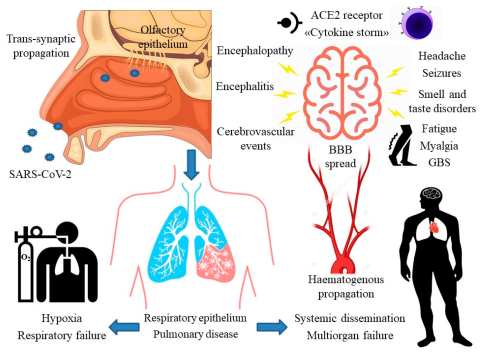
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) has recently garnered attention due to a notable surge in reported cases, particularly in China. As a common respiratory illness, HMPV resembles other viral infections, often manifesting with symptoms similar to those of a cold. Health experts emphasize the need for awareness surrounding HMPV symptoms, highlighting its potential to spread through coughing, sneezing, and contact with contaminated surfaces. Understanding how HMPV spreads is crucial for both individuals and public health officials in curbing its transmission. With no specific antiviral treatment currently available, focusing on HMPV prevention tips, such as good hygiene practices, becomes essential during the peak respiratory season.
The emergence of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) in various regions has raised significant health concerns, especially as it increases during the cold months. Often mistaken for other respiratory viruses, HMPV’s impact encompasses a range of symptoms including congestion, cough, and fever. In light of this, it’s important to explore not only how HMPV spreads but also effective HMPV treatment options that prioritize supportive care. Understanding this virus’s dynamics is critical for both healthcare providers and the general public, who must stay informed about HMPV prevention tips to reduce infection rates. With the ongoing focus on respiratory illnesses, familiarity with HMPV can play a crucial role in managing health during peak viral seasons.
Understanding Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Human Metapneumovirus, commonly known as HMPV, is a respiratory virus that was first identified in 2001. It belongs to the Pneumoviridae family, which also includes viruses like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). HMPV is known to cause infections that resemble those caused by other respiratory illnesses, showing symptoms such as cough, fever, and nasal congestion. While many people may have little awareness of this virus, it circulates annually during the respiratory virus season, which typically peaks in winter.
By increasing awareness and diagnostic capabilities in healthcare settings, more cases of HMPV are being identified. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), improvements in testing have allowed for more accurate diagnoses in hospitals and clinics. As healthcare professionals grow more familiar with HMPV, public health responses are likely to improve, aiding in better management and treatment of infections caused by this virus.
Recognizing HMPV Symptoms
Symptoms of HMPV typically manifest between three to six days after exposure, making it crucial for early recognition, especially among vulnerable populations such as young children and older adults. Common HMPV symptoms include cough, nasal congestion, fever, and in more severe cases, shortness of breath. The challenge lies in the fact that these symptoms can easily be confused with other respiratory viruses, which is why it is often underdiagnosed.
Healthcare providers advise that if symptoms worsen, patients should seek medical attention, particularly if they are at risk for severe outcomes. Understanding these symptoms can be pivotal in determining the right course of action and discerning whether additional diagnostic tests, including those for COVID-19, influenza, or RSV, might be necessary.
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads primarily through respiratory secretions, similar to many other viral infections. It can be transmitted via coughing and sneezing, close personal contact, or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus before touching the face. The CDC emphasizes that the virus circulates predominantly in winter months, showing a trend much akin to influenza and RSV, thereby posing a heightened risk during the cold season when viruses thrive in close quarters.
Interestingly, by the time individuals reach five years of age, most have already been exposed to HMPV, though they might not recall the illness as symptoms can be mild. However, reinfection is possible, and while this often leads to milder symptoms, those with weakened immune systems or older adults may face more severe reactions upon reinfection.
Current Treatment for HMPV
Currently, there are no specific antiviral treatments for human metapneumovirus, which means management of the illness focuses primarily on supportive care. For patients exhibiting moderate to severe symptoms, healthcare providers may administer bronchodilators to alleviate wheezing and help clear the airways, along with providing fluids for hydration purposes. Treatment plans are tailored according to the severity of the symptoms.
In cases of co-infection with bacterial pathogens, antibiotics may also be required to address secondary infections. The absence of specific medications underscores the need for raising awareness about HMPV and the importance of supportive care protocols to enable better patient outcomes.
Preventive Measures Against HMPV
Given that there is no vaccine available for HMPV, prevention focuses on diligent personal hygiene practices. It is vital for individuals to wash their hands regularly with soap and water, cover their mouths and noses while coughing or sneezing, and avoid contact with others if they feel unwell. These preventive measures are not only effective for HMPV but also for various other respiratory viruses prevalent during the winter months.
Healthcare experts suggest that at-risk individuals—such as older adults, frail individuals, and those with compromised immune systems—should take extra precautions, including wearing masks in crowded indoor settings and maintaining physical distance. Additionally, vaccinations against other respiratory viruses like influenza and COVID-19 can help reduce the risk of complications and assist in distinguishing between different illnesses during peak infection seasons.
The Impact of HMPV Cases Rising in China
Recent reports have highlighted a concerning uptick in HMPV cases in China, coinciding with the respiratory virus season. Chinese health officials are closely monitoring these developments amidst reports of increased acute respiratory infections overall. The World Health Organization has stated that while there is a spike in cases, the severity and overall scale of respiratory infectious diseases are lower compared to previous years, suggesting a need for heightened surveillance but not alarm.
The rise in cases in China can serve as a reminder for other nations, including the U.S., to prepare and educate the public about the risks of human metapneumovirus. As travel and trade resume, it becomes increasingly important to maintain awareness and readiness against potential outbreaks of various respiratory viruses, including HMPV.
HMPV and Winter Respiratory Virus Season
The winter months are notorious for being the respiratory virus season when illnesses like influenza, COVID-19, RSV, and HMPV circulate more widely. Dr. William Schaffner from Vanderbilt University Medical Center highlighted that close contact during the holiday season increases the chances of virus transmission. Many people gather indoors, where the risk of spreading respiratory viruses is significantly heightened.
As more data emerges, it becomes apparent that HMPV should not be overlooked. Each winter, clinicians are advised to evaluate symptoms carefully and consider the full spectrum of respiratory pathogens, putting an emphasis on preventive measures during this critical period.
Discussing HMPV Awareness for Public Health
Heightened awareness of HMPV among the public and healthcare professionals is essential for improving detection and management of infections. The growing body of knowledge and testing capabilities means that HMPV can be identified more readily in various healthcare settings than in previous years. Greater awareness leads to better-informed patients and practitioners alike, streamlining the process of care.
As health campaigns promote awareness of HMPV, they should also emphasize the importance of preventive measures and seasonal vaccinations to combat more widespread respiratory illness. The connection between infections and the rise of HMPV cases during the winter months should be a focal point in public health messaging.
The Future of HMPV Research
With the increasing prevalence of human metapneumovirus, there exists a pressing need for advanced research on HMPV. Investigating the virus’s genetics, transmission patterns, and immune responses can provide insights critical for developing treatments, and potentially, vaccines. As the medical community continues to learn more about HMPV, comprehensive strategies can be devised to address the gap in effective prevention and treatment options.
Future studies could also explore the relationship between HMPV co-infections and the severity of symptoms in patients suffering from other respiratory conditions. By understanding these dynamics, healthcare professionals can optimize patient care and develop better protocols for managing respiratory viruses, particularly during peak seasons.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of HMPV?
Symptoms of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) include cough, nasal congestion, fever, and shortness of breath. The virus has an incubation period of three to six days and is often indistinguishable from other respiratory viruses. Individuals at higher risk, such as young children and adults over 65, may experience more severe symptoms.
How does HMPV spread between individuals?
HMPV spreads through respiratory secretions when an infected person coughs or sneezes, close personal contact, and by touching contaminated surfaces. It’s common for HMPV to circulate during winter months when people are more likely to be in close contact indoors.
Is there a specific treatment available for HMPV?
Currently, there are no antiviral treatments for human metapneumovirus (HMPV). Management focuses on supportive care, such as bronchodilators for wheezing or fluids for dehydration. Antibiotics may be prescribed in case of bacterial co-infections.
What preventive tips can help avoid HMPV infection?
To prevent HMPV infection, practice good hygiene: wash hands frequently, cover your nose and mouth when sneezing or coughing, and stay home if you’re feeling unwell. High-risk individuals should consider wearing masks in crowded indoor settings and participate in social distancing.
Is there a vaccine available for HMPV?
There is currently no vaccine to prevent human metapneumovirus (HMPV). However, getting vaccinated against other respiratory illnesses such as COVID-19, flu, and RSV can help reduce the risk of severe co-infections.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| What is HMPV? | A virus causing upper and lower respiratory illnesses, it was discovered in 2001 and is part of the Pneumoviridae family, along with RSV. |
| Symptoms | Includes cough, nasal congestion, fever, and shortness of breath, often indistinguishable from other respiratory infections. |
| transmission | Spreads through respiratory secretions, close contact, and contaminated surfaces; rises in winter, peaking during colder months. |
| Treatment | No antivirals; treatment focuses on supportive care, including fluid management and bronchodilators for wheezing. |
| Prevention | No vaccine; emphasizes hygiene, staying home when unwell, and possibly wearing masks in large gatherings for high-risk groups. |
Summary
HMPV, or human metapneumovirus, is gaining attention recently due to a rise in cases reported in China. While its symptoms are similar to other respiratory viruses, it is crucial to recognize its impact, especially during the winter respiratory virus season. Observing preventive measures, such as practicing good hygiene and understanding transmission routes, can help mitigate the spread of HMPV. No specific treatment exists, but supportive care can manage symptoms effectively. By staying informed and cautious, individuals can better protect themselves and reduce their risk during this peak season.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.