Avian Influenza, commonly referred to as bird flu, poses a significant threat to both poultry and public health worldwide. Among the various strains, the H7N9 virus has gained particular attention due to its potential to mutate and become more lethal, raising concerns about the avian flu threat to humans. Recent genetic analysis has revealed troubling mutations in H7N9 viruses, emphasizing the urgency for effective surveillance and control measures. Furthermore, understanding the effectiveness of influenza vaccines against such dangerous strains is crucial as they play a pivotal role in mitigating severe outbreaks. As antibiotic stewardship becomes increasingly important, the emergence of antimicrobial resistance complicates the landscape of infectious disease management, underscoring the need for robust health strategies in combating not just avian influenza but also related public health challenges.
Bird flu, scientifically known as Avian Influenza, encompasses a range of influenza viruses that primarily affect birds. The H7N9 strain, in particular, is noted for its capacity to pose serious health risks to humans, which raises significant alarm in agricultural and health sectors. With numerous outbreaks historically resulting from mutations in these viruses, the avian influenza crisis highlights the necessity for effective vaccines and rapid response measures. Additionally, linked concerns regarding the measles outbreak and rising antimicrobial resistance indicate a broader spectrum of health threats that require comprehensive surveillance and proactive strategies. Addressing Avian Influenza, therefore, is not only about controlling a specific virus but also about safeguarding public health within the wider context of infectious disease management.
Avian Influenza: Understanding the H7N9 Threat
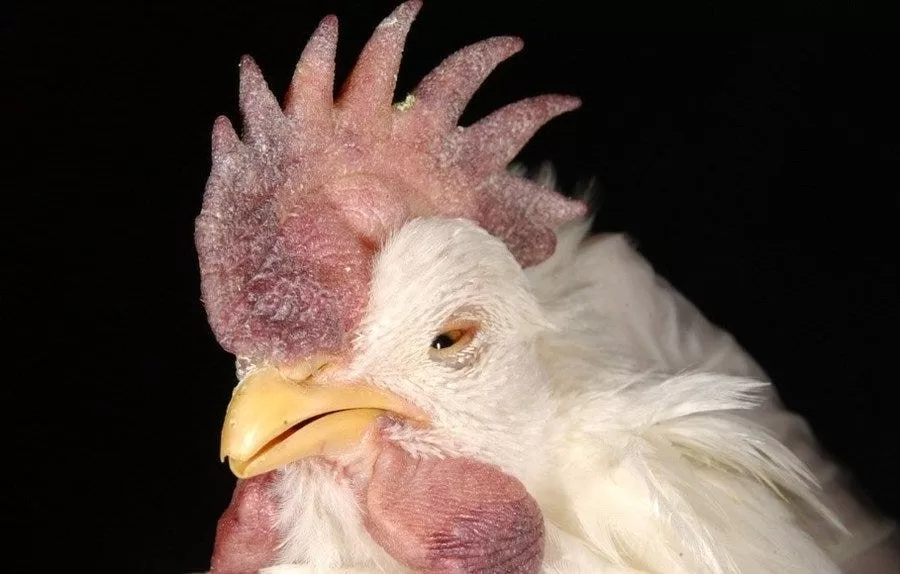
Avian influenza, particularly the H7N9 virus, has raised significant concerns among health officials worldwide due to its potential for mutations that can increase virulence and transmissibility. Recent genetic analyses have revealed alarming changes in H7N9 strains collected from poultry in China, suggesting that this strain not only poses threats to birds but also to human health. The mutations uncovered during studies indicate that H7N9 can adapt and potentially lead to more severe outbreaks among poultry populations, subsequently heightening the risk to humans who come into contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
Moreover, controlling the spread of H7N9 is becoming increasingly urgent as low-pathogenic strains can evolve into highly pathogenic variants. The findings from the October 24 report highlight the importance of monitoring and implementing rigorous biosecurity measures to prevent a significant public health crisis. Experts emphasize that culling infected poultry alone may not suffice; comprehensive strategies involving vaccination and surveillance are paramount to manage not only the current strains but also to anticipate future variants of avian influenza that could further threaten human populations.
Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness: Insights from Australia
The recent findings from Australia’s flu vaccine effectiveness studies spotlight critical challenges in combating influenza, particularly the H3N2 strain. With an overall effectiveness of merely 33%, the results indicate a worrying trend for public health, especially since the vaccine offers considerably low protection against the dominant H3N2 variant. This underscores an urgent need for ongoing research into vaccine development that addresses the evolving nature of influenza viruses, as current vaccines appear unable to keep pace with viral mutations.
Additionally, the poor performance of vaccines against H3N2 raises concerns about the upcoming flu season in the Northern Hemisphere. Health officials are worried that a predominance of this strain could lead to widespread infections and considerable morbidity, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with preexisting health conditions. This situation calls for enhanced vaccine technologies, such as cell-based vaccines, that could offer better antigenic match and protection and ultimately improve overall influenza vaccination strategies.
Measles Outbreak in Somalia: Response and Prevention Strategies
Somalia is currently grappling with a significant measles outbreak, recording nearly 19,000 cases amid deteriorating conditions exacerbated by famine and displacement. The alarming increase in measles cases, largely affecting children, highlights the critical need for robust vaccination programs and public health interventions. The World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that Somalia’s minimum vaccination coverage stands at a dismal 60%, far below the recommended target of 95%. To mitigate this public health crisis, enhanced vaccination campaigns targeting over 4 million children are scheduled to commence.
The stark reality of this outbreak serves as a reminder of the vulnerabilities in global vaccination coverage, especially in regions under socioeconomic strain. The collaboration between global health organizations and local authorities is vital in reinforcing health systems, establishing rapid outbreak response mechanisms, and ensuring that immunization drives effectively reach children in high-risk areas. This multi-faceted approach is essential not only to combat the current outbreak but also to prevent future measles resurgence, reinforcing the broader goal of achieving global immunization targets.
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Global Concern
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has emerged as a formidable challenge in public health, prompting European health and food safety agencies to establish indicators tracking progress in combating this threat. Identifying resistant strains of bacteria such as *E. coli* and *MRSA* will help monitor the effectiveness of measures aimed at reducing antimicrobial use in both humans and food-producing animals. The implementation of these indicators reflects a global commitment to addressing AMR, which can undermine the effectiveness of antibiotic treatments and lead to increased morbidity and mortality rates.
The rising prevalence of resistant bacteria in food sources emphasizes the intertwined nature of human and environmental health. The alarming identification of carbapenem-resistant *Enterobacteriaceae* in German seafood underscores the urgent necessity for surveillance and regulations across the food supply chain. Public health initiatives must integrate antimicrobial stewardship to ensure responsible antibiotic use and preserve the efficacy of existing treatments. This approach not only calls for policy development but also for raising awareness among healthcare providers, farmers, and consumers about the perils of antimicrobial misuse.
Leveraging Technology in Vaccine Development
In light of the pressing challenges associated with vaccine effectiveness against rapidly evolving influenza strains, leveraging advanced technologies in vaccine development has never been more crucial. Innovations such as mRNA technology have demonstrated promise in providing a robust immune response against several viral infections. This technology could facilitate quicker responses to outbreaks by producing vaccines tailored to circulating strains within a fraction of the time traditionally required for conventional vaccines.
Furthermore, incorporating genetic mapping and bioinformatics to track viral mutations can greatly enhance our response to emerging threats like the H7N9 avian influenza. By understanding the genetic evolution of these viruses, researchers can prioritize specific vaccine composition and distribution strategies, thereby maximizing public health impact. This multifaceted technological approach presents an opportunity to revolutionize how we prepare for and respond to infectious disease challenges in the future.
Global Vaccination Efforts: Lessons from History
The significant reduction in global measles deaths is a testament to the impact of robust vaccination initiatives initiated since the early 2000s. With combined efforts from organizations such as WHO and UNICEF, the death toll from measles has drastically decreased from 550,000 in 2000 to about 90,000 last year. Such major improvements highlight the critical role that comprehensive vaccination programs and effective public health messaging play in achieving health goals.
However, the stagnation of vaccine coverage at the crucial 85% level indicates that there is still much work to be done. Historical lessons show that complacency can lead to setbacks; thus, it is crucial to continuously engage communities and improve immunization services to maintain momentum towards potential measles eradication. These lessons are also transferable to other infectious diseases, emphasizing that collaboration, innovation, and community involvement are vital to achieving lasting global health outcomes.
The Impact of Avian Influenza on Global Agriculture
Avian influenza, particularly strains like H7N9, poses significant threats not only to public health but also to global agricultural economies. The poultry industry, a crucial provider of food worldwide, suffers greatly when outbreaks lead to extensive culling measures and trade restrictions. The socio-economic ripple effects extend beyond farmers to impact entire communities reliant on poultry production for their livelihoods, demonstrating how infectious diseases can jeopardize food security.
To mitigate the impact of these outbreaks, it’s imperative for governments and agricultural stakeholders to implement stringent biosecurity measures and disease monitoring systems. Furthermore, research into vaccination strategies for poultry can assist in controlling the spread of avian flu, thus protecting both animal health and the livelihoods of those dependent on poultry farming. In this way, a proactive response can help stabilize agricultural markets and safeguard food supplies.
Combating Antimicrobial Resistance Through Global Cooperation
As antimicrobial resistance threatens global health, international cooperation is essential in developing comprehensive strategies to address this multifaceted challenge. The establishment of surveillance networks to monitor AMR trends and share data between nations is a priority to facilitate informed public health decisions. By fostering collaboration among countries, researchers can better understand the transmission dynamics of resistant pathogens and develop targeted interventions.
Additionally, funding initiatives focused on research and development of new antibiotics and alternative therapies must be increased. Governments, pharmaceutical industries, and health organizations should work together to prioritize the discovery of innovative solutions that can effectively combat resistant infections. Such collaborative efforts are crucial in sustaining effective health outcomes and ensuring that current and future generations can benefit from effective antimicrobial therapies.
Public Health Messaging: Encouraging Vaccination Uptake
Effective public health messaging plays a pivotal role in increasing vaccination uptake and combatting misinformation around vaccines. Campaigns must clearly communicate the safety and efficacy of vaccines, addressing common misconceptions and fears that may deter individuals from seeking immunization. Engaging community leaders and healthcare providers to disseminate these messages can enhance trust and encourage participation in vaccination programs.
Promoting the benefits of vaccination in preventing outbreaks, such as those seen with measles or seasonal influenza, can also foster community accountability. By framing vaccinations as a collective responsibility that protects not only individuals but also vulnerable populations, effective communication strategies can lead to higher vaccination rates. Ultimately, a commitment to transparent and responsive public health messaging is critical for ensuring that populations worldwide remain resilient against vaccine-preventable diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current threat level of the H7N9 virus and its impact on avian influenza outbreaks?
The H7N9 virus poses a significant avian influenza threat as findings from recent genetic analyses indicate mutations that increase its virulence and transmissibility. Researchers have identified several strains from poultry in China that have adapted to spread more effectively among animals, which raises concerns for potential human infections. Effective control measures are essential to mitigate this threat to both poultry and public health.
How effective are influenza vaccines against avian influenza, specifically H3N2 strains?
Recent estimates have shown that the influenza vaccine effectiveness (VE) can be quite variable. For example, the 2017 data from Australia indicated a VE of only 10% against the H3N2 strain, which is noteworthy given that H3N2 is known to co-circulate with avian influenza viruses. This highlights challenges in vaccine development and the need for ongoing surveillance to enhance vaccine effectiveness against circulating strains.
What should I know about avian influenza and its possible mutations affecting human health?
Avian influenza, particularly the H7N9 virus, has shown potential for mutations that may increase its lethality and transmissibility to humans. Recent research underscores the importance of monitoring and controlling low-pathogenic strains, as they can mutate into more harmful forms. This poses a greater public health risk and necessitates rigorous surveillance and preventive measures.
How can antimicrobial resistance relate to avian influenza control measures?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) can complicate the control of avian influenza by limiting treatment options for secondary bacterial infections that may follow viral infections. As avian influenza controls often involve culling and antibiotic use in poultry, careful management of antibiotic resistance is essential to prevent adverse outcomes. Integrating AMR stewardship into avian disease management is crucial for public health.
Are there any recent developments regarding avian influenza and seasonal flu vaccine recommendations?
Recent findings suggest that the current influenza vaccines may offer limited protection against certain strains like H3N2, which co-circulates with avian influenza viruses. It’s crucial for health authorities to adapt vaccine formulations based on circulating virus strains to improve overall effectiveness for both seasonal influenza and avian influenza responses.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Avian Influenza Strains | Genetic mutations in H7N9 strains from China may increase the threat to humans and poultry. |
| Monitoring of H7N9 Virus Evolution | Over 100,000 poultry samples were studied to track mutations across multiple provinces. |
| Infection Experiments | Mice and ferrets experiments show new strains could be more lethal and transmissible. |
| Need for Control Measures | Experts emphasize that culling alone is insufficient; both forms of the virus need control. |
| Flu Vaccine Effectiveness | Australia reports only 33% effectiveness of the flu vaccine against several strains. |
| Surveillance of Measles Outbreak | Somalia faces a significant measles outbreak, with plans for a vaccination campaign. |
| Antimicrobial Resistance | New indicators established in Europe to track progress on combating AMR. |
| Leptospirosis Cases | Reports of leptospirosis outbreaks following flooding in Louisiana and Puerto Rico. |
Summary
Avian Influenza remains a significant global health concern, particularly with emerging strains like H7N9 presenting increased risks. Recent studies have highlighted genetic mutations that enhance the virus’s virulence and transmissibility, which raises alarms for both poultry health and human safety. Effective monitoring and control measures are essential to prevent outbreaks and mitigate the health threats posed by Avian Influenza. As research continues, prioritizing the eradication of both low and highly pathogenic strains is critical for public health safety.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.