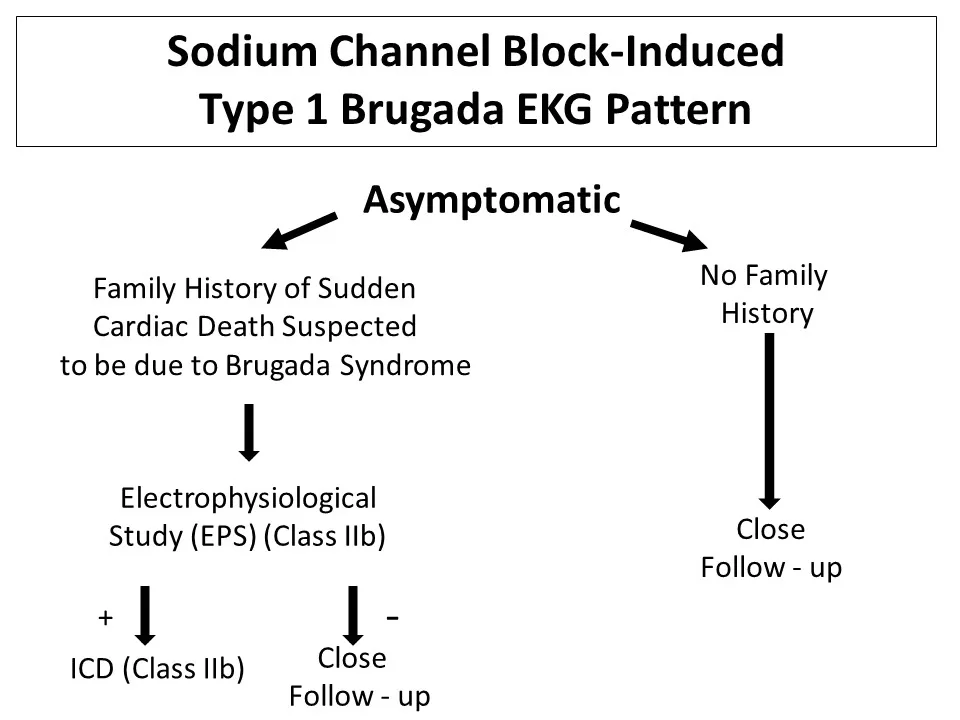
Brugada syndrome treatment options are crucial for managing this inherited cardiac disorder, characterized by abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) findings and an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Affected individuals, particularly males of Southeast Asian descent, need effective strategies to mitigate alarming arrhythmias and improve cardiac health. Among the most prominent treatment modalities are the Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) therapy, aimed at detecting and treating life-threatening arrhythmias, and epicardial ablation, which targets the underlying electrical disruptions in the heart. Additionally, pharmacological therapies can enhance arrhythmia treatment, while lifestyle modifications play a vital supportive role. Understanding these diverse treatment options is essential for empowering patients and optimizing their cardiac well-being.
Brugada syndrome is also recognized as a genetic cardiac arrhythmia that significantly raises the risk of life-threatening heart conditions. Management techniques for this syndrome focus on a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle changes to prevent severe consequences. One notable approach is the use of an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD), designed to restore normal heart function during dangerous arrhythmias. Furthermore, techniques like epicardial catheter ablation are gaining attention as promising options to rectify abnormal heart pathways. It is critical for patients and healthcare providers to work collaboratively, ensuring effective strategies are in place to safeguard cardiovascular health.
Understanding Brugada Syndrome: Symptoms and Diagnosis
Brugada syndrome is an inherited cardiac condition that primarily affects the electrical activity of the heart. Recognized through distinct electrocardiogram (ECG) patterns, it presents a significant risk of life-threatening arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Symptoms often remain elusive, with many patients experiencing no signs until a serious event occurs, such as syncope or cardiac arrest. Therefore, identifying the syndrome early through rigorous screening, particularly in at-risk populations, is crucial for effective management.
The challenge lies in the variable clinical presentation of Brugada syndrome. In some instances, affected individuals may experience palpitations or dizziness, while others remain asymptomatic. Genetic tests and electrophysiological studies can confirm the diagnosis, allowing for appropriate intervention before clinical symptoms escalate. Awareness and education about these symptoms are vital for both doctors and patients, promoting timely diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main treatment options for Brugada syndrome?
The primary treatment options for Brugada syndrome include Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) therapy, pharmacological management using antiarrhythmic medications, and epicardial catheter ablation. Each option targets the specific needs of the patient depending on their risk level and clinical presentation.
How does ICD therapy work in the management of Brugada syndrome?
ICD therapy is a crucial intervention for managing Brugada syndrome, especially in high-risk patients. The Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator monitors heart rhythms and delivers electric shocks to correct dangerous arrhythmias, significantly enhancing survival rates for those with a history of cardiac events.
What role does epicardial catheter ablation play in Brugada syndrome treatment?
Epicardial catheter ablation is used for patients with recurrent arrhythmias who may not respond well to ICD therapy. This procedure targets and destroys abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that contribute to arrhythmias, offering a potential solution for improved cardiac health.
Are there any pharmacological therapies available for Brugada syndrome?
Yes, pharmacological therapies, including antiarrhythmic drugs like ajmaline and procainamide, can be considered for managing Brugada syndrome. These medications help in diagnosing the variant forms of the syndrome and may serve as adjunct therapies alongside ICD treatment for certain patients.
What lifestyle modifications are recommended for patients with Brugada syndrome?
Patients with Brugada syndrome are advised to implement lifestyle modifications such as avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, steering clear of specific medications that may exacerbate arrhythmias, and refraining from intense physical activities without medical supervision to ensure optimal cardiac health.
| Treatment Option | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) | A device that detects and corrects life-threatening arrhythmias by delivering shocks to the heart. | Recommended for high-risk patients with a history of cardiac arrest or recurrent arrhythmias; requires regular follow-ups to monitor its function. |
| Pharmacological Therapy | Medications like ajmaline and procainamide may help manage Brugada syndrome in lower risk patients. | Research is ongoing into newer antiarrhythmic drugs tailored to individual patient profiles. |
| Epicardial Catheter Ablation | A procedure that targets and destroys problematic electrical pathways in the heart. | Considered for patients experiencing recurrent arrhythmias despite ICD; efficacy being investigated. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Changes to avoid triggers such as excessive alcohol consumption and certain medications. | Essential for symptom management; regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring heart health. |
Summary
Brugada syndrome treatment options are critical for managing this inherited cardiac condition effectively. The primary approach involves the use of an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD), which can prevent sudden cardiac death by monitoring and correcting dangerous arrhythmias. In addition, pharmacological therapies and epicardial catheter ablation offer potential alternatives for patients at lower risk or those not adequately managed by an ICD alone. Importantly, lifestyle modifications play a key role in reducing the risk of arrhythmias, and regular monitoring with healthcare providers ensures tailored treatment strategies. By understanding and leveraging these diverse treatment options, patients can significantly improve their health outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.