygiene (such as frequent handwashing), and avoid close contact with infected individuals during peak RSV seasons. Staying informed about the symptoms and seeking timely medical care can also help mitigate serious health complications.
How does RSV affect health economics related to adult respiratory infections?
The economic burden of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) on healthcare systems is substantial. Research shows that Direct healthcare costs for adults with RSV-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI) average over €20,181 within a year, which is more than double the €8,085 spent on non-infected counterparts. This highlights the financial impact of RSV infections and underscores the need for effective preventive strategies such as vaccination.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Adults with RSV-associated acute respiratory infection face a 2.7-fold higher risk of mortality within one year compared to the general population. |
| RSV-ARI exacerbates existing respiratory conditions like COPD and asthma, leading to significantly worse health outcomes. |
| Hospitalization rates for RSV-ARI patients are more than double that of the control group, indicating a severe impact on health. |
| The economic burden of RSV-ARI on healthcare systems is substantial, with higher healthcare costs for affected patients. |
| Vaccination is crucial for high-risk populations to prevent severe outcomes from RSV, according to study authors. |
Summary
Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Adults poses significant health risks, notably increasing the chance of mortality nearly threefold in those affected. Recent research highlights that adults diagnosed with RSV-associated acute respiratory infection face a 2.7-fold higher risk of death within a year compared to the general population. This virus not only complicates existing respiratory issues, leading to increased hospitalizations and exacerbations of chronic conditions, but also presents a considerable economic burden on healthcare systems. The importance of vaccinations for vulnerable populations cannot be overstated, as they provide a strong defense against severe complications from this potentially deadly virus.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.