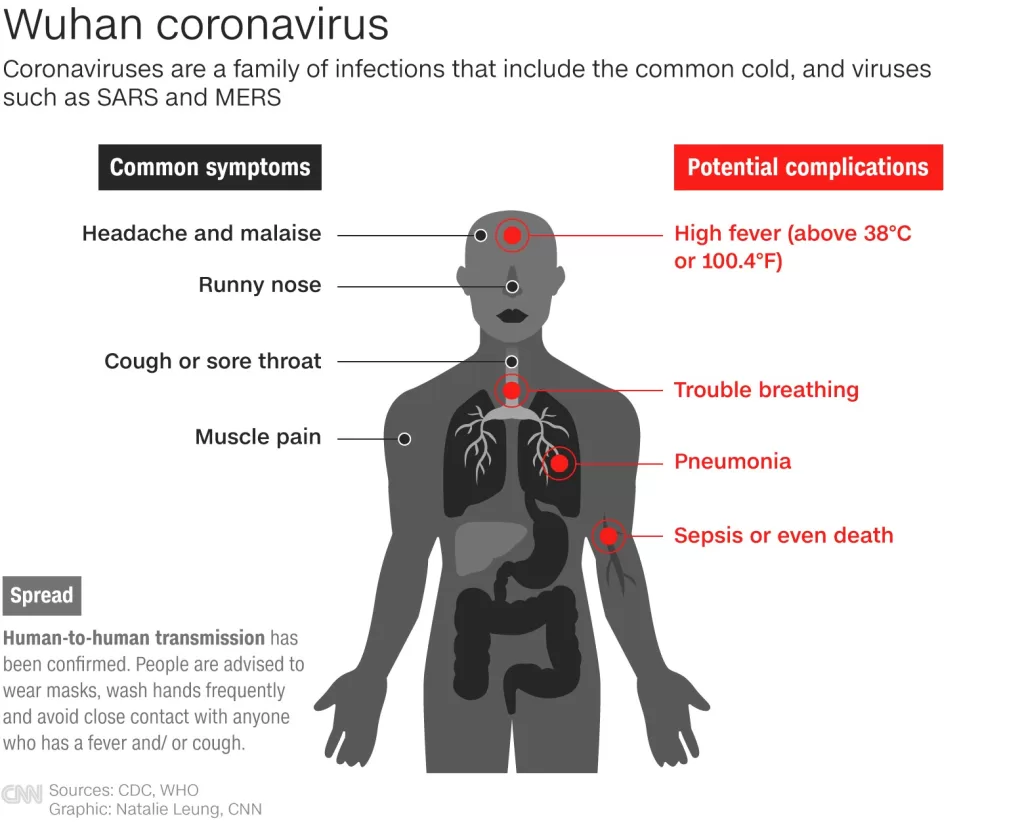
COVID-19 health impacts have been profound and wide-reaching, affecting not just physical health but also overall quality of life after COVID infection. Recent studies have highlighted that patients who experienced moderate to severe forms of COVID-19 often continue to suffer from long-term COVID symptoms, even one year post-recovery. Research such as the RECoVERED trial reinforces these findings, revealing diminished health-related quality of life (HRQL) among these individuals. The implications of COVID-19 treatment efficacy are critical, as they directly influence long-term patient outcomes, prompting ongoing investigations into effective therapies. As we navigate this pandemic’s aftermath, understanding the nuances of COVID-19 study results becomes essential for improving future health interventions and support systems.
The ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic have raised significant concerns about the lasting health effects experienced by survivors. Many individuals are grappling with chronic symptoms that severely disrupt their daily lives, a condition commonly referred to as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Studies reveal that the severity of initial illness plays a critical role in determining subsequent patient wellness, with those suffering from moderate to severe symptoms facing deeper repercussions. Additionally, advancements in treatment strategies have showcased varying degrees of effectiveness, ultimately shaping how healthcare providers address the challenges posed by this virus. As researchers continue to unveil the complexities of COVID-19 recovery, insights into patient health outcomes remain crucial for fostering better recovery programs.
Understanding Quality of Life Post COVID-19
The recent study published in *BMC Medicine* highlights a significant correlation between the severity of COVID-19 illness and long-term quality of life outcomes. Individuals who suffered from moderate to severe COVID-19 reported diminished health-related quality of life (HRQL) even one year after their initial diagnosis. This indicates that the impacts of the virus extend well beyond the acute phase, affecting physical and emotional well-being. Researchers involved in the RECoVERED trial emphasize the importance of ongoing monitoring for these patients to address their unique health challenges and enhance patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the findings of this study reveal that individuals with multiple high-risk comorbidities exhibited even poorer quality of life scores, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions in this vulnerable population. The research team utilized the SF-36 health survey to assess various HRQL dimensions, suggesting that healthcare providers must integrate long-term assessment strategies into ongoing COVID-19 treatment plans. Understanding these quality of life dynamics is crucial for healthcare planning, as it can inform policies that aim to improve the overall well-being of COVID-19 survivors.
COVID-19 Treatment Efficacy: The Role of Oral Zinc
A remarkable study published in *Clinical Infectious Diseases* has garnered attention regarding the efficacy of oral zinc in treating COVID-19 patients. The randomized controlled trial revealed that individuals who received oral zinc supplements showed nearly a 40% reduction in mortality rates and ICU admissions when compared to those on placebo. This significant finding not only supports the efficacy of zinc as a supplementary treatment but also underscores its potential role in improving patient outcomes during the pandemic.
Additionally, the trial involved a diverse group of participants, both hospitalized and outpatient COVID-19 patients, aged around 54.2 years. The results suggest a need for a reassessment of treatment protocols, where oral zinc could be included as a standard adjunct therapy, especially for patients at higher risk of severe illness. As healthcare systems continue to grapple with COVID-19, integrating such treatments could markedly improve the overall health and recovery trajectories for affected individuals.
Long-Term COVID Symptoms and Their Impact
The long-term effects of COVID-19, often referred to as “long COVID,” continue to pose challenges for many survivors. Studies have indicated that a disproportionate number of individuals who experienced moderate to severe symptoms face ongoing health issues, such as fatigue, breathing difficulties, and cognitive impairments, long after their initial recovery. Understanding the nature of these long-term COVID symptoms is critical for developing effective rehabilitation programs and support systems for these patients.
Furthermore, early identification of patients at risk for long COVID may lead to timely interventions that could alleviate some of these ongoing health burdens. Healthcare providers are increasingly focusing on comprehensive follow-up care, recognizing that survivors may require additional resources and support to manage these protracted symptoms. The knowledge gleaned from current COVID-19 studies can inform better approaches to patient care and foster an improved understanding of the factors influencing long-term recovery.
COVID-19 Study Results: Insights and Implications
The growing body of research on COVID-19 brings invaluable insights into how the virus affects different populations and what can be done to mitigate its impact. Studies like the RECoVERED trial not only reveal long-term quality of life issues faced by COVID-19 survivors but also inform best practices for treatment and follow-up care. The implications of these findings extend to public health policy, emphasizing the necessity of comprehensive strategies to address the aftermath of the pandemic.
Furthermore, these studies play a pivotal role in shaping future research areas, highlighting the need for targeted investigations into specific demographics affected by the virus. By evaluating COVID-19 study results, health authorities can better allocate resources, develop targeted health interventions, and foster a community-oriented approach to health crises, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes across diverse populations.
COVID-19 Patient Outcomes: A Comparative Analysis
Examining COVID-19 patient outcomes provides crucial insights into the effectiveness of different treatment protocols and health support systems. Data suggests that patients who received comprehensive care, including early intervention and subsequent monitoring, often experience better recovery trajectories. The comparative analysis of treatment efficacy highlights the significance of personalized healthcare measures tailored to individual patient needs, which can greatly enhance health outcomes.
Moreover, understanding variations in patient outcomes informs healthcare providers about the importance of pre-existing conditions and their impact on disease severity. Tailored approaches to treatment that account for these variables are vital for optimizing patient care and achieving successful recovery rates among those affected by COVID-19. By continuously evaluating these outcomes, healthcare systems can improve protocols, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and compassionate care possible.
The Importance of Follow-up Care for COVID-19 Survivors
As new research sheds light on the lasting impacts of COVID-19, the importance of follow-up care cannot be overstated. Patients who have experienced moderate to severe symptoms are at a heightened risk for persistent health issues, making it imperative for healthcare systems to implement robust follow-up protocols. This includes regular check-ups, mental health screenings, and tailored rehabilitation programs to ensure that survivors receive comprehensive support as they navigate their recovery journey.
Proactive follow-up care can significantly improve health-related quality of life for COVID-19 survivors by addressing both physical and emotional ramifications of the illness. Health practitioners must be vigilant in monitoring these individuals, as early intervention can lead to better management of long-term COVID symptoms and ultimately enhance their quality of life. Such strategies are essential in supporting the reintegration of survivors into their communities and daily activities.
COVID-19 Epidemiology: Trends Over Time
The ongoing analysis of COVID-19 epidemiology reveals changing trends in infection rates, disease severity, and patient demographics over time. The emergence of new strains and shifts in public health responses significantly influence these trends. Continuing to monitor and understand these epidemiological patterns is crucial for integrating lessons learned into future pandemic preparedness and response.
Moreover, the implications of these trends extend beyond immediate health outcomes; they affect socioeconomic factors and healthcare resource allocation. By examining the epidemiological data, healthcare policymakers can anticipate and prepare for future outbreaks, ensuring that communities are equipped to handle potential healthcare crises effectively.
Resilience in the Face of COVID-19 Health Impacts
Resilience among individuals and communities plays a fundamental role in managing the health impacts of COVID-19. Many people have demonstrated remarkable adaptability during this crisis, finding ways to cope with the psychological and physical effects of the virus. This resilience not only aids in individual recovery but also fosters community solidarity, which is essential in times of widespread public health challenges.
Encouraging resilience through community support networks and mental health resources can help buffer the adverse effects of long-term COVID symptoms. Healthcare providers and community leaders must work together to cultivate environments that promote coping strategies, mindfulness, and social connection, ultimately enhancing the overall health and well-being of those impacted by the pandemic.
Addressing COVID-19 Related Mental Health Challenges
The mental health challenges associated with COVID-19 are becoming progressively more recognized as integral components of post-pandemic recovery. Many individuals, particularly those who experienced severe illness, report increased levels of anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms. Addressing these concerns through integrated health services is necessary for holistic care for COVID-19 survivors.
Mental health support services need to be accessible and tailored to the unique experiences of those impacted by COVID-19. This includes creating safe spaces for dialogue, providing therapy options, and implementing outreach programs that promote mental wellness. By prioritizing mental health alongside physical recovery, healthcare providers can play a pivotal role in enhancing quality of life for individuals navigating the aftermath of COVID-19.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does COVID-19 affect quality of life after recovery?
Research has shown that individuals who experienced moderate to severe COVID-19 may face long-lasting impairments in their quality of life (QoL) even a year after recovery. A study found that these individuals reported lower health-related quality of life (HRQL) scores across multiple dimensions, including physical and emotional functioning, compared to the general population.
What are the long-term COVID symptoms that affect patient outcomes?
Long-term COVID symptoms can significantly affect patient outcomes, with studies indicating that individuals may experience issues such as fatigue, cognitive impairment, and reduced physical capabilities long after the initial infection. These ongoing health problems can lead to a diminished quality of life and increased healthcare needs.
What do recent COVID-19 study results indicate about treatment efficacy?
Recent studies highlight the efficacy of treatments for COVID-19, such as oral zinc, which has demonstrated a reduction in the risk of death and ICU admissions by nearly 40% in COVID-19 patients. Such findings underscore the importance of effective treatment strategies to improve health outcomes for affected individuals.
How does experiencing moderate to severe COVID-19 impact long-term health?
Individuals who experienced moderate to severe COVID-19 often encounter persistent health challenges, with studies showing significant reductions in health-related quality of life (HRQL) even 12 months post-infection. The impacts can include chronic physical and emotional health issues that necessitate ongoing medical attention.
What can be done to improve quality of life after COVID-19?
Improving quality of life after COVID-19 involves a multifaceted approach, including access to rehabilitation, mental health support, and ongoing medical care to address lingering symptoms. Personalized recovery plans that focus on physical activity, nutrition, and mental well-being can significantly enhance health-related quality of life for survivors.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| COVID-19 Health Impacts | A study found individuals with moderate to severe COVID-19 experience long-term impaired quality of life, particularly in physical and emotional health dimensions. |
| Zinc Treatment | Oral zinc significantly reduced death and ICU admissions among COVID-19 patients by nearly 40%, indicating a potential therapeutic benefit. |
| Ebola Update | An additional Ebola case and five new deaths reported in Uganda during an outbreak of the Sudan strain. |
| H5N1 Avian Flu | Spain detected H5N1 avian influenza in two poultry workers linked to infected birds. |
| H3N2 Flu Case | A variant H3N2 case was reported in New Mexico in a child recovering from exposure to pigs. |
| Polio Cases Increase | New polio cases were reported in Mozambique, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Madagascar, and Nigeria. |
| Procalcitonin Study | Research indicates procalcitonin levels may influence antibiotic treatment decisions in COVID-19 patients. |
| Antibiotic Use Survey in Egypt | A survey indicated high knowledge of antibiotics among Egyptian doctors, but inconsistencies in prescriptions were noted. |
Summary
COVID-19 health impacts remain significant, as evidenced by a recent study indicating that individuals who suffered from moderate to severe cases continue to experience impaired health-related quality of life twelve months after recovery. These findings highlight the lasting consequences of COVID-19 on physical and emotional well-being, necessitating further research and tailored interventions for affected populations. Additionally, novel treatments like oral zinc show promise in improving outcomes for COVID-19 patients, underscoring the need for ongoing studies in this field.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.