The use of 16S rRNA PCR for pediatric infections has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in the diagnosis of difficult bacterial infections in children. This innovative technique leverages the ribosomal RNA gene to identify pathogens in patients whose infections might otherwise evade detection through standard bacterial culture methods. Recent findings from a Mayo Clinic study indicate that this molecular method shows a significant capability to pinpoint bacteria in normally sterile body fluids and tissues, enhancing pediatric infection diagnosis. With a noteworthy positivity rate, especially in pleural fluid specimens, 16S rRNA PCR offers a reliable alternative for clinicians grappling with complex cases. By integrating PCR bacterial diagnosis into clinical practice, healthcare professionals can improve antimicrobial stewardship, ensuring that children receive targeted and effective treatment.
Exploring the landscape of pediatric bacterial infections, 16S rRNA gene amplification serves as a pivotal diagnostic tool that identifies a wide array of bacterial pathogens. This molecular technique, distinct from traditional cultures, provides potent insights into the microbial landscape, particularly in pediatric cases where standard methods fall short. By employing 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing, clinicians can delve into a comprehensive bacterial culture analysis, facilitating more accurate assessment of infectious diseases. Recent data underscore the effectiveness of this methodology in discerning pathogens hidden in sterile tissue and fluid specimens, marking a significant advancement in pediatric infection diagnosis. As hospitals increasingly adopt these innovative strategies, the potential for improved outcomes in young patients becomes remarkably promising.
Introduction to 16S rRNA PCR for Pediatric Infections
The 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) PCR method has emerged as a significant advancement in the diagnosis of bacterial infections, particularly in pediatric patients. Traditional diagnostic methods, including bacterial culture analysis, often have limitations, especially in cases where fastidious organisms are involved or specimens are sterile and difficult to culture. The role of 16S rRNA PCR in identifying these pathogens is crucial, as it allows for the amplification of bacterial DNA, leading to a higher detection rate of otherwise missed infections.
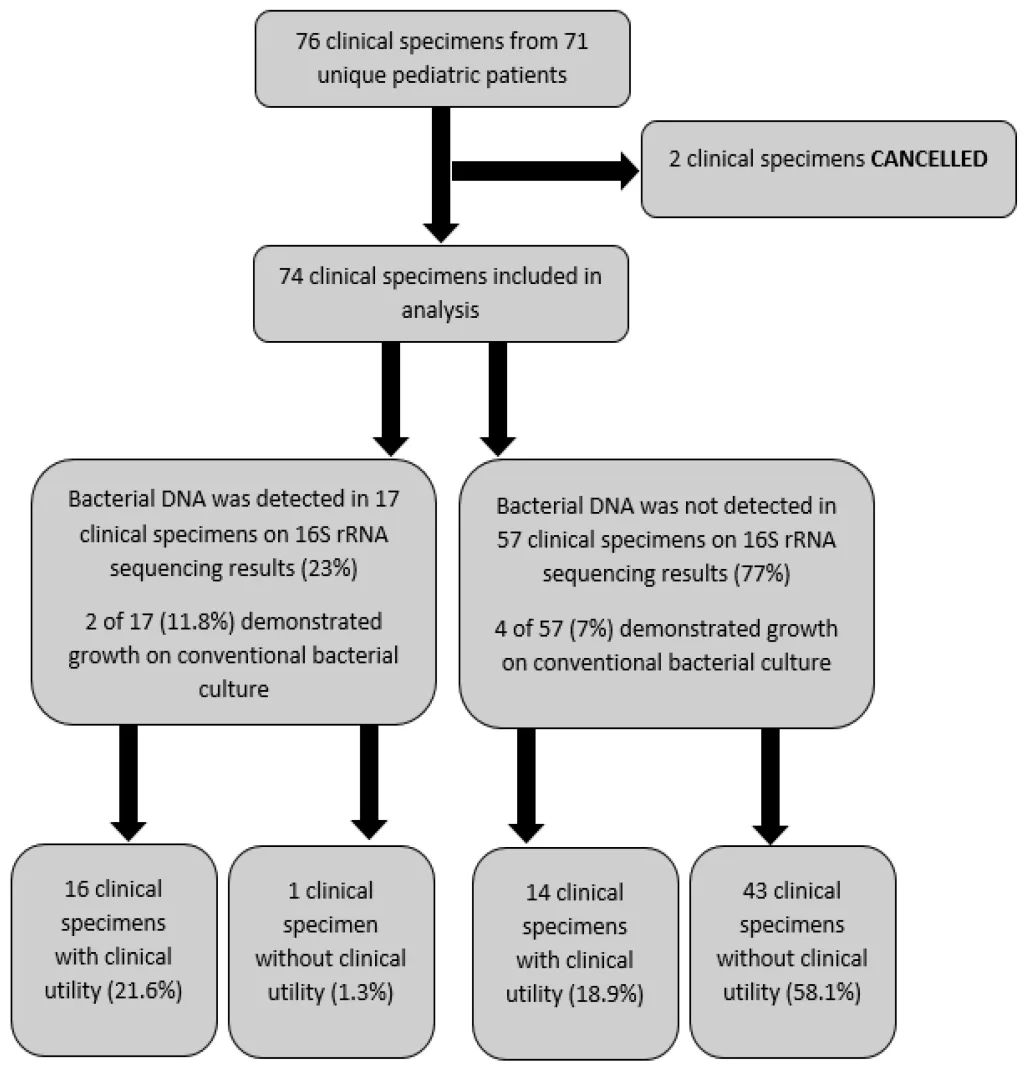
In the context of pediatric infection diagnosis, the ability to effectively utilize 16S rRNA PCR can significantly alter the management and outcomes for young patients. The Mayo Clinic study highlighted the importance of this method, revealing a 20% overall positivity rate from specimens collected between September 2020 and December 2023. By employing this molecular technique, clinicians can expedite treatment options and improve results for children suffering from complex infections.
Mayo Clinic Study Findings: The Impact of Specimen Type
The results from the Mayo Clinic study emphasize a crucial finding regarding specimen types and their positivity rates. Specifically, fluid specimens exhibited a higher likelihood of yielding positive results when subjected to 16S rRNA PCR testing compared to tissue samples. Pleural fluid, in particular, stood out with a 50% positivity rate, thus demonstrating its vital role in pediatric diagnostics. This evidence supports the assertion that selecting the appropriate specimen type is essential for achieving accurate diagnostic outcomes in pediatric infections.
Moreover, the study sheds light on the broader implications of using fluid specimens in conjunction with 16S rRNA PCR for detecting bacterial pathogens. A significant portion of positive samples originated from culture-negative groups, underscoring the utility of this molecular diagnostic approach. As healthcare professionals aim for precise identification of infections in pediatric patients, the integration of such innovative methodologies could redefine standard practices for bacterial diagnosis and enhance clinical decision-making.
Understanding the Clinical Application of 16S rRNA PCR
The clinical application of 16S rRNA PCR and sequencing has unfolded as a groundbreaking approach in pediatric infection diagnosis. This technique not only aids in elucidating difficult cases where traditional bacterial cultures may provide false negatives, but it also yields consistent results that can reinforce existing culture findings. The inclusion of this molecular diagnostic tool is essential for improving antimicrobial stewardship, which helps in minimizing unnecessary antibiotic use and resistance development.
As we continue to refine pediatric diagnostic frameworks, the integration of 16S rRNA PCR into routine clinical practice represents a significant leap forward. Successful identification of bacterial pathogens can lead to more targeted therapies and better patient outcomes. However, to optimize its efficacy, it is crucial to further explore variations in diagnostic yields across different specimen types, patient demographics, and infection profiles.
The Role of Bacterial Culture Analysis in Pediatric Diagnostics
Traditionally, bacterial culture analysis has been the gold standard for diagnosing infections in pediatrics; however, the limitations of culture methods are well-documented. These methods are often time-consuming, and in some cases, they may fail to identify certain pathogens due to the fastidious nature of some bacteria. The incorporation of 16S rRNA PCR can complement these traditional methods, offering a swift alternative to confirm or rule out infections that elude conventional testing.
The Mayo Clinic study illuminates the necessity of bridging conventional testing with advanced molecular techniques. While culture results remain an essential element of infection diagnosis, the ability to utilize 16S rRNA PCR provides a more comprehensive evaluation of a patient’s microbial landscape. This combined approach can enable clinicians to make informed decisions and refine treatment protocols, ultimately enhancing patient care in the pediatric setting.
Specimen Selection: The Key to Successful Diagnosis
Choosing the right specimen is pivotal in the diagnostic journey for pediatric infections. The findings from the Mayo Clinic study illustrate that specific types of fluid specimens yield significantly higher positivity rates for 16S rRNA PCR compared to other sample types such as tissue. This insight reaffirms the importance of clinical judgment in specimen selection, ensuring that the most appropriate samples are prioritized to maximize diagnostic yield.
In practice, this means clinicians must be adept at determining which specimens are likely to produce the most relevant results when using PCR technology. Whether it be pleural, synovial, or other sterile fluid types, enhancing specimen selection strategies could dramatically improve the accuracy of pediatric infection diagnoses. As we advance in microbial diagnostics, emphasizing effective specimen collection methods will remain a vital aspect of clinical practice.
16S rRNA PCR: A Transformative Approach in Pediatric Infectious Diseases
The transformative nature of 16S rRNA PCR in addressing pediatric infectious diseases cannot be overstated. By providing a means to identify bacterial pathogens that traditional cultures may overlook, this technique offers healthcare professionals a powerful tool in complex clinical scenarios. As pediatricians increasingly face challenges related to difficult-to-diagnose bacterial infections, the role of this molecular tool becomes ever more significant.
This shift in diagnostic approach can lead to quicker interventions and tailored treatment plans, which are crucial in pediatrics where timely management of infections can drastically affect outcomes. As illustrated in the Mayo Clinic findings, the reliance on 16S rRNA PCR and sequencing paves the way for a more effective and precise methodology in addressing the unique challenges posed by pediatric infections.
Enhancing Antimicrobial Stewardship through Molecular Diagnostics
The integration of 16S rRNA PCR into pediatric infection diagnosis plays a vital role in enhancing antimicrobial stewardship. By ensuring rapid and accurate identification of pathogens, this technology empowers clinicians to deploy the right antibiotic therapy sooner, mitigating the risk of resistance development. The focus on responsible prescribing practices is especially crucial in pediatrics, where the potential for adverse effects from unnecessary antibiotic therapy is a significant concern.
The Mayo Clinic study reinforces this premise, demonstrating how molecular diagnostics can complement existing practices to promote better patient care. By utilizing advanced techniques like 16S rRNA PCR, healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of bacterial infections with improved precision, allowing them to make informed decisions that align with stewardship principles. This shift not only optimizes individual patient outcomes but also safeguards public health by preserving antibiotic efficacy.
Future Directions for 16S rRNA PCR and Pediatric Diagnostic Strategies
As the findings from the Mayo Clinic study suggest, there is a promising future for 16S rRNA PCR in the realm of pediatric diagnostics. However, to fully capitalize on its potential, ongoing research is crucial. Future studies should focus on refining the selection of specimen types, particularly emphasizing those most likely to yield positive results. Incorporating broad collaborative efforts among clinical microbiologists, pediatricians, and infectious disease specialists will enable a deeper understanding of the molecular diagnostics landscape.
Furthermore, establishing standardized protocols for the implementation of 16S rRNA PCR could solidify its position within pediatric infectious disease diagnostics. Through continued innovation and adaptation, 16S rRNA PCR has the potential to transform diagnostic practices and ultimately improve patient outcomes within the pediatric population.
Integrating 16S rRNA PCR into Clinical Practice
Incorporating 16S rRNA PCR into routine clinical practice presents several opportunities and challenges. While the benefits of the technology are evident in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, training and resources must be developed to ensure its effective application. Healthcare settings need to invest in capacity building—including lab facilities, personnel training, and analytical frameworks—to support the integration of this molecular diagnostic tool.
As clinicians become more familiar with the advantages and limitations of 16S rRNA PCR, they can leverage the method not only to improve accuracy in diagnosing complex infections but also to make better-informed treatment choices. This integration will require collaboration across disciplines and a commitment to continuous education, ultimately fostering a culture that prioritizes advanced diagnostic techniques in pediatric care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of 16S rRNA PCR in pediatric infection diagnosis?
16S rRNA PCR plays a crucial role in pediatric infection diagnosis by identifying bacterial pathogens in normally sterile specimens. This molecular method enhances detection rates, particularly in challenging cases where traditional culture methods may fail to pinpoint the infection.
How effective is 16S ribosomal RNA PCR compared to bacterial culture analysis for pediatric infections?
The effectiveness of 16S ribosomal RNA PCR often surpasses that of bacterial culture analysis, particularly in pediatric infections. In a study at Mayo Clinic, 16S PCR showed a 20% positivity rate, with many positive results coming from culture-negative specimens, underscoring its value in complex cases.
What types of specimens are most effective for 16S rRNA PCR testing in pediatric patients?
Fluid specimens, especially pleural fluid, have shown the highest effectiveness for 16S rRNA PCR testing in pediatric patients. The positivity rate for pleural fluid was notably higher than for tissue specimens, making it a vital option for accurate diagnosis.
Why might 16S rRNA PCR be preferred over traditional diagnostic methods for pediatric infections?
16S rRNA PCR may be preferred over traditional diagnostic methods due to its ability to detect fastidious bacteria and its higher sensitivity in infectious cases that are culture-negative. This method provides a quicker and more reliable diagnosis, especially in severe infections requiring prompt treatment.
What findings were reported in the Mayo Clinic study on 16S rRNA PCR for pediatric infections?
The Mayo Clinic study found that of 162 16S rRNA PCR tests performed on pediatric patients, 20% returned positive, with fluid specimens demonstrating a higher positivity rate than tissue samples. These results highlight the importance of 16S rRNA PCR and sequencing in accurately diagnosing pediatric infections.
Can 16S rRNA PCR aid in antimicrobial drug stewardship for pediatric patients?
Yes, 16S rRNA PCR can significantly aid in antimicrobial drug stewardship by providing accurate bacterial identifications and enabling targeted therapies. This reduces unnecessary antibiotic use, ensuring better patient care and combating antibiotic resistance among pediatric patients.
What limitations exist with using 16S rRNA PCR in pediatric infection diagnosis?
While 16S rRNA PCR is highly effective, limitations include variability in diagnostic yield based on specimen type and patient characteristics. Additionally, results may occasionally require correlation with clinical findings and additional tests for comprehensive assessment.
How does the 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing contribute to pediatric infection diagnosis?
16S ribosomal RNA sequencing enhances pediatric infection diagnosis by allowing detailed identification of bacterial species, even those difficult to culture. This molecular technique thus supports clinicians in determining appropriate treatment strategies for complex infections.
Is 16S rRNA PCR useful for children with compromised immune systems?
Yes, 16S rRNA PCR is particularly beneficial for children with compromised immune systems who may present with atypical infections. This method aids in rapidly diagnosing infections that might otherwise go undetected by conventional culture methods.
What future research is needed regarding 16S rRNA PCR for pediatric infections?
Future research should focus on optimizing specimen selection and understanding the clinical utility of 16S rRNA PCR in pediatric infection diagnosis. Additional studies may help refine its use in various clinical scenarios to enhance patient outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Overview | Retrospective study on the use of 16S rRNA PCR and sequencing for pediatric infections conducted at Mayo Clinic from September 2020 to December 2023. |
| Test Performance | 162 tests on 124 patients; positivity rate of 20%; pleural fluid had the highest positivity rate at 50%. |
| Clinical Significance | High diagnostic yield for complex infections. Particularly effective in culture-negative cases. |
| Specimen Types | Fluid specimens yielded higher positivity rates than tissue specimens (Odds ratio 3.07). Pleural fluid was essential. |
| Reportable Cases | Out of 33 positives, only 4 (12%) required reporting to the state health department for communicable diseases. |
| Conclusion | 16S rRNA PCR and sequencing significantly enhance the diagnosis of pediatric infections, particularly with fluid specimens. |
Summary
16S rRNA PCR for pediatric infections is a valuable diagnostic method that addresses challenging cases where traditional cultures fail. This technique’s ability to accurately identify bacterial pathogens from normally sterile body fluids makes it particularly relevant in diagnosing complex infections. The study conducted at Mayo Clinic emphasizes the superior performance of pleural fluid specimens, demonstrating a significant correlation between specimen type and diagnostic yield. As pediatric healthcare evolves, incorporating 16S rRNA PCR into clinical practice can improve patient outcomes by ensuring timely and accurate identification of infections, particularly in immunocompromised children.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.