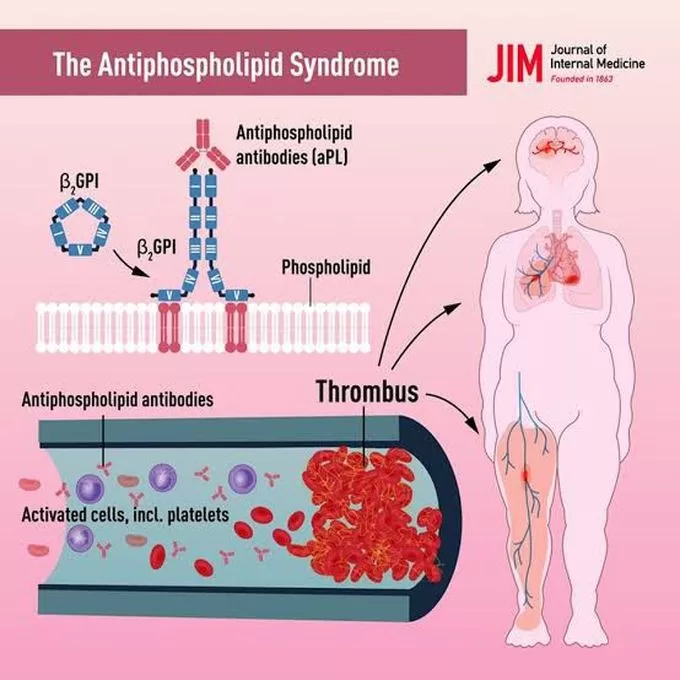
Understanding Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers, as this complex autoimmune disorder can lead to serious health complications, particularly concerning blood clot formation. Characterized by the presence of specific antibodies, APS significantly increases the risk of thrombotic events, which can severely impact individuals during pregnancy and beyond. Recent advancements in APS diagnosis and testing have paved the way for improved treatment options, aiming to enhance patient outcomes and prevent complications. As ongoing autoimmune disorder research sheds light on APS, it is essential to grasp the implications of this syndrome, especially in relation to pregnancy and the need for effective management strategies. This article aims to provide insights into the latest developments in Antiphospholipid Syndrome treatment and the importance of understanding this condition.
Antiphospholipid syndrome, often referred to as APS, is an autoimmune condition that poses significant health risks due to its association with increased thrombosis and pregnancy complications. This syndrome manifests through the presence of certain antibodies in the bloodstream, which can lead to a variety of adverse events, including miscarriages and severe clotting issues. The intersection of pregnancy and APS is particularly critical, as it necessitates tailored treatment approaches to mitigate risks effectively. In the realm of autoimmune disorder research, understanding the nuances of APS is essential for developing effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. By exploring the latest insights into APS diagnosis and treatment, we can better support individuals affected by this condition.
Understanding Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Key Symptoms and Risk Factors
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder that significantly increases the risk of abnormal blood clotting and various pregnancy complications. Common symptoms include recurrent thrombosis, which can manifest as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or stroke. Additionally, women with APS may experience repeated miscarriages or other adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as stillbirths. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention, which can help mitigate the severe consequences of this syndrome.
Risk factors for developing APS often include a history of autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, and family history of clotting disorders. Lifestyle factors, including obesity and smoking, may also exacerbate the risk. As research continues to evolve, understanding the interplay between these risk factors and APS could lead to improved prevention strategies and more effective treatment protocols.
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Treatment: Current Approaches and Innovations
The treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome primarily revolves around anticoagulation therapy aimed at preventing thrombotic events. Standard treatment regimens often include the use of anticoagulants such as warfarin or low-molecular-weight heparin. However, recent studies are exploring innovative therapies that could enhance treatment efficacy, particularly in patients with recurrent clotting despite standard therapy. Research is focusing on the potential role of novel medications that target specific pathways involved in clot formation.
Additionally, multidisciplinary care is advocated for managing APS effectively. This approach not only includes medical treatment but also psychological support and lifestyle modifications. Patients are encouraged to engage in healthy living practices, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, which can enhance overall outcomes. As ongoing research continues to identify new therapeutic targets, the future of APS treatment looks promising, with the potential for personalized treatment plans that cater to individual patient needs.
Pregnancy and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Navigating Risks and Treatments
Pregnancy poses unique challenges for women with antiphospholipid syndrome, as they face heightened risks of thrombotic events and pregnancy loss. Understanding the implications of APS during pregnancy is critical for ensuring the health of both mother and child. Current treatment protocols often involve the use of low-dose aspirin and heparin to reduce the risk of complications. Recent studies suggest that these treatments can significantly improve pregnancy outcomes for women affected by APS, but ongoing research is necessary to refine these strategies further.
Moreover, patient education plays a vital role in managing APS during pregnancy. Women must be informed about the signs of potential complications and the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment regimens. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to navigate the complexities of APS in pregnant women, ensuring that timely interventions can be made when necessary. Understanding these dynamics can empower women with APS to achieve healthier pregnancies.
APS Diagnosis and Testing: Enhancing Accuracy and Early Detection
Diagnosing antiphospholipid syndrome can be a complex process that requires comprehensive evaluation and testing. Key diagnostic criteria include the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies in conjunction with clinical history, such as previous thrombotic events or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Advances in laboratory testing techniques have improved the accuracy and speed of APS diagnosis, allowing for earlier intervention and management to prevent severe complications.
Additionally, healthcare providers are increasingly utilizing a combination of clinical assessment and advanced testing protocols to identify APS more effectively. This includes standardized criteria for diagnosis, which helps streamline the process and ensure that patients receive timely care. As our understanding of APS deepens, the refinement of diagnostic methods will be crucial in reducing the burden of this disorder and improving patient outcomes.
The Future of Autoimmune Disorder Research: Implications for Antiphospholipid Syndrome
The field of autoimmune disorder research is rapidly evolving, with promising implications for conditions like antiphospholipid syndrome. Ongoing studies are aimed at unraveling the complex mechanisms underlying APS, which could lead to groundbreaking therapies that target the root causes of the disease rather than just its symptoms. By understanding the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to APS, researchers hope to develop more effective and personalized treatment options.
Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and patients is essential for advancing the knowledge and management of APS. This collaborative approach can foster the development of innovative clinical trials and studies that explore novel therapeutic strategies. As the understanding of autoimmune disorders grows, the potential for improved patient outcomes and quality of life for those affected by antiphospholipid syndrome becomes increasingly attainable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Antiphospholipid Syndrome and its relation to thrombotic events?
Understanding antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is essential as it is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, leading to an increased risk of thrombotic events. These events include recurrent venous or arterial clots, which can significantly impact health outcomes.
How is APS diagnosed and what tests are used?
APS diagnosis involves understanding antiphospholipid syndrome through a combination of clinical evaluations and specific tests, such as lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibody tests. Accurate APS diagnosis is crucial for timely treatment and management.
What are the treatment options available for Antiphospholipid Syndrome?
Understanding Antiphospholipid Syndrome treatment is vital for managing the condition. Current treatment typically includes anticoagulants like heparin and low-dose aspirin. Research into innovative therapies is ongoing, focusing on improving outcomes for patients.
How does Antiphospholipid Syndrome affect pregnancy?
Pregnancy and antiphospholipid syndrome can lead to complications such as miscarriage and thrombosis. Understanding the implications of APS during pregnancy is crucial, as it requires specialized treatment to enhance outcomes and prevent adverse events.
What recent research has been conducted on Antiphospholipid Syndrome?
Autoimmune disorder research related to understanding antiphospholipid syndrome has shown promising developments in management strategies aimed at preventing thrombotic events. Ongoing studies focus on tailoring treatments specifically for APS patients, particularly during pregnancy.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of APS | An autoimmune disorder characterized by antiphospholipid antibodies leading to increased blood clot risk. |
| Symptoms | Recurrent venous or arterial thrombosis, miscarriages, and pregnancy losses. |
| Diagnosis | Involves clinical evaluation and tests for antiphospholipid antibodies. |
| Recent Research | Focus on innovative management strategies and targeting metabolic pathways. |
| Pregnancy Implications | Need for tailored therapies; current treatments include low-dose aspirin and heparin. |
| Treatment Efficacy | Demand for more effective therapies to reduce pregnancy loss rates. |
Summary
Understanding antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is essential for those affected by this autoimmune disorder, as it directly influences treatment and management strategies. APS can lead to serious complications, particularly in pregnant women, making awareness and early diagnosis pivotal. Recent advancements in research highlight innovative treatment options aimed at improving outcomes for patients. Understanding the complex interplay between APS and various factors, including pregnancy, aids healthcare professionals in developing effective strategies to reduce risks and enhance the quality of life for those diagnosed with this condition. By staying informed about the latest findings and treatment protocols, individuals can better navigate the challenges posed by APS.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.