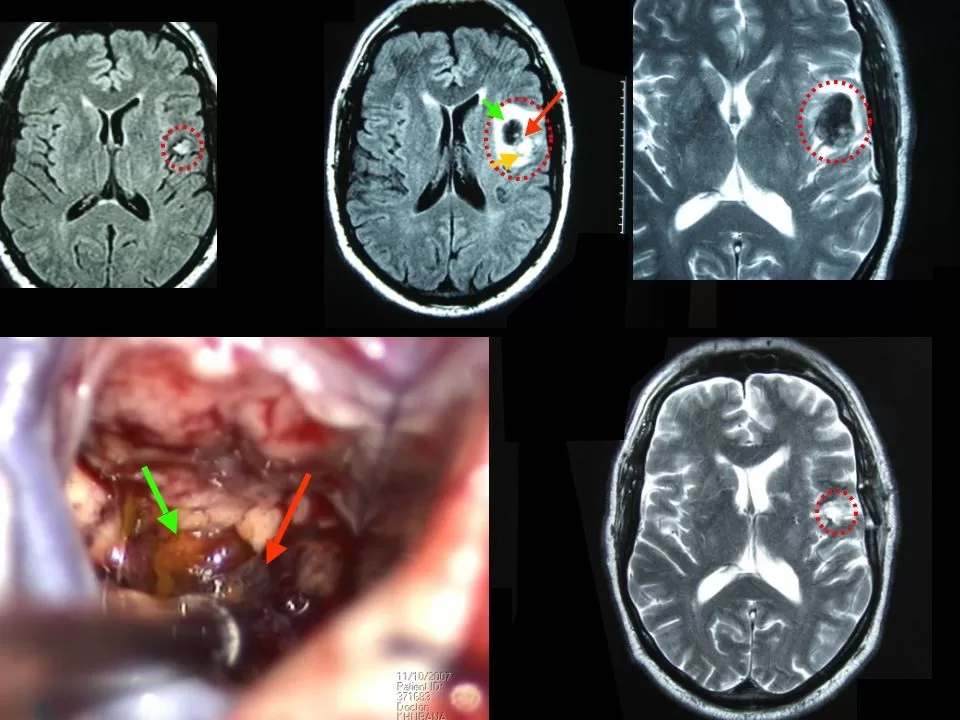
Cavernoma, also referred to as cavernous malformation, is a vascular abnormality that warrants significant attention due to its potential impact on neurological health. These lesions are characterized by a cluster of dilated, thin-walled blood vessels, often situated in the brain, brainstem, or spinal cord, which can lead to a variety of symptoms including seizures and chronic headaches. Understanding cavernoma symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management, as the condition can sometimes result in severe complications such as hemorrhagic cavernoma. Exploring the causes of cavernoma, researchers have identified both genetic factors and sporadic mutations that contribute to its formation, highlighting the importance of genetics in this field. When considering cavernoma treatment options, both observation and surgical intervention may play significant roles, tailored to individual patient needs.
Known interchangeably as cavernous malformations, cavernomas consist of an abnormally structured network of blood vessels that can lead to serious medical challenges. Characterized by their delicate, perforated walls, these vascular lesions can either remain silent or trigger various neurological symptoms that impact everyday life. In essence, cavernoma encompasses a range of conditions wherein abnormal blood vessel formations may occur in critical areas of the central nervous system. Understanding the nature of this vascular condition involves not only recognizing its symptoms but also exploring potential treatment avenues and its underlying genetic causes. Consequently, insights into cavernous malformations assist patients and healthcare providers alike in navigating the complexities of this medical condition.
What are Cavernomas?
Cavernomas, also referred to as cavernous malformations, are vascular anomalies characterized by clusters of abnormal blood vessels in the central nervous system. These malformations can be formed in the brain, brainstem, or spinal cord, with varying implications for health and well-being. The architecture of these vessels is notably thin-walled, increasing their predisposition to hemorrhaging. As a result, many individuals diagnosed with cavernomas experience devastating symptoms that could affect their nervous system functions.
Understanding the formation and structure of cavernomas is essential for both medical professionals and patients alike. The lesions can remain asymptomatic for extended periods; however, they can also lead to severe neurological deficits when they hemorrhage. This condition could manifest through symptoms like chronic headaches or seizures. Therefore, early detection through MRI imaging is critical in providing the required management for those affected by cavernomas.
Recognizing Cavernoma Symptoms
The symptoms of cavernomas can range widely, making them challenging to diagnose. Seizures are one of the most common indicators, affecting approximately 20-30% of patients with cavernous malformations. These seizures may vary in severity and can appear as focal or generalized episodes. Chronic headaches, often resembling migraines, are another frequent complaint among affected individuals, which may drastically affect their quality of life.
Beyond seizures and headaches, more severe neurological deficits can arise, particularly if a cavernoma is located in vital areas of the brain. Symptoms such as weakness, difficulty in speech, or sensory loss could emerge, mimicking stroke-like presentations. Identifying these symptoms early on is crucial, as prompt intervention can lead to better management strategies and improved patient outcomes.
Understanding the Causes of Cavernomas
The underlying causes of cavernomas and their formation still puzzle researchers and clinicians alike. While genetic factors are believed to play a key role, cavernomas may arise either sporadically in individuals without any family history or through inherited conditions. Sporadic cavernomas develop due to random genetic mutations affecting blood vessel structure. In contrast, familial cavernomas have been linked to specific genetic mutations, which have been identified in several key genes.
Recognizing the potential hereditary aspect of cavernoma development prompts a comprehensive approach to family health. Individuals with a family history of cavernomas may benefit from genetic counseling and screening to catch any abnormalities early. This proactive strategy can facilitate earlier interventions for relatives who may be at risk.
Cavernoma Treatment Options Explained
Addressing cavernomas depends largely on the symptoms presented and the overall health of the patient. For asymptomatic cases, healthcare providers often recommend an observational approach. Regular MRI scans are utilized to monitor any changes in the cavernoma’s size or condition, ensuring that any developments can be addressed promptly without unnecessary risk from intervention.
For those who exhibit symptoms, treatment strategies include the utilization of medications to manage seizures and alleviate headaches, thus enhancing the quality of life. In more serious cases where symptoms persist or worsen, surgical intervention may be required. This surgery focuses on removing the cavernoma to alleviate pressure and restore normal functionality, underscoring the importance of a tailored treatment plan that considers the unique needs of each patient.
Future Directions in Cavernoma Research
As research advances, understanding cavernomas becomes increasingly nuanced, with ongoing studies delving into the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to their development. Emerging evidence suggests that genetic screening could play a vital role in predicting risk and improving treatment outcomes. Greater awareness and understanding of cavernous malformations may lead to novel therapeutic strategies and improved surveillance for at-risk populations.
The future of cavernoma management may also see advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques and refined post-operative care protocols, aimed at reducing complications and enhancing recovery times. Additionally, collaborative efforts within the medical community may lead to more effective approaches for both symptomatic and asymptomatic management of cavernomas, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of cavernoma?
Cavernoma symptoms can vary widely, but the most common include seizures (affecting about 20-30% of patients), persistent chronic headaches, and neurological deficits reminiscent of stroke symptoms. Hemorrhagic cavernomas can lead to sudden neurological changes, requiring prompt medical attention.
What causes cavernoma and are there genetic links?
Cavernoma causes remain partially understood, with research suggesting genetic predispositions play a significant role. Sporadic cavernomas can develop due to random mutations, while familial cavernomas are linked to genetic mutations such as KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10, implicating a hereditary component.
How is cavernoma treated when symptoms are present?
Treatment for symptomatic cavernomas often involves a tailored approach. For those experiencing significant symptoms such as seizures or headaches, management may include medications for symptom relief. In more severe cases, surgical intervention to remove the cavernoma can alleviate symptoms and prevent future hemorrhages.
Is surgery always necessary for patients with cavernoma?
Not always. Many patients with asymptomatic cavernomas may be monitored through regular MRI scans, as observation can be an effective strategy. Surgery is generally reserved for symptomatic cavernomas causing significant issues, such as recurring seizures or hemorrhaging.
What is a hemorrhagic cavernoma and what risks does it pose?
A hemorrhagic cavernoma refers to a cavernoma that has experienced bleeding, which can lead to acute neurological deficits and necessitates immediate medical assessment. This condition poses risks of increased pressure on surrounding brain tissues, causing more severe symptoms and complications.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Cavernomas are vascular abnormalities formed by enlarged, thin-walled blood vessels in the brain, brainstem, or spinal cord. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include seizures, chronic headaches, neurological deficits, and the risk of hemorrhaging. |
| Causes | Cavernomas may occur sporadically due to random genetic mutations or be familial, linked to genetic mutations like KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10. |
| Treatment Options | Treatment can include observation for asymptomatic cases, anti-seizure medications for symptomatic patients, or surgical intervention for severe cases. |
Summary
Cavernoma is a vascular malformation that can pose significant health risks, making it essential to understand its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. While some individuals may remain asymptomatic, others experience various neurological symptoms that necessitate medical attention. With a focus on patient-centric care, treatment can be tailored to meet individual needs, whether through observation, medication, or surgery. Continued research into the genetic underpinnings of cavernomas represents hope for improved treatment strategies and outcomes in the future.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.