Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is a fast-growing blood cancer that primarily affects children, although adults can also be diagnosed with this aggressive disease. Understanding the acute lymphoblastic leukaemia symptoms is crucial for early detection and intervention, as they often mimic less serious illnesses. With advancements in research, the landscape of ALL treatment options has evolved, leading to improved survival rates for many patients. Chromosomal abnormalities in ALL can significantly influence treatment decisions and outcomes, making genetic profiling an essential part of patient care. This article delves into vital childhood cancer statistics and the ongoing efforts to raise awareness about ALL and its impact on young lives.
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, commonly referred to as ALL, is a type of leukemia that is characterized by the rapid proliferation of immature lymphocytes. Often considered a pediatric cancer, ALL poses unique challenges and risks not only to children but also to adults, as it does not discriminate based on age. The symptoms associated with this condition can often lead to misdiagnosis, highlighting the importance of awareness among parents and caregivers. Treatment strategies for ALL have become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating various therapeutic approaches tailored to individual patient needs. By examining the genetic factors and survival statistics related to ALL, we can better understand its complexities and the ongoing efforts to combat this formidable disease.
Recognizing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Symptoms
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia symptoms can be subtle and easily mistaken for less severe health issues, making awareness critical for early detection. Common signs such as persistent fatigue, unexplained fevers, and frequent infections can indicate a serious underlying condition. Children, in particular, may exhibit unusual bruising or bleeding that parents might overlook. Paying close attention to these symptoms can lead to timely medical evaluations, which are essential for a prompt diagnosis and treatment plan.
Parents and caregivers should be vigilant about any changes in their child’s health. For instance, if a child shows signs of bone or joint pain that seems out of the ordinary, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Early recognition and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis for children diagnosed with ALL. Regular check-ups and open communication with medical professionals can ensure that symptoms are not disregarded and that appropriate investigations are conducted.
Exploring Treatment Options for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
The treatment landscape for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) has evolved dramatically over the years, offering patients a range of options that cater to their unique needs. Chemotherapy remains the cornerstone of ALL treatment, typically administered in phases designed to first induce remission, then consolidate gains, and finally maintain remission. This structured approach not only aims to eradicate cancer cells but also helps to prevent potential relapses.
In addition to chemotherapy, targeted therapies have emerged as a promising avenue for treatment, focusing on the specific genetic abnormalities present in ALL patients. For example, therapies targeting the Philadelphia chromosome have shown significant efficacy in improving patient outcomes. Furthermore, stem cell transplants are considered for high-risk patients, providing a chance for a cure in cases where traditional treatments may not suffice. The ongoing advancements in treatment options offer hope for improved survival rates in ALL patients.
Understanding Survival Rates and Prognosis in ALL
Survival rates for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia have improved remarkably, particularly among children, where rates can exceed 90% due to advancements in treatment protocols. However, these statistics can vary significantly based on several factors, including the presence of chromosomal abnormalities, such as the Philadelphia chromosome, and a patient’s overall response to initial treatments. Understanding these variables is crucial for clinicians and families as they navigate the treatment landscape.
Moreover, age and health at diagnosis play a pivotal role in determining prognosis. Generally, younger patients tend to respond better to treatment than adults. Ongoing research continues to explore the genetic landscape of ALL, aiming to optimize treatment strategies and improve survival rates further. Families dealing with an ALL diagnosis should stay informed about the latest findings, as they can influence treatment decisions and long-term outlook.
The Role of Chromosomal Abnormalities in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
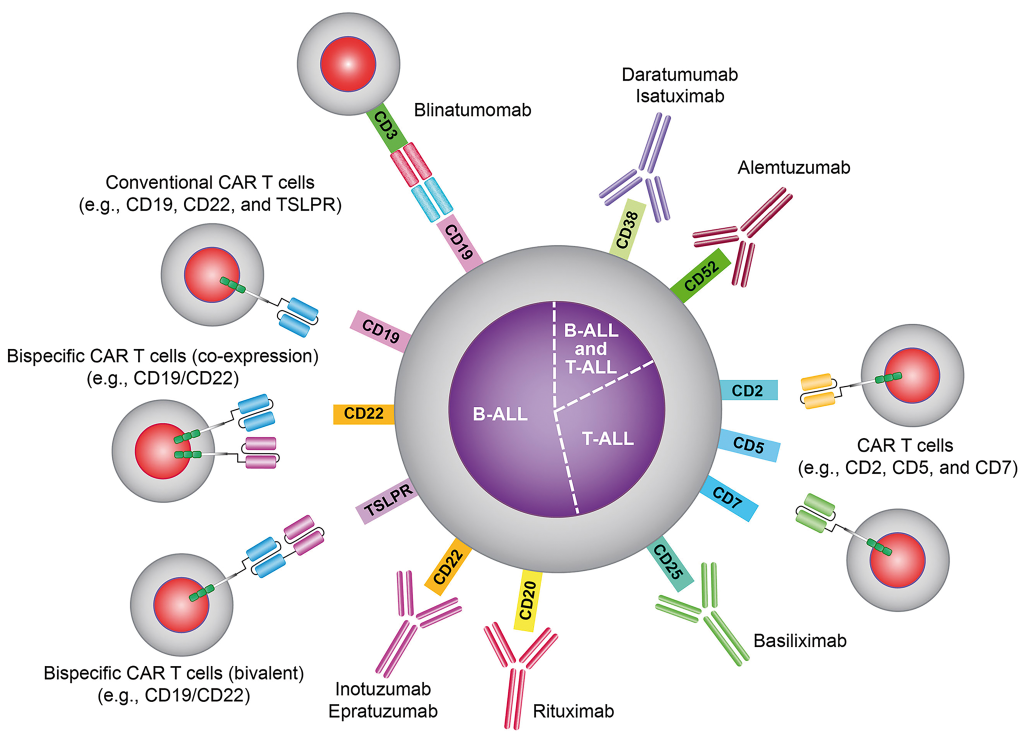
Chromosomal abnormalities are critical in understanding the biology of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and significantly influence treatment decisions and prognosis. The presence of the Philadelphia chromosome, for instance, is associated with a more aggressive form of ALL and often requires intensified treatment strategies, including the use of targeted therapies. Recognizing these genetic markers early in the diagnostic process can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans that enhance the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Additionally, other chromosomal translocations and mutations play a role in determining the risk stratification of ALL patients. Studies have shown that specific genetic alterations can dictate not only the treatment regimen but also the potential for relapse. As research progresses, the ability to identify and understand these chromosomal abnormalities will continue to improve, leading to more personalized and effective treatment options for individuals battling acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
The Impact of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia on Childhood Cancer Statistics
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is the most common type of leukemia diagnosed in children, accounting for a significant portion of childhood cancer statistics. The incidence of ALL has remained relatively stable, but the advancements in treatment have drastically improved survival rates over the past few decades. This rise in survival rates reflects the effectiveness of modern treatment protocols, supportive care, and the emphasis on early diagnosis and intervention.
However, the challenges faced by families affected by ALL extend beyond survival statistics. The emotional, financial, and psychological impacts of a cancer diagnosis in children can be profound. Support systems and educational initiatives are crucial in helping families navigate these challenges. As awareness increases and more resources become available, the hope is to continue improving not only survival rates but also the quality of life for children undergoing treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL)?
Common acute lymphoblastic leukaemia symptoms include fatigue, unexplained fevers, frequent infections, easy bruising or bleeding, and bone or joint pain. Awareness of these symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What are the treatment options available for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL)?
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treatment options primarily consist of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplants. Each treatment plan is tailored to the patient’s specific needs and the characteristics of their disease.
What are the survival rates for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL)?
Survival rates for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia have improved significantly, exceeding 90% in many cases. Factors influencing these rates include genetic abnormalities, response to treatment, and patient age.
How do chromosomal abnormalities affect acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) treatment?
Chromosomal abnormalities in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia can greatly impact treatment and prognosis. For example, the Philadelphia chromosome is associated with poorer outcomes and may require more aggressive therapy.
What do childhood cancer statistics indicate about acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL)?
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is the most common type of childhood cancer, highlighting the need for increased awareness and research. Statistics show that with advancements in treatment, many children diagnosed with ALL can achieve long-term remission.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview | Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is a fast-growing blood cancer affecting mainly children. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include fatigue, unexplained fever, frequent infections, easy bruising, and bone or joint pain. |
| Treatment Options | Primary treatments include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and possibly stem cell transplants. |
| Survival Rates | Survival rates exceed 90% in children, influenced by genetic factors and response to treatment. |
| Chromosomal Abnormalities | Abnormalities like the Philadelphia chromosome significantly affect prognosis and treatment. |
| Impact on Children | ALL is the most common childhood cancer, necessitating special consideration for emotional and psychological needs. |
| Research and Resources | Research articles provide insights into genetics and treatment responses for better understanding of ALL. |
Summary
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia is a serious and fast-growing blood cancer that primarily affects children, although it can also occur in adults. Advances in research and treatment have significantly improved the prognosis for patients, particularly for children, with survival rates exceeding 90% in many cases. However, the disease remains challenging due to its aggressive nature and the potential for severe symptoms that can be easily overlooked. Education and awareness are crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment, highlighting the importance of recognizing symptoms such as fatigue and unexplained fevers. As ongoing research continues to enhance our understanding of the genetic factors and treatment responses associated with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia, it is essential for families and patients to stay informed and engaged in their healthcare journey.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.