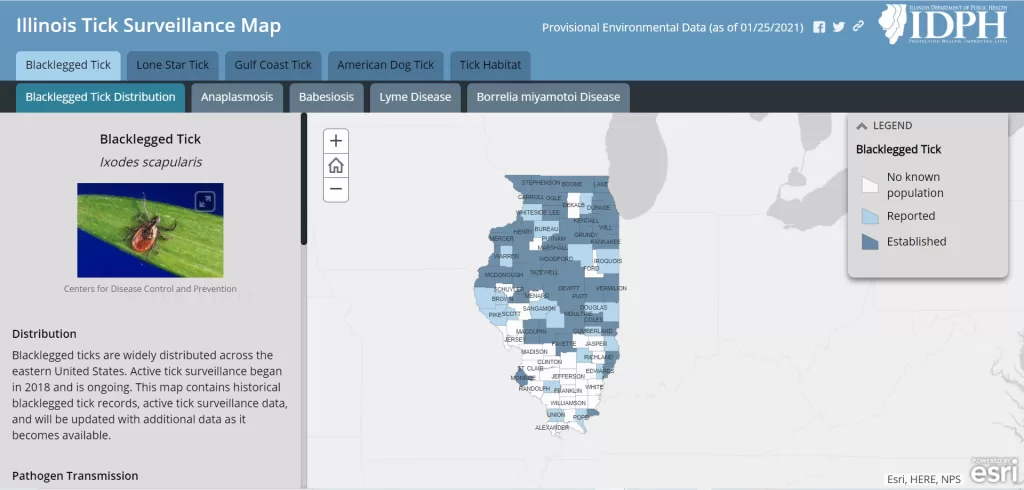
Tick Surveillance plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health by monitoring the presence of ticks that transmit dangerous diseases. The rise of tick-borne diseases, including Lyme disease, has alarmed health officials and researchers alike, as the number of reported cases has doubled in the past two decades. Through initiatives like the National Tick Surveillance Program, experts track the distribution and population dynamics of ticks, ensuring timely communication about their risks. As the CDC enhances tick monitoring, they equip communities with crucial information for Lyme disease prevention and other related health threats. Understanding these risks is essential for public safety, fostering greater awareness about the impact of ticks on community health and lifestyle.
Ticks are small arachnids that can pose significant health threats through the diseases they transmit, commonly referred to as vector-borne illnesses. The collective efforts, seen in programs such as the National Tick Surveillance Program, involve assessing tick populations and the pathogens they carry, which is crucial for effective Lyme disease prevention strategies. These initiatives, alongside comprehensive CDC tick monitoring, strive to inform the public about the potential dangers when enjoying the outdoors. As awareness about public health and ticks increases, communities can adopt proactive measures to manage the risks associated with tick encounters. By mapping out affected areas and educating people, health officials aim to reduce the prevalence of tick-borne diseases.
The Importance of Tick Surveillance in Public Health
Tick surveillance plays a vital role in safeguarding public health, particularly as the incidence of tick-borne diseases continues to rise. With advancements in the CDC’s National Tick Surveillance Program (NTSP), health officials can now track the spread of ticks and their associated pathogens more effectively. This surveillance is not merely about counting ticks; it encompasses understanding their distribution and the diseases they may harbor, such as Lyme disease, which affects hundreds of thousands of Americans each year.
Effective tick surveillance equips health departments with essential data to implement timely preventive measures, enabling communities to engage meaningfully in Lyme disease prevention. By identifying high-risk areas, public health officials can disseminate targeted information about risks and protective strategies, significantly enhancing public awareness. This effort helps foster a community’s resilience against tick-borne illnesses and underlines the importance of continuous monitoring as essential to public health.
Understanding Tick-Borne Diseases and Their Risks
Tick-borne diseases, such as Lyme disease and Anaplasmosis, have become critical public health concerns across the United States. The sharp increase in reported cases over the past two decades demands a focused response from health officials and the public alike. Knowledge of disease transmission dynamics and geographical hotspots is vital, and here, surveillance mechanisms like the NTSP serve as powerful tools to identify and address these threats. As states gather more data through the program, the correlation between tick populations and disease outbreaks becomes clearer, leading to informed public health interventions.
Education plays a central role in controlling the spread of tick-borne diseases. When communities understand where ticks are most prevalent and the diseases they can transmit, they can take appropriate precautions. Simple actions like staying on marked trails and using insect repellents can significantly reduce exposure to ticks. Public health initiatives must prioritize knowledge-sharing about these risks, leveraging geographic data and local surveillance insights to empower individuals to protect themselves effectively.
How the NTSP Supports State Health Departments
State health departments are crucial in managing the threats posed by tick-borne diseases. However, many face considerable challenges due to limited resources for comprehensive tick surveillance. The NTSP addresses these challenges by providing essential support, allowing state health departments to enhance their monitoring efforts significantly. This collaboration has enabled stakeholders to consistently collect and analyze data across multiple regions, leading to an improved understanding of tick distribution and the pathogens they may carry.
Since more than 36 states have partnered with the NTSP, the program has generated robust datasets essential for crafting strategic public health policies. The county-level maps produced from this data are instrumental for local health officials, allowing them to identify areas with elevated tick risks and formulate specific intervention plans. By breaking down silos and promoting a collaborative approach, the NTSP empowers state health departments to protect populations more effectively from the dangers of tick-borne diseases.
Data Collection Methods in Tick Surveillance
The effectiveness of the National Tick Surveillance Program hinges on how data is collected and utilized. Active surveillance, involving direct collections of ticks from the environment, provides invaluable insights into tick populations and the pathogens they may harbor. While this method yields precise data, it requires significant resources that many health departments lack. On the other hand, passive surveillance, which relies on public submissions of tick specimens, presents a cost-effective alternative but comes with its limitations in accuracy, particularly regarding location details.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both active and passive surveillance methods is essential for public health officials to develop comprehensive strategies for monitoring tick-borne diseases. Integration of data from both approaches can provide a clearer picture of tick populations, guiding effective prevention efforts. Continuous evaluation and adaptation of surveillance methodologies are crucial to ensure that public health responses remain relevant and effective in combating the evolving threats posed by tick-borne diseases.
Public Awareness and Education on Tick Safety
Increasing public awareness about tick safety is fundamental for effective Lyme disease prevention and minimizing the risk of tick-borne illnesses. Education campaigns play a pivotal role in informing the public about the potential dangers of ticks and encouraging the adoption of preventive measures. Through initiatives supported by the NTSP, residents can learn how to identify tick-infested areas and the importance of wearing protective clothing and using registered repellents.
Moreover, educating the public extends beyond mere awareness; it involves empowering individuals to actively engage in prevention efforts. Information on checking for ticks after outdoor activities and recognizing early symptoms of tick-borne diseases can significantly impact community health outcomes. By fostering an informed populace, public health organizations can effectively reduce the prevalence of tick-borne diseases, highlighting the critical role of education in enhancing community resilience against such public health threats.
The Future of Tick Surveillance Initiatives
As the landscape of tick-borne diseases continues to evolve, future initiatives like the NTSP must adapt to the changing epidemiological patterns. Expanding the focus beyond just Lyme disease to include other tick species and transmitted pathogens will be vital for comprehensive public health strategies. For example, understanding diseases carried by Amblyomma and Dermacentor ticks can inform better prevention and preparedness efforts.
Moreover, incorporating technological advancements, such as geographical information systems (GIS) and machine learning models, can enhance the precision of tick surveillance. As researchers integrate epidemiological data with surveillance findings, public health officials will gain deeper insights into the dynamics of tick-borne diseases, enabling them to allocate resources better and devise targeted outreach strategies. A proactive and data-driven approach will be essential for keeping communities safe as we move into this new era of tick management.
Community Engagement in Tick Prevention Efforts
Engaging communities in tick prevention not only fosters local stewardship but also enhances the effectiveness of public health initiatives. Collaboration between health departments and community stakeholders can lead to tailored educational programs that resonate with local populations. For example, organizing community events where residents can learn about ticks, their habitats, and prevention strategies can empower individuals and communities alike.
Another effective practice is leveraging local volunteers to participate in tick surveys and monitoring activities. By involving community members in tick surveillance efforts, public health officials can gather critical data while simultaneously raising awareness about tick-borne diseases. Such initiatives strengthen community ties and provide residents with a sense of ownership over their health safety, ultimately leading to more effective responses to tick threats.
The Role of Technology in Tick Monitoring
Technology is transforming the field of tick surveillance, facilitating more efficient data collection and analysis. Smartphone apps and digital platforms enable the public to report tick encounters, streamlining passive surveillance efforts and increasing the volume of data available to health authorities. This technological integration allows for real-time tracking of tick populations and the diseases they transmit, enhancing the capacity of health departments to respond to potential outbreaks.
Additionally, automated mapping tools can analyze and visualize tick distribution patterns, providing critical insights for public health interventions. As technology becomes more integrated into tick monitoring efforts, health departments can make data-driven decisions that prioritize resources effectively and target interventions where they are needed most. Embracing these innovations will be essential for advancing tick surveillance and ensuring public safety in the face of rising tick-borne disease threats.
Impact of Climate Change on Tick Distribution
Climate change significantly impacts tick distribution and the risk of tick-borne diseases, altering the ecological factors that influence tick populations. Warmer temperatures, increased precipitation, and changing landscapes can create favorable conditions for tick survival and expand their habitats. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for public health officials as they adapt surveillance strategies to monitor shifting tick populations and disease risks effectively.
The NTSP must consider climate-related changes to inform prevention strategies and educate the public about emerging risks associated with ticks. As certain geographical areas become more susceptible to tick infestations, targeted messaging and increased community engagement will be pivotal in addressing the public health implications of climate change on tick-borne diseases. By proactively adjusting strategies, health departments can ensure effective responses to this evolving challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the National Tick Surveillance Program and how does it help with tick surveillance?
The National Tick Surveillance Program (NTSP) is a federal initiative launched by the CDC in 2018 to systematically map tick populations across the U.S. It aids in tick surveillance by providing funding and resources to state health departments, enabling them to gather crucial data about tick species, their distribution, and the pathogens they carry. By improving tick monitoring efforts, the NTSP helps public health officials identify risks for vector-borne diseases like Lyme disease.
How does tick surveillance impact public health regarding Lyme disease?
Tick surveillance is critical for public health as it helps in identifying areas at high risk for Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses. By monitoring tick populations and their pathogens, health officials can issue warnings, promote prevention strategies, and guide healthcare providers on testing protocols for Lyme disease. Increased understanding of where ticks are prevalent allows for targeted public health interventions.
Why is it important to monitor ticks for tick-borne diseases?
Monitoring ticks for tick-borne diseases is essential to protect public health. With the rising incidence of diseases like Lyme disease, surveillance helps identify areas where these risk factors are highest. Understanding which ticks carry specific pathogens enables health departments to communicate risks effectively and promote preventive measures, reducing the likelihood of tick-borne disease transmission.
What methods are used in tick surveillance to collect data on ticks and diseases?
The National Tick Surveillance Program employs both active and passive surveillance methods. Active surveillance involves direct collection of ticks from environments and animals, providing precise data on tick populations and the pathogens they carry. In contrast, passive surveillance relies on submitted ticks from the public and healthcare providers, which helps identify tick species but may lack precision in diagnosing prevalence and disease presence.
How can the public participate in tick surveillance efforts?
The public can participate in tick surveillance by submitting ticks they find on themselves or pets to health departments or researchers. This passive surveillance method contributes valuable data on tick species and potential pathogens. Additionally, individuals can engage in preventive actions, such as using insect repellent and checking for ticks after outdoor activities, helping to mitigate the risk of tick-borne diseases.
What does the data from the National Tick Surveillance Program tell us about tick populations?
Data from the National Tick Surveillance Program reveal crucial information about the distribution and prevalence of tick populations across different regions. This mapping effort not only identifies hotspots for ticks, particularly Ixodes scapularis, the primary vector for Lyme disease, but also allows public health officials to assess the potential risks for tick-borne diseases in various communities, enhancing prevention strategies.
How do health departments utilize tick surveillance data to inform communities?
Health departments utilize data from tick surveillance to educate communities about the risks of tick-borne diseases. By sharing findings on tick populations and the potential risk of Lyme disease, officials can promote preventive measures, such as protective clothing and repellents. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices when engaging in outdoor activities and helps reduce the incidence of tick-borne diseases.
What challenges do health departments face in tick surveillance?
Health departments face several challenges in tick surveillance, including limited funding and resources for extensive tick surveys and data collection. The reliance on passive surveillance methods can lead to gaps in data accuracy and may not capture the full extent of tick presence and their pathogens. Addressing these challenges is crucial for improving our understanding of tick-borne disease risks.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview of Tick Surveillance | The National Tick Surveillance Program (NTSP), initiated by the CDC in 2018, aims to improve tick monitoring across the U.S. |
| Growth of the Program | Since 2018, 36 states have joined the program, increasing data reporting on ticks and their associated diseases. |
| Importance of Tick Monitoring | Tick-borne diseases, like Lyme disease, have doubled over the past two decades, necessitating improved surveillance efforts. |
| Methods of Data Collection | The NTSP employs both active surveillance (direct collection of ticks) and passive surveillance (public submissions) to gather comprehensive data. |
| Impact on Public Health | The NTSP helps identify risk areas, guides preventive measures, and enhances public education regarding tick-borne diseases. |
| Future Directions | Expanding the program to include other pathogenic ticks to further protect public health is in consideration. |
Summary
Tick surveillance plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health by effectively mapping the distribution of ticks and the diseases they carry. Through initiatives like the National Tick Surveillance Program (NTSP), public health officials are empowered to understand the risks associated with tick-borne illnesses and take informed preventive measures. With the NTSP, targeted actions are taken to minimize the impact of tick-borne diseases, ensuring that communities remain safe while enjoying outdoor activities.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.