Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) symptoms in older adults can often be mistaken for other common infections, making early detection crucial. Unlike its reputation as a childhood virus, RSV poses significant health risks for the elderly, leading to an estimated 160,000 hospitalizations and 10,000 fatalities in the U.S. each year. Symptoms of RSV can include runny nose, congestion, cough, and fatigue, mirroring those of flu and COVID-19 infections. Left unchecked, mild RSV infections can escalate into severe respiratory complications, making it vital for older individuals to recognize the signs early. As healthcare professionals recommend the RSV vaccine for at-risk demographics, understanding and monitoring RSV symptoms in older adults becomes imperative for effective prevention and treatment.
As the colder months approach, the rise of respiratory viruses brings significant concern, particularly for senior citizens. Older adults often experience symptoms resembling traditional illnesses such as influenza and the common cold when infected with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), yet these signs can easily be overlooked or misattributed. The range of symptoms, which includes congestion, cough, and even mild fever, makes it essential to remain vigilant during this crucial season. The presence of RSV in the elderly population prompts a re-evaluation of preventive measures, including vaccination and symptom awareness, to mitigate severe health outcomes. Addressing RSV treatment options and the importance of timely intervention can play a key role in safeguarding older adults from serious complications.
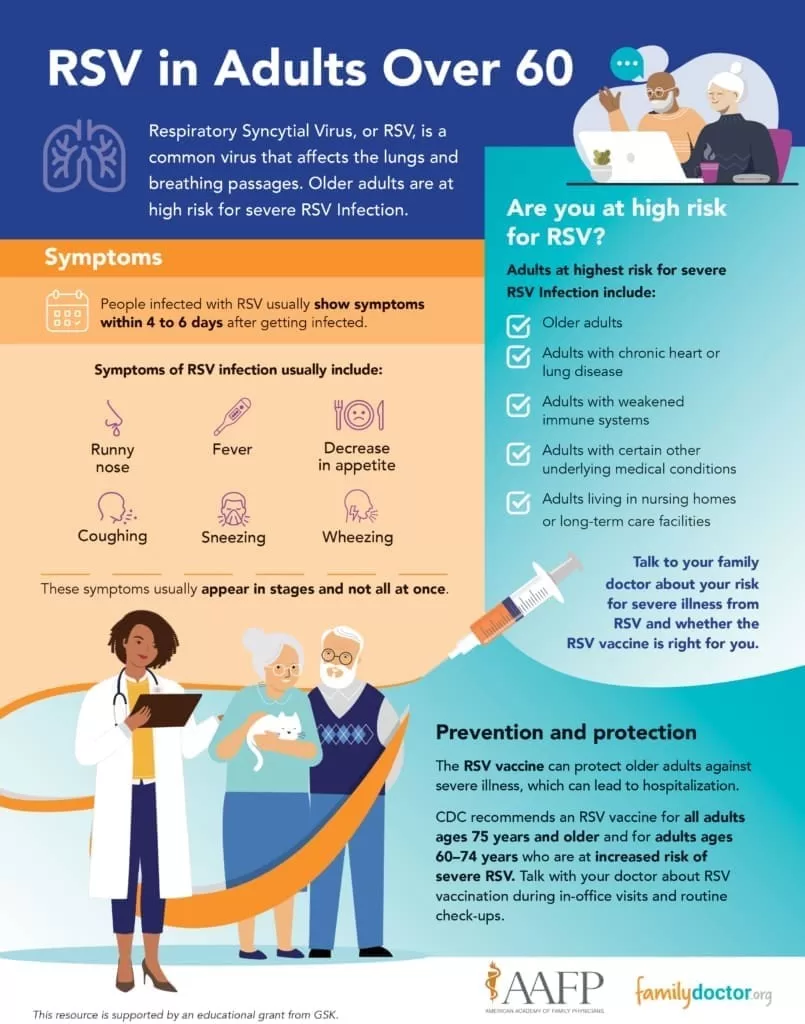
Understanding RSV Symptoms in Older Adults
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is often overlooked as a seasonal illness affecting older adults. The symptoms of RSV can closely mimic those of more familiar respiratory diseases like influenza and COVID-19, which can lead to misdiagnosis. Older individuals are particularly susceptible to RSV infection, as their immune systems may not respond as robustly to infections. Common RSV symptoms include a runny nose, congestion, cough, and mild fever. Additionally, signs such as fatigue and headaches can make it challenging to differentiate RSV from other respiratory viruses without a careful assessment.
Recognizing RSV symptoms early is crucial, especially since the virus can lead to more severe respiratory conditions in older adults. For instance, a persistent cough that intensifies over a few days may indicate that a mild infection is transitioning into a more serious health issue. Older adults experiencing any of these common RSV symptoms should monitor their condition closely and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms worsen.
It’s important to remember that RSV is not just a childhood illness; it can cause serious complications in older populations. Awareness of the symptoms of RSV in older adults is vital for timely intervention. With the added risk factors associated with advanced age and pre-existing health conditions, the implications of contracting RSV should not be underestimated.
In the event of severe symptoms such as wheezing, difficulty breathing, or extreme tiredness, immediate medical attention is necessary. The likelihood of developing serious complications like pneumonia or bronchitis increases significantly in older adults, underscoring the importance of recognizing RSV symptoms promptly.
Preventing RSV Infection with Vaccination
The introduction of the RSV vaccine has been a promising development in the fight against respiratory syncytial virus, particularly for vulnerable populations like older adults. Health professionals recommend that individuals aged 75 and older receive the RSV vaccine, especially if they missed the initial rollout in 2023. The vaccine is designed to mitigate the risks associated with RSV infection, which can lead to severe complications in older individuals.
Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing RSV infection and reducing hospital admissions due to severe symptoms. In addition to the vaccine, it is essential for older adults to practice standard preventative measures such as good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with those who are ill, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to strengthen their immune response. Given that older adults are at a heightened risk for serious illness from RSV, proactive measures such as these are critical.
Moreover, boosting awareness about RSV and its potential impact on older populations could further enhance prevention efforts. Encouraging older adults and their caregivers to initiate discussions with healthcare providers about the RSV vaccine can help protect them against this dangerous respiratory virus. With the right preventive strategies in place, the risk of severe RSV infection and its associated complications can be significantly reduced.
Healthcare professionals are optimistic that widespread adoption of the RSV vaccine will lead to a notable decrease in hospitalizations and deaths among older adults. Ongoing education about RSV symptoms and available treatments is equally important to ensure that those affected receive timely and appropriate care.
The Connection Between RSV and Other Respiratory Viruses
RSV is part of a larger family of respiratory viruses that can wreak havoc during the fall and winter months. Symptoms of RSV often overlap with those of other viral infections like the flu and COVID-19, making differentiation challenging. This is particularly concerning for older adults, who may have existing health issues that complicate their response to any respiratory illness. Being aware of these interconnected risks allows for better public health strategies and individual preparedness.
Understanding that RSV can present similarly to other respiratory viruses also emphasizes the need for testing and accurate diagnosis. If older adults exhibit symptoms such as fever, cough, or fatigue, healthcare providers may need to perform tests to confirm whether they are dealing with RSV or another virus. This can guide appropriate treatment strategies, especially since there are currently no specific antiviral treatments for RSV.
Furthermore, respiratory viruses can simultaneously circulate in the population, increasing the burden on healthcare systems during peak seasons. Older adults, particularly those with chronic respiratory conditions, are at heightened risk from this cumulative effect. It’s crucial that community awareness campaigns highlight measures that can reduce transmission of all respiratory viruses, including promotional efforts around the RSV vaccine.
In summary, recognizing the relationship between RSV and other respiratory viruses is essential for managing health outcomes in older adults. Increased awareness of RSV, alongside effective vaccination strategies and public health initiatives, can help mitigate the spread and impact of all respiratory viruses in this vulnerable population.
Recognizing When RSV Symptoms Worsen
While many individuals recover from RSV with symptomatic treatment, older adults must remain vigilant for exacerbation of symptoms signaling a more severe infection. Indicators like extreme fatigue, a persistent cough that produces phlegm, or difficulty breathing require immediate medical evaluation. These symptoms often signify that RSV is leading to more severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, which are especially dangerous for older adults.
An important aspect of managing RSV in older patients is tracking any change in their health status. Sudden changes in mental state, or visible signs like bluish skin around the lips or nails, can indicate respiratory distress that should be addressed promptly. Older adults and caregivers should be educated on these warning signs to ensure timely medical intervention, which can be critical in preventing severe health consequences.
Additionally, understanding that a worsening cough can result from developing pneumonia emphasizes the necessity for monitoring symptoms closely. Those with underlying health conditions such as asthma or COPD must prioritize their health by seeking treatment if they notice these developments. Not only can early intervention alleviate symptoms, but it can also significantly improve outcomes for older patients suffering from RSV.
Ultimately, recognizing when RSV symptoms worsen gives older adults a fighting chance against potentially serious health complications. Open communication with healthcare providers and regular health check-ups can equip elders and their families with the tools needed to navigate RSV challenges effectively.
RSV Treatment Options for Older Adults
Currently, there are no specific antiviral treatments available for RSV, particularly for adults, which places an emphasis on prevention and supportive care. For older adults experiencing mild symptoms, over-the-counter medications can help manage discomfort. Pain relievers like acetaminophen can alleviate aches, while expectorants such as guaifenesin can help relieve cough by loosening mucus. It’s essential, however, that any medication regimen is discussed with a healthcare provider to avoid complications.
Moreover, staying hydrated is a critical component of care for RSV-infected individuals, particularly older patients. Dehydration can significantly worsen health outcomes in elderly individuals battling a respiratory infection. Encouraging fluid intake, whether through water, broth, or electrolyte solutions, can help maintain hydration and support recovery.
Preventing RSV is paramount since treatments are limited. The introduction of the RSV vaccine holds promise for reducing the incidence of severe illness among older adults. Public health campaigns should continue to emphasize the importance of vaccination and educating older adults about the signs and symptoms of RSV to facilitate early intervention.
In conclusion, while treatment options for RSV remain somewhat limited in adults, understanding supportive care strategies and proactive vaccination can significantly impact health outcomes for older populations. Ongoing research and development of effective antiviral therapies will ultimately enhance management and prevention of RSV.
The Importance of Hydration During RSV Infection
With RSV infection, hydration becomes a critical factor in recovery, especially among older adults. Dehydration can exacerbate already existing respiratory symptoms and lead to further complications. As RSV often causes symptoms like fever and fatigue, it’s easily possible for older individuals to become dehydrated. Encouraging fluid intake, whether through water, herbal teas, or clear broth, can support recovery by preventing dehydration and helping to thin mucus.
Additionally, hydration plays a vital role in the overall health of older adults battling respiratory illnesses. While discussing treatment options, caregivers and family members should emphasize the importance of keeping patients well-hydrated. This approach not only alleviates symptoms but may also promote better overall health and immune function, which is essential for recovery from RSV.
Furthermore, hydration practices can be coupled with other supportive care measures to enhance the overall treatment strategy for older adults with RSV. Considering the limitation of specific antiviral medications for RSV, advocating for fluid intake and maintaining balanced electrolytes become essential elements in the management of respiratory viruses.
In summary, adequate hydration is a fundamental aspect of supportive care for older adults impacted by RSV. Encouraging patients to drink plenty of fluids not only aids in symptom relief but also contributes to their overall well-being during recovery.
RSV Vaccine: A Game Changer for Older Adults
The recent development of an RSV vaccine marks a monumental shift in how older adults can protect themselves against this potentially dangerous respiratory virus. With recommendations for individuals 75 and older to receive the vaccine, it serves as a preventive measure that can substantially reduce hospitalization rates and the severe impact of RSV infections. Public health initiatives are crucial in educating older populations about the new vaccine options and the associated benefits.
Furthermore, the vaccine is not only recommended for the oldest age groups but also for those aged 60 to 74 with underlying health conditions, emphasizing the vulnerability of this demographic. As public awareness grows regarding the implications of RSV for older adults, ensuring that high-risk individuals receive the vaccine is a priority for health professionals. The goal is to empower older adults through vaccination to safeguard their health against RSV and its risks.
In conclusion, the RSV vaccine represents a significant advancement in preventive health measures for older adults. With the potential to reduce severe infections and associated complications, widespread vaccination efforts can lend reassurance to older patients and their families. Continuous public health messaging will be key in making sure that those at risk understand the importance of getting vaccinated against RSV.
As more research unfolds, ongoing improvements in vaccine availability and education will play an imperative role in reducing the incidence of RSV within older populations, consequently helping to diminish the burden of respiratory viruses during peak seasons.
Understanding RSV Complications in Older Adults
Complications from RSV can be particularly severe for older adults who may have weakened immune systems or pre-existing health conditions. Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and heart disease can complicate RSV infections, leading to hospitalizations and even fatalities. It underscores the importance of recognizing symptoms early, as timely medical intervention can mitigate the risks of severe complications.
Moreover, older adults are at a higher risk for conditions like pneumonia when infected with RSV. The CDC reports that RSV is responsible for a considerable number of hospitalizations among the elderly, further affirming the need for heightened awareness and preventive measures. Families and caregivers should be proactive about monitoring health changes, especially during RSV season, to identify potential red flags that might indicate worsening health status.
Understanding RSV complications will assist caregivers in taking the necessary precautionary measures to help older adults navigate the colder months safely. Keeping in regular contact with healthcare providers and ensuring that patients stay updated with vaccinations can significantly reduce the impact of RSV.
In conclusion, awareness of the RSV-related complications and being proactive in prevention and monitoring strategies are vital for safeguarding the health of older adults. This can lead to a more informed and prepared response should RSV infections arise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of RSV infection in older adults?
The common symptoms of RSV infection in older adults include congestion, cough, fever, lack of energy, mild headache, runny nose, and sore throat. These symptoms can sometimes mimic those of other respiratory viruses, making it important for older adults to monitor their health closely.
How can I recognize if my RSV symptoms are getting severe as an older adult?
Older adults should look for signs that their RSV infection is turning severe, such as extreme tiredness, persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, low appetite, bluish skin or nails, and sudden changes in mental state. If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Is there a specific RSV treatment for adults experiencing symptoms?
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for RSV in adults. The primary recommendation is prevention through vaccination, especially for older adults. For mild RSV symptoms, over-the-counter medications can be used to relieve discomfort, but consulting a healthcare provider is advisable before starting any treatment.
What preventative measures can older adults take against RSV infection?
Older adults can reduce the risk of RSV infection by getting vaccinated, especially those aged 75 and older or those aged 60 to 74 with underlying health conditions. Practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and keeping up-to-date with vaccinations for flu and COVID-19 can also help protect against respiratory viruses.
Can RSV symptoms in older adults lead to serious complications?
Yes, symptoms of RSV in older adults can lead to serious complications, especially in those with pre-existing health conditions like chronic heart and lung diseases. Severe RSV can result in lower respiratory infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis, making prompt recognition and treatment essential.
What age group is most at risk for severe RSV infection symptoms?
Older adults, particularly those aged 60 and above, are most at risk for severe symptoms and complications from RSV infection. Additionally, individuals with compromised immune systems or existing respiratory conditions like COPD are also more vulnerable.
What should older adults do if they suspect they have RSV?
If older adults suspect they have RSV symptoms, they should monitor their health closely for worsening symptoms and seek medical advice. Staying hydrated, resting, and using over-the-counter medications for symptom relief can be helpful, but medical consultation is crucial if symptoms escalate.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Congestion | Nasal blockage leading to difficulty breathing through the nose. |
| Cough | Persistent cough that can indicate airway irritation. |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature signaling infection. |
| Lack of energy | Feeling excessively tired or fatigued. |
| Mild headache | Light pain or discomfort in the head. |
| Runny nose | Excessive mucus secretion from the nasal passage. |
| Sore throat | Pain or irritation in the throat, especially when swallowing. |
Summary
RSV symptoms in older adults can be often mistaken for other common respiratory illnesses. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early recognition and treatment, especially for those who may be at a higher risk of complications from the virus. If you or a loved one is experiencing congestion, cough, fever, lack of energy, mild headache, runny nose, or sore throat, it is essential to monitor the situation closely and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen. Preventive measures, such as the RSV vaccine, are vital for older adults to reduce the risk of severe illness.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.