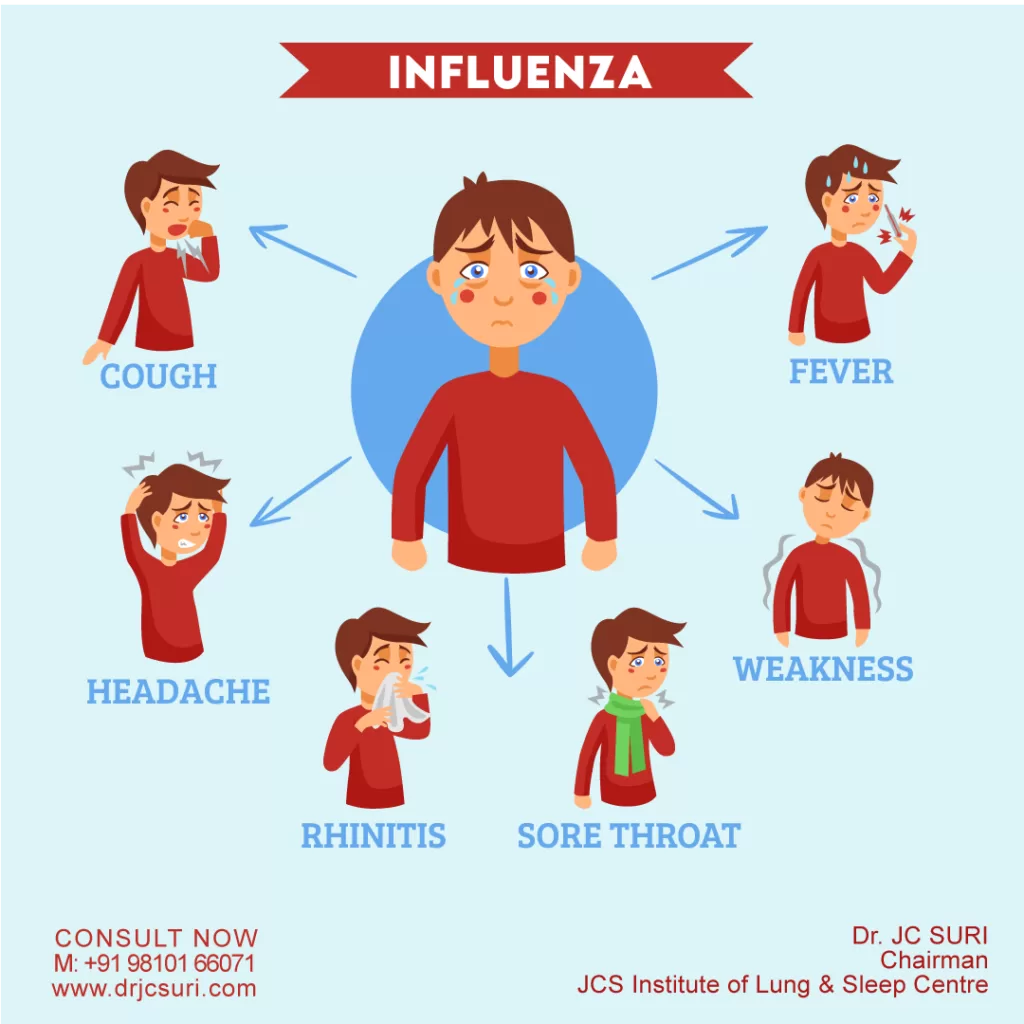
Influenza symptoms can be particularly uncomfortable, often catching individuals off guard with their sudden onset. Characterized by fever, cough, and muscle aches, flu symptoms can mimic those of other respiratory illnesses, leading to confusion about what is influenza. While many recover without severe complications, it’s crucial to understand the potential for serious health issues if not properly managed. In this guide, we will explore the flu symptoms in detail, alongside important information on influenza prevention, treatment strategies, and possible complications. By arming yourself with knowledge about flu symptoms, you can better prepare to tackle this contagious illness during peak season.
When discussing the flu, or influenza, it’s essential to recognize its impact on the respiratory system and the common indicators that signal infection. Often referred to in everyday conversations as the ‘battle against the seasonal flu’, understanding the distinctive features of flu symptoms can greatly aid in timely recognition and treatment. This contagious virus can lead not only to discomfort but also to severe health challenges if left unchecked. Recognizing signs like a sudden fever, cough, and persistent fatigue can help individuals act swiftly to mitigate their risk and understand how to treat influenza effectively. As we delve deeper, we’ll also touch on related terms such as respiratory infections and viral illnesses that share overlapping characteristics with the flu.
Understanding Influenza: What You Need to Know
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease that primarily targets the respiratory system, leading to a range of symptoms such as cough, fever, and muscle aches. Despite being commonly referred to as the flu, it’s essential to differentiate influenza from other viral infections like the stomach flu, which primarily cause gastrointestinal upset. Influenza viruses vary each season, making it crucial for individuals to stay informed about the characteristics of the virus and the potential impacts on their health.
Recognizing the flu’s seriousness is vital, especially since it can lead to severe health complications for high-risk populations, including young children, the elderly, and individuals with preexisting health conditions. Understanding what influenza is, alongside awareness of transmission methods and symptoms, can empower individuals to take preventive measures and seek timely medical attention when necessary.
Common Influenza Symptoms: How to Identify the Flu
Flu symptoms typically manifest suddenly and can often be mistaken for other respiratory illnesses like the common cold. Key influenza symptoms include fever, cough, body aches, and fatigue, appearing within a day or two of exposure to the virus. Unlike cold symptoms, which can develop gradually, influenza symptoms come on rapidly, often overwhelming individuals and interrupting daily activities.
In children, flu symptoms can also present additional challenges, including increased irritability, ear pain, and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea or diarrhea. Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for effective intervention and can aid in preventing severe complications that may arise from the flu.
Influenza Prevention: Essential Measures to Stay Safe
Preventing influenza is crucial, especially during peak flu season when the virus spreads easily. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends an annual flu shot for everyone over six months of age as the most effective preventive measure. Although the vaccine may not guarantee immunity, it significantly reduces the risk of contracting the virus and the severity of symptoms if infected.
In addition to vaccination, maintaining good hygiene practices is essential to limit the spread of influenza. This includes frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and keeping commonly touched surfaces clean and disinfected. By enforcing these preventive measures, individuals can contribute to community health and reduce the overall incidence of flu.
How to Treat Influenza: Effective Approaches
Treatment for influenza mostly involves self-care strategies that help ease symptoms. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can alleviate discomfort caused by fever, muscle aches, and nasal congestion. Antiviral medications prescribed by healthcare providers may also be effective in shortening the duration of the illness, particularly when taken within the first 48 hours of symptom onset.
In some cases, especially for high-risk patients, hospitalization and intensive care may be required to manage severe symptoms or complications. It is crucial for individuals experiencing flu symptoms to monitor their health and consult healthcare professionals if symptoms worsen or if there are signs of complications such as difficulty breathing or chest pain.
Recognizing Influenza Complications: When to Seek Help
While influenza may seem mild for many, it can potentially lead to severe complications that require immediate medical intervention. Common influenza complications include pneumonia, bronchitis, and exacerbation of preexisting chronic health conditions, such as asthma or heart disease. Understanding who is at greater risk and the signs that indicate complications can save lives and improve recovery outcomes.
Symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, confusion, or severe weakness should prompt immediate medical attention. Especially in children, indicators like rapid breathing and dehydration are critical signs that necessitate urgent care. Being vigilant about these indicators can help mitigate severe health risks associated with influenza complications.
Understanding the Causes of Influenza
Influenza is primarily caused by influenza viruses that spread from person to person through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The contagious nature of these viruses can make outbreaks prevalent during specific seasons, often referred to as flu season. Understanding the transmission methods can help individuals take effective measures to protect themselves and others.
In addition to direct transmission, the virus can also thrive on various surfaces, leading to potential indirect spread. Thus, it’s essential to maintain good hygiene practices, including regular handwashing and disinfecting surfaces, to reduce the risk of infection and contribute to broader public health efforts.
Assessing Risk Factors for Influenza Infection
Certain populations face an increased risk of influenza infection and complications, including young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic health issues. Factors such as crowded living environments or compromised immune systems further elevate this risk. Understanding these risk factors is critical, as it helps individuals prioritize their health and take precautions during flu seasons.
Being aware of personal risk factors can empower individuals to engage in preventive practices, such as getting vaccinated early and maintaining strong hygiene protocols. The more informed a community is about these risks, the better prepared it is to mitigate the flu’s impact on public health.
Controlling the Spread of Influenza
Controlling the spread of influenza involves a combination of vaccination and diligent hygiene practices. It’s crucial for individuals to wash their hands regularly, ensure they cough or sneeze into the elbow or a tissue, and maintain cleanliness in shared spaces. Implementing these measures can significantly limit the virus’s transmission, especially in environments where close contact is common, such as schools and workplaces.
Another effective strategy is to avoid large crowds during peak flu season, as this reduces the likelihood of exposure to the virus. Encouraging community awareness and participation in preventive activities can help protect vulnerable populations and decrease overall flu rates in the community.
Flu Season: Being Prepared and Informed
As flu season approaches, it’s vital for individuals to be prepared and well-informed about the impending risks associated with influenza. Understanding the symptoms, facilitation of vaccinations, and readiness to implement preventive measures can not only protect oneself but also contribute to the wellbeing of the community. Preparation begins with knowledge, making it easier to identify and respond to the flu early.
Additionally, keeping abreast of public health advisories and flu activity reports can provide valuable insights into the season’s severity and help individuals make informed decisions about their health and safety. With preparedness, individuals can navigate flu season with confidence, reducing their risk of infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common influenza symptoms to watch out for?
Common influenza symptoms include fever, cough, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and chills. These symptoms typically appear suddenly within 1 to 3 days after exposure to the influenza virus.
How does influenza differ from other respiratory illnesses regarding symptoms?
Influenza symptoms can resemble those of the common cold but usually appear more abruptly and are often more severe. Key flu symptoms include high fever and significant fatigue, which are less common in other respiratory infections.
What complications can arise from untreated influenza symptoms?
While most influenza cases resolve without complications, untreated flu symptoms can lead to serious complications like lung infections, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or even heart infections, especially in high-risk individuals.
How can I prevent influenza symptoms from occurring?
To prevent influenza symptoms, it is crucial to get an annual flu vaccination, practice good hygiene by washing your hands frequently, and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
When should someone with influenza symptoms see a doctor?
Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience severe influenza symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe dizziness, or confusion. Prompt care is particularly important for those at high risk for complications.
What should I do if my child exhibits influenza symptoms?
If a child shows influenza symptoms such as high fever, persistent cough, or signs of dehydration, contact a healthcare provider. Children may also exhibit irritability or ear pain, which may require medical evaluation.
How is influenza transmitted and how do symptoms develop?
Influenza is transmitted through droplets from coughs or sneezes of infected individuals. Symptoms develop quickly, typically within 1-3 days after exposure to the influenza virus.
What are the signs of severe influenza complications?
Signs of severe complications from influenza can include difficulty breathing, chest pain, confusion, severe weakness, and in children, rapid breathing or dehydration. Medical assistance should be sought immediately if these symptoms occur.
Can influenza symptoms lead to hospitalization?
Yes, severe influenza symptoms can lead to hospitalization, particularly in high-risk groups such as young children, elderly individuals, and those with chronic health issues.
How can I treat influenza symptoms at home?
Influenza symptoms can often be treated at home with rest, hydration, over-the-counter medications for fever and aches, and warm fluids for sore throats. However, seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or if complications arise.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview | Influenza is a viral infection affecting the respiratory system, distinct from stomach flu. It can lead to severe complications. |
| Symptoms | Common influenza symptoms include fever, cough, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, sore throat, and nasal congestion. Symptoms appear suddenly. |
| When to See a Doctor | Seek medical attention if experiencing severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or confusion, particularly if at risk for complications. |
| Causes | Influenza viruses spread through respiratory droplets from coughs or sneezes and remain contagious for about 5-7 days. |
| Risk Factors | Young children, elderly adults, compromised immune systems, chronic conditions, and pregnancy increase flu risk. |
| Complications | High-risk groups may suffer from lung infections, heart infections, or muscle damage, while healthy individuals typically recover. |
| Prevention | Annual flu vaccination is recommended for those over 6 months old to lower risks of illness and complications. |
| Controlling Spread | Practice good hygiene, wash hands regularly, cover mouths when coughing or sneezing, and avoid crowds. |
Summary
Influenza symptoms can arise suddenly and may include fever, cough, and body aches. Recognizing these symptoms promptly is crucial for seeking the necessary medical attention and preventing severe complications. The flu is highly contagious, and adequate preventive measures, including vaccination and good hygiene practices, can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.